Some of the brightest colors in nature are created by tiny nanostructures with a structure similar to beer foam or a sponge, according to Yale University researchers. Most colors in nature—from the color of our skin to the green of trees—are produced by pigments. But the bright blue feathers found in many birds, such as Bluebirds and Blue Jays, are instead produced by nanostructures. Under an electron microscope, these structures look like sponges with air bubbles.
If you’ve ever been sleep-deprived, you know how it correlates to baseball and the feeling that your brain is batting below the
Mendoza Line and you just aren't seeing the ball very well. Or you just feel muddled.
A study published in
Science has molecular and structural evidence saying proteins that build up in the brains of sleep-deprived fruit flies drop to lower levels in the brains of the well-rested - basically spring training, or a good cleaning, for your brain. The proteins are located in the synapses, those specialized parts of neurons that allow brain cells to communicate with other neurons.
Scientists, this is your future research partner. A 'Robot Scientist' named Adam has been created and the group behind it believe it is the first machine to have independently discovered new scientific knowledge. Adam is a computer system that fully automates the scientific process.
Yes, Charles Darwin did important things for science, but what we really want to know is how he squandered his money as a student. Did he drink and smoke a lot? Yeah, actually, which makes him all the more likable.
200 years after the great naturalist's birth, his successors at Christ's College, Cambridge, have unearthed bills which record intimate details about the young Darwin's previously unknown day-to-day life during his student years.
The six record books were published online March 23rd at The Complete Work Of Charles Darwin Online (
http://darwin-online.org.uk/), making them freely available to readers anywhere in the world.
Some of the symptoms of the autistic condition Asperger Syndrome, such as a need for routine and resistance to change, could be linked to levels of the stress hormone cortisol, suggests new research led by the University of Bath.
Normally, people have a surge of this hormone shortly after waking, with levels gradually decreasing throughout the day. It is thought this surge makes the brain alert, preparing the body for the day and helping the person to be aware of changes happening around them.
However, a study led by Dr Mark Brosnan and Dr Julie Turner-Cobb from the Department of Psychology at the University of Bath, and Dr David Jessop from the University of Bristol, has found that children with Asperger Syndrome (AS) do not experience this surge.
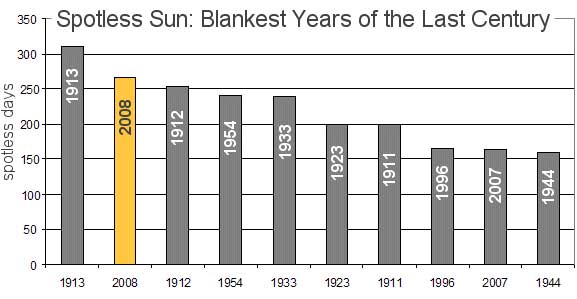
The sunspot cycle is behaving a little like the stock market. Just when you think it has hit bottom, it goes even lower.
2008 was a bear. There were no sunspots observed on 266 of the year's 366 days (73 percent). To find a year with more blank suns, you have to go all the way back to 1913, which had 311 spotless days. Prompted by these numbers, some observers suggested that the solar cycle had hit bottom in 2008.
Maybe not. Sunspot counts for 2009 have dropped even lower. As of March 31st, there were no sunspots on 78 of the year's 90 days (87 percent).
A team of astronomers, led by Stefan Kraus and Gerd Weigelt from the Max-Planck-Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfR) in Bonn, used ESO's Very Large telescope Interferometer (VLTI) to obtain the sharpest ever image of the young double star Theta 1 Ori C in the Orion Trapezium Cluster, the most massive star in the nearest high-mass star-forming region.
We all know that people sometimes change their behavior when someone is looking their way. A new study in Current Biology shows that jackdaws, birds related to crows and ravens with eyes that appear similar to human eyes, can do the same.
"Jackdaws seem to recognize the eye's role in visual perception, or at the very least they are extremely sensitive to the way that human eyes are oriented," said Auguste von Bayern, formerly of the University of Cambridge and now at the University of Oxford.
Long before they became famous as barbaric raiders, Vikings played nice with British and Irish culture, according to findings at a recent Cambridge University conference.
The conference, entitled "Between the Islands", was organized by the University's Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse and Celtic and its Centre for Research in the Arts, Social Sciences and Humanities (CRASSH) and had more than 20 cutting-edge studies which reveal how the Vikings shared technology, swapped ideas and often lived side-by-side in relative harmony with their Anglo-Saxon and Celtic contemporaries.
Smokers who do not want to quit right now but would like to at least reduce their smoking are twice as likely to stop smoking in the long-term if they use nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) to help them cut down gradually, according to research published on bmj.com.
The research is the first of its kind to focus on sustained smoking abstinence using NRT for smokers who have no immediate plans to stop smoking.