Before the invention of modern science and technology, where many diverse foods can be grown in areas once considered inhospitable, the whims of nature determined what you ate, and if you ate at all.
Was Charles Darwin a one-hit wonder? According to scientists who take a gene’s-eye view of evolution, the 19th-century English naturalist contributed one crucial idea to understanding how species change: natural selection, or “design without a designer”.
However, a book of Darwin’s that is little read by modern evolutionists – The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals – turns out to contain valuable lessons for scientists seeking to understand how and why humans do what we do.
A recent
study found that a virtual reality experience is able to reduce stress among COVID-19 frontline healthcare workers.
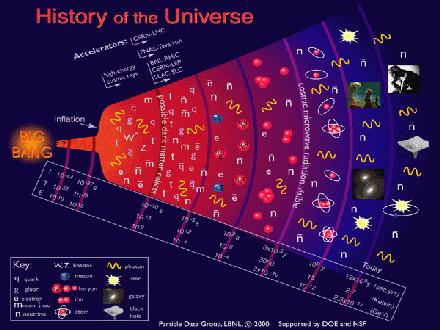
Protons are the fundamental subatomic particles. Under the Standard Model, we know that protons are composite particles with three valence quarks, which, along with neutrons, form hardons.
Galaxy clusters grow over time under gravity and, in the present-day universe, can contain hundreds or even thousands of galaxies, as well as hot gas and dark matter. As time goes by, their galaxies burn through the fuel available and evolve from vigorously star-forming galaxies into red and dead galaxies.
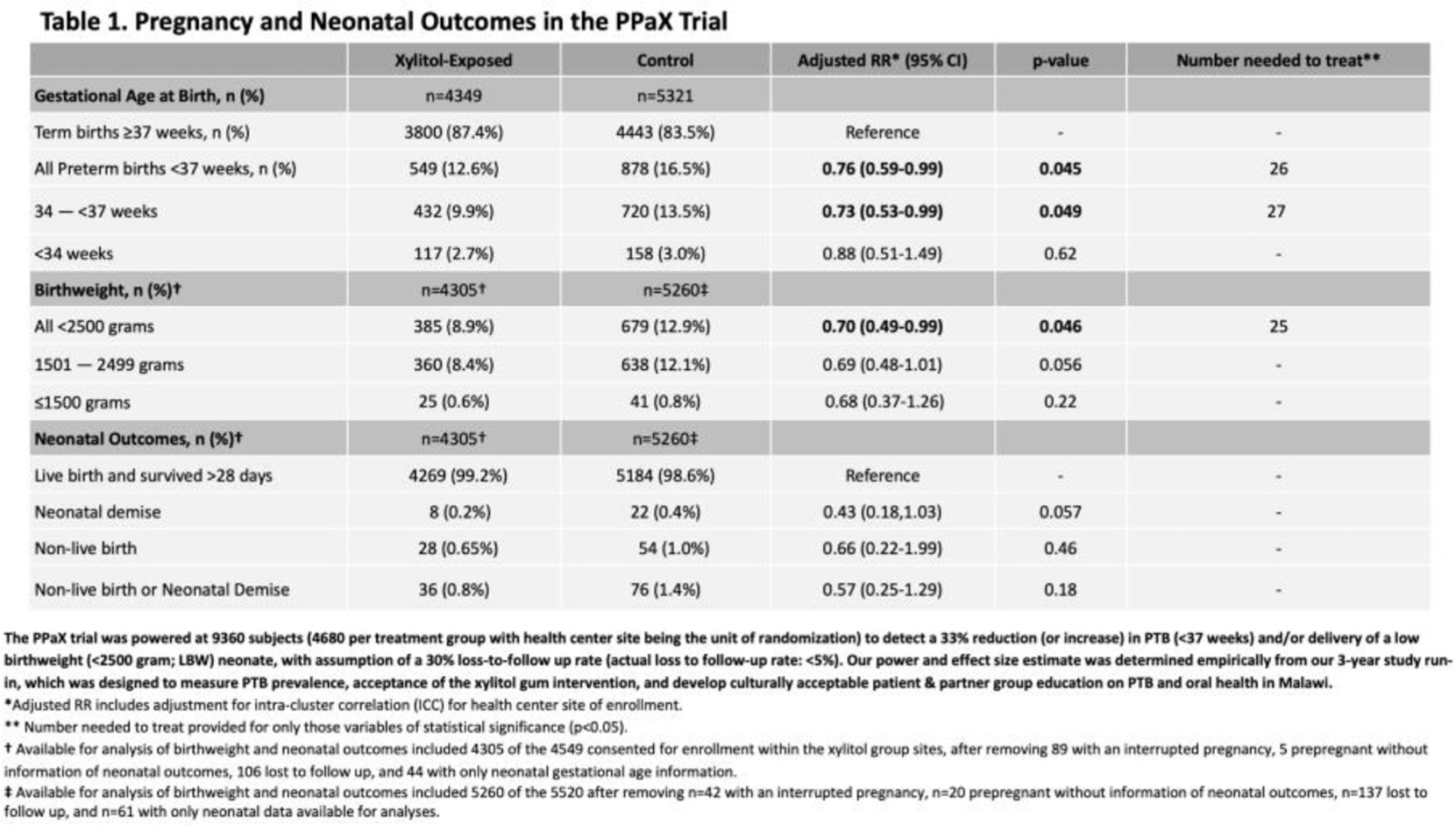
In the last few decades more has been learned about the impact of oral health on the entire human biological system. And more is being done to reduce factors that lead to an estimated 15 million babiesborn prematurely or preterm (defined as delivery before the 37th week of pregnancy) each year. Preterm babies are at greater risk of experiencing serious health problems.
Due to correlation between preterm births and poor oral care, researchers have looked at various ways to improve dental health during pregnancy, including “deep-teeth cleaning” like scaling and planing to remove plaque and tarter on the teeth and below the gum line, but that hasn't seemed to be very effective.
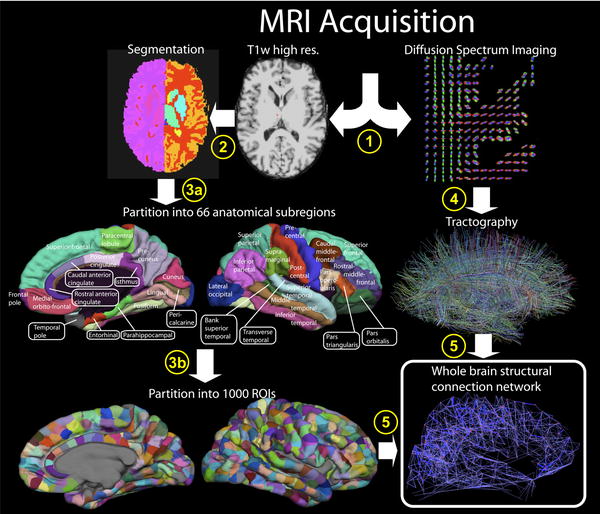
