Friederike Range and Zsófia Virányi from the Unit of Comparative Cognition at the Messerli Research Institute at University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna have an alternate idea, the "Canine Cooperation Hypothesis". They believe that since wolves already are tolerant, attentive and cooperative, the relationship of wolves to their pack mates could have provided the basis for today's human-dog relationship.
Additional selection, at least for social attentiveness and tolerance, was not necessary during canine domestication.
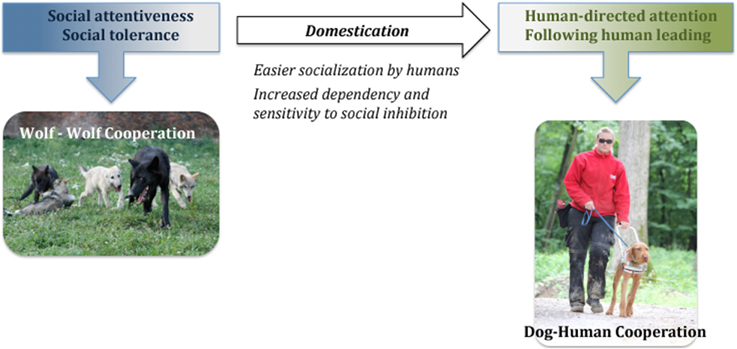
Canine Cooperation Hypothesis . doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01582
The researchers believe that wolves are not less socially attentive than dogs, it is just that dogs cooperate more easily with humans because they more readily accept people as social partners and more easily lose their fear of humans. To test their hypothesis, Range and Virányi examined the social attentiveness and tolerance of wolves and dogs within their packs and toward humans.
Various behavioral tests showed that wolves and dogs have quite similar social skills. Among other things, the researchers tested how well wolves and dogs can find food that has been hidden by a conspecific or by a human. Both wolves and dogs used information provided by a human to find the hidden food.
In another study, they showed that wolves followed the gaze of humans. To solve the task, the animals may need to be capable of making a mental representation of the "looker's" perspective. Wolves can do this quite well.
Another experiment gave dogs and wolves the chance to observe conspecifics as they opened a box. When it was the observer's turn to do the same, the wolves proved to be the better imitators, successfully opening the box more often than dogs. "Overall, the tests showed that wolves are very attentive to humans and to each other. Hypotheses which claim that wolves have limited social skills in this respect in comparison to dogs are therefore incorrect," Range points out.
Testing dogs and wolves in packs
At the Wolf Science Center in Ernstbrunn in Lower Austria, Range and Virányi investigated the social behavior of dogs and wolves that grew up with members of their species and with humans.
"The animals are socialized both with conspecifics and with humans. To be able to compare the behavior of dogs and wolves and to investigate the effects of domestication, it is important that the animals live in the same conditions," Virányi says.
Citation: Friederike Range and Zsófia Virányi,"Tracking the evolutionary origins of dog-human cooperation: the "Canine Cooperation Hypothesis"", Frontiers in Psychology. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01582





Comments