Want to teach a robot to tend the garden? It will go faster if you let the crowd help. University of Washington computer scientists at the 2014 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Hong Kong showed that crowdsourcing can be a quick and effective way to teach a robot how to complete tasks
Learning by imitating a human is a proven approach to teach a robot to perform tasks, but it can take a lot of time. Imagine having to teach a robot how to load the dishwasher – it might take many repetitious lessons for the robot to learn how to hold different types of cookware and cutlery and how to most efficiently fill the machine.
But if the robot could learn a task's basic steps, then ask the online community for additional input, it could collect more data on how to complete this task efficiently and correctly.

The University of Washington's robot builds a turtle model.
Credit: University of Washington
But if the robot could learn a task's basic steps, then ask the online community for additional input, it could collect more data on how to complete this task efficiently and correctly.
"We're trying to create a method for a robot to seek help from the whole world when it's puzzled by something," said Rajesh Rao, an associate professor of computer science and engineering and director of the Center for Sensorimotor Neural Engineering at the University of Washington. "This is a way to go beyond just one-on-one interaction between a human and a robot by also learning from other humans around the world."
"Because our robots use machine-learning techniques, they require a lot of data to build accurate models of the task. The more data they have, the better model they can build. Our solution is to get that data from crowdsourcing," said Maya Cakmak, a UW assistant professor of computer science and engineering.
The research team, led by professors Rao and Cakmak, also includes UW computer science and engineering graduate student Michael Jae-Yoon Chung and undergraduate Maxwell Forbes. The team designed a study that taps into the online crowdsourcing community to teach a robot a model-building task. To begin, study participants built a simple model – a car, tree, turtle and snake, among others – out of colored Lego blocks. Then, they asked the robot to build a similar object. But based on the few examples provided by the participants, the robot was unable to build complete models.
To gather more input about building the objects, the robots turned to the crowd. They hired people on Amazon Mechanical Turk, a crowdsourcing site, to build similar models of a car, tree, turtle, snake and others. From more than 100 crowd-generated models of each shape, the robot searched for the best models to build based on difficulty to construct, similarity to the original and the online community's ratings of the models.
The robot then built the best models of each participant's shape.
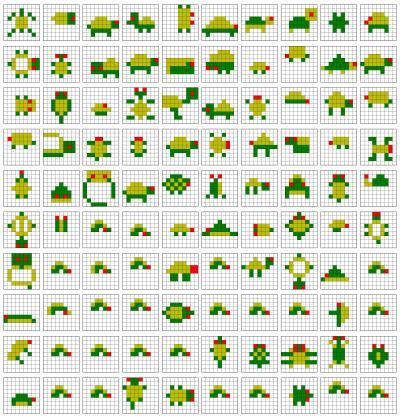
Some of the crowdsourced designs for the word "turtle." Credit: University of Washington
This type of learning is called "goal-based imitation," and it leverages the growing ability of robots to infer what their human operators want, relying on the robot to come up with the best possible way of achieving the goal when considering factors such as time and difficulty. For example, a robot might "watch" a human building a turtle model, infer the important qualities to carry over, then build a model that resembles the original, but is perhaps simpler so it's easier for the robot to construct.
"The end result is still a turtle, but it's something that is manageable for the robot and similar enough to the original model, so it achieves the same goal," Cakmak explained.
Study participants generally preferred crowdsourced versions that looked the most like their original designs. In general, the robot's final models were simpler than the starting designs – and it was able to successfully build these models, which wasn't always the case when starting with the study participants' initial designs.
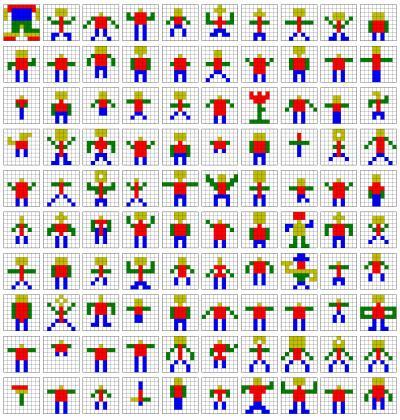
Some of the crowdsourced designs for the word "person.
Credit: University of Washington
The team applied the same idea to learning manipulation actions on a two-armed robot. This time, users physically demonstrated new actions to the robot. Then, the robot imagined new scenarios in which it did not know how to perform those actions. Using abstract, interactive visualizations of the action, it asked the crowd to provide new ways of performing actions in those new scenarios. This work will be presented at the Conference on Human Computation and Crowdsourcing in November.
Other research teams at Brown University, Worcester Polytechnic Institute and Cornell University are working on similar ideas for developing robots that have the ability to learn new capabilities through crowdsourcing.
The UW team is now looking at using crowdsourcing and community-sourcing to teach robots more complex tasks such as finding and fetching items in a multi-floor building. The researchers envision a future in which our personal robots will engage increasingly with humans online, learning new skills and tasks to better assist us in everyday life.





Comments