Our auditory system is able to detect sounds at an implicit level. The brain can distinguish between even very similar sounds, but we do not always recognize these differences. A new study demonstrated using sound perception during passive listening; when the subject is not trying to explicitly hear the differences.
The result was that the human brain unconsciously distinguishes between even very similar sound signals during passive listening.
Although unconventional, the ideas of Gregory Ryskin on vacuum energy sound interesting to me, so I invited him to share them with you in this guest post.
Ryskin's physics journey began with fluid dynamics, first in Russia, then in the US, at Caltech. Later, the flow of complex fluids, such as polymer solutions or liquid crystals. Then Brownian motion and Markov processes. In 2000, he became interested in geology and geophysics, particularly in the causes of mass extinctions and the origin of the Earth’s magnetic field. His current research is focused on cosmology. His academic home is Northwestern University, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering.
The text below is Gregory's.
---
The rise of the omicron variant has caused havoc around the world, just as the emergence of the delta and alpha variants did before. A pattern has emerged, with the world scrambling to respond to a new form of the coronavirus every six or so months. How can we reduce the risk of new variants appearing again and again?
Firstly, let’s consider how they emerge. A virus reproduces by making copies of itself. Every time it replicates, there’s a tiny chance that an error occurs in the copying of the virus’s genetic sequence.
We may be our own worst critics, but America continues to lead the world in science, science literacy, and science policy. Anyone who has tried to navigate science policy in Europe knows how bad it can get when the discourse is hijacked by government-funded environmental groups who use taxpayer money to prevent sane efforts at progress for European taxpayers.
Compared to Europe, American scientists have it good.