 El Niño Climate Effects Shaped By Ocean Salt
El Niño Climate Effects Shaped By Ocean SaltOnce the weather got political, more attention became focused on the cyclical climate phenomenon...
 Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?
Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?Glioblastoma, a deadly brain cancer, is treated with surgery to remove as much of the tumor as...
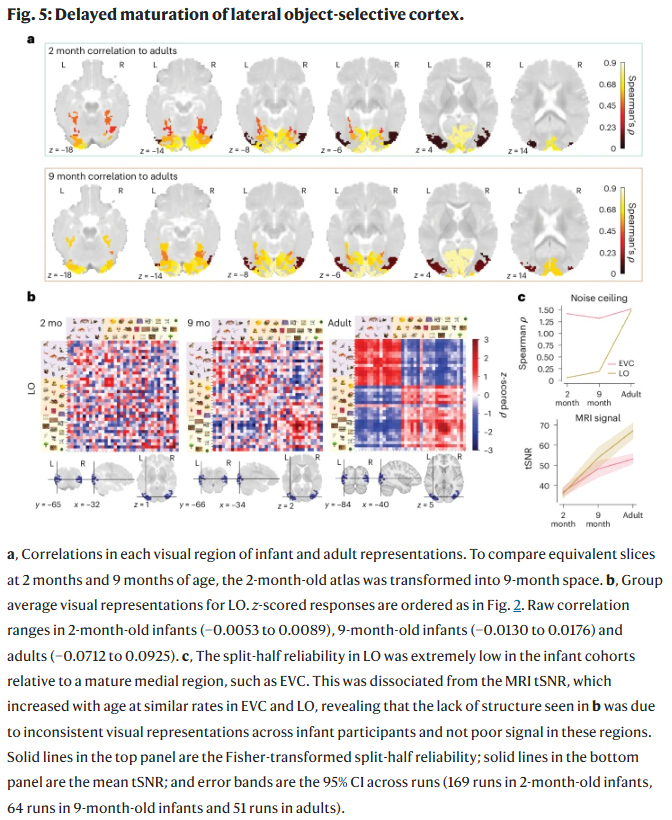 At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize Objects
At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize ObjectsAt two months of age, infants lack language and fine motor control but their minds may be understanding...
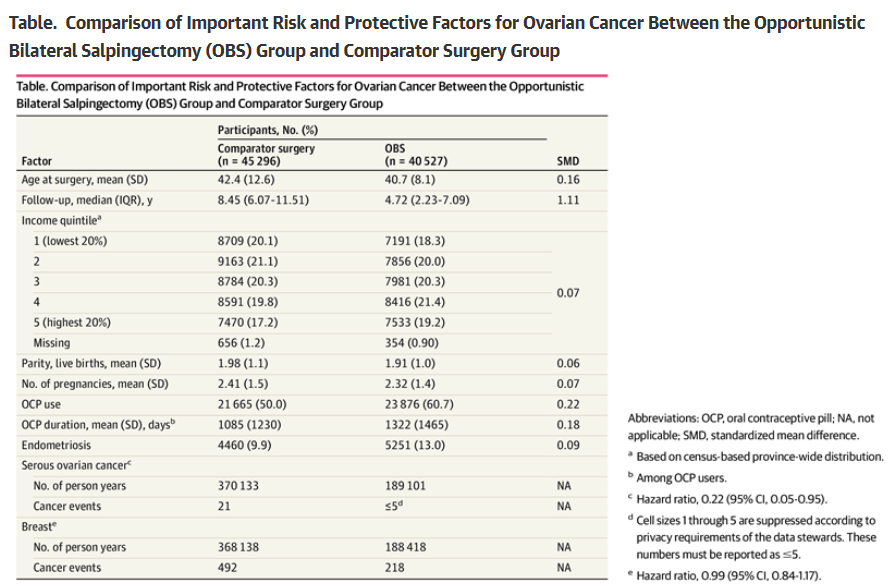 Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%
Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%Opportunistic salpingectomy, proactively removing a person’s fallopian tubes when they are already...








