 A 900-Meter Clue Beneath The Granite: China’s Jinlin Crater Reshapes Our Understanding Of Holocene Impacts
A 900-Meter Clue Beneath The Granite: China’s Jinlin Crater Reshapes Our Understanding Of Holocene ImpactsFor decades, scientists have assumed that the Holocene—the relatively quiet geological epoch...
 The 53-Year Odyssey Of Kosmos 482 And The Push For Sustainable Space
The 53-Year Odyssey Of Kosmos 482 And The Push For Sustainable SpaceA Fallen Spacefarer Returns to Earth...
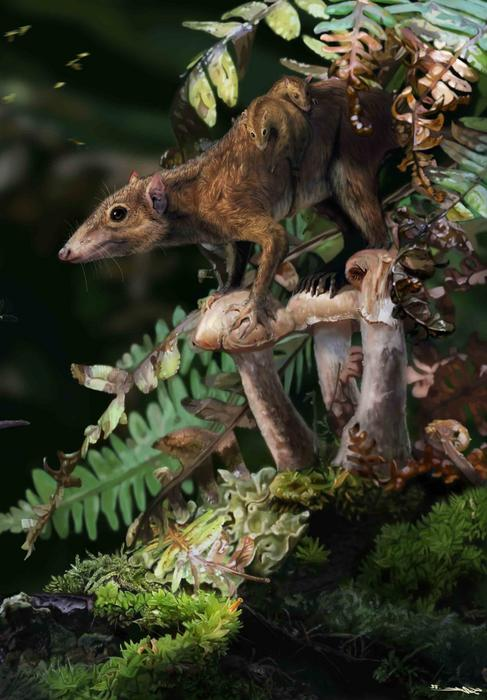 Mammals On The Ground Before The Dinosaurs Were Gone
Mammals On The Ground Before The Dinosaurs Were GoneFor decades, natural history books have taught that when a catastrophic asteroid struck Earth...