For children and immune-compromised adults in developing countries, diarrheal disease induced by rotavirus can be life threatening.
Rotavirus is the leading cause of diarrhea in infants and young children worldwide, causing more than 114 million episodes of diarrhea annually in children under the age of 5, 80% of which occur in developing countries. More than 600,000 children die annually from rotavirus (RV) infection
Current rotaviral vaccines are highly effective in the Western world, but are not as effective in developing countries. Additionally, these vaccines are not appropriate for use outside of a very narrow age window or in immune compromised individuals.
In the Journal of Clinical Investigation Yoshikazu Yuki and colleagues at the University of Tokyo report the development of a strain of rice that produces a rotavirus-specific antibody. Both normal and immune deficient mice fed the engineered rice were protected against rotavirus. Their transgenic rice expresses the neutralizing variable domain of a rotavirus-specific llama heavy-chain antibody fragment (MucoRice-ARP1).
MucoRice-ARP1 was produced at high levels in rice seeds using an over-expression system and RNAi technology to suppress the production of major rice endogenous storage proteins. Orally administered MucoRice-ARP1 markedly decreased the viral load in immuno-competent and immunodeficient mice.
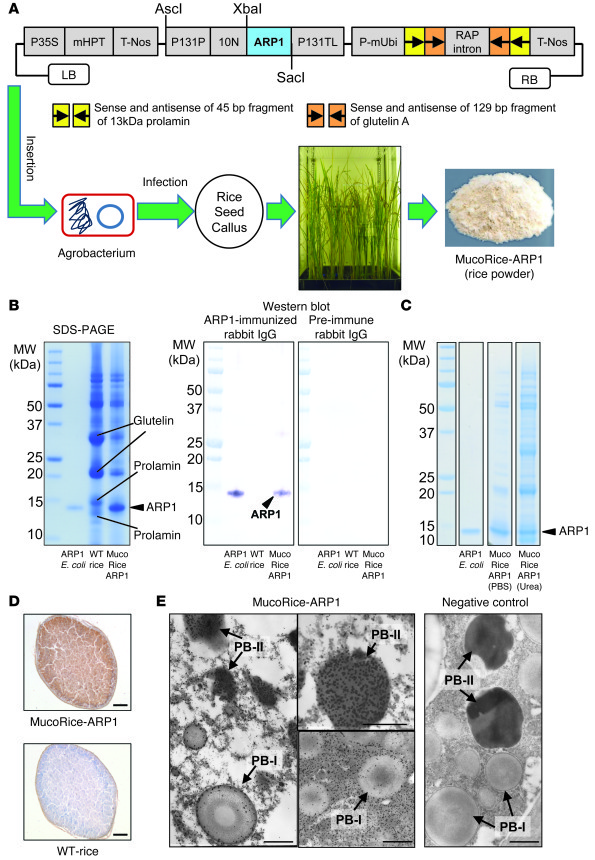
Expression and localization of water-soluble ARP1 in transgenic rice. (A) Inserted plasmid for overexpression of ARP1 in rice seeds. P35S, CaMV35S promoter; mHPT, modified hygromycin phosphotransferase; P131P, 13-kDa prolamin promoter; 10N, signal sequence of 10-kDa prolamin; P131TL, 13-kDa prolamin terminator; T-Nos, nos terminator; RAP intron, rice aspartic protease intron; P-mUbi, ubiquitin promoter; LB, T-DNA left border; RB, T-DNA right border. (B) Production of MucoRice-ARP1. SDS-PAGE showed predominant expression of the transgenic protein with a molecular weight of approximately 12 kDa (arrowhead). Original rice proteins (arrows; 22- to 23-kDa and 34- to 37-kDa subunits of glutelin and 13-kDa prolamin) in nontransformed WT rice were markedly suppressed in MucoRice-ARP1. Western blotting revealed that a transgenic protein of 12 kDa was specifically detected using the anti-ARP1 antibody. ARP1 E. coli, ARP1 purified from E. coli. (C) Solubility of MucoRice-ARP1. MucoRice-ARP1 (PBS), extracts of MucoRice-ARP1 in PBS; MucoRice-ARP1 (urea), extracts of MucoRice-ARP1 in 8 M urea. (D) Immunohistochemistry showed that ARP1 had accumulated throughout the whole MucoRice-ARP1 seed, whereas it was not detected in a WT rice seed. Scale bars: 1 mm. (E) Immune electron microscopy showed that ARP1 is observed as black spots (left and middle panels). ARP1 is predominantly localized in the PB-II and the interspace between the PB-I and PB-II (left and middle panels). ARP1 is also slightly found at the surface of PB-I (left panel and lower middle panel). ARP1 is not detected in a WT rice seed used as a negative control (right panel). Scale bars: 1 μm.
The researchers also report that the rice maintains its efficacy even after long-term storage (greater than one year) and heat exposure (94°C for 30 minutes).
They say this study provides a low cost, efficient strategy for prevention of rotavirus infection.
Citation: Daisuke Tokuhara, Beatriz ρlvarez, Mio Mejima, Tomoko Hiroiwa, Yuko Takahash, Shiho Kurokawa, Masaharu Kuroda, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Tomonori Nochi, Hiroshi Sagara, Farah Aladin, Harold Marcotte, Leon G.J. Frenken, Miren Iturriza-Gómara, Hiroshi Kiyono, Lennart Hammarström and Yoshikazu Yuki, 'Rice-based oral antibody fragment prophylaxis and therapy against rotavirus infection', J Clin Invest. doi:10.1172/JCI70266





Comments