Vegetarians must have felt a little left out when hearing stories of startling weight loss by people consuming nothing except bacon and cheddar cheese.
It was only a matter of time before a study came along showing that vegetarians could get thin too. Of course, the secret ingredient was, as always, participants consuming fewer calories than they burned. Again.
But the non-weight benefits are worth discussion. Overweight individuals who ate a low-calorie, low-carbohydrate diet high in plant-based proteins for four weeks lost weight and experienced improvements in blood cholesterol levels and other heart disease risk factors, according to a report in the June 8 issue of Archives of Internal Medicine.
If you've ever been an engineering student, taught engineering or hired a young engineer, this will sound familiar: tales of students splitting up group projects so they don't have to work together or a student stating he didn't bother with the directions but still got the right answer or students who do the whole project an hour before class.
Expert engineers waiting to happen? Maybe some day, but that stuff irks hiring managers in the real world, where huge mistakes and sloppy work bring on costly overruns and maybe lawsuits.
Do you think high fructose corn syrup makes you fatter than sugar? You're not alone. In the culture wars, they like lines blurry and corporations who got rid of corn syrup have been using that as a marketing claim.
Three top researchers say they have corrected inaccuracies and misunderstandings concerning high fructose corn syrup's impact on the American diet and examined how the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) considers this sweetener in light of the upcoming 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans in their session, 'High Fructose Corn Syrup: Sorting Myth from Reality', at the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) Annual Meeting in Anaheim, California.
More than 100 feet deep in Lake Huron, on a wide stoney ridge that 9,000 years ago was a land bridge, University of Michigan researchers have found the first archeological evidence of human activity preserved beneath the Great Lakes.
The researchers located what they believe to be caribou-hunting structures and camps used by the early hunters of the period.
"This is the first time we've identified structures like these on the lake bottom," said John O'Shea, curator of Great Lakes Archaeology in the Museum of Anthropology and professor in the Department of Anthropology. "Scientifically, it's important because the entire ancient landscape has been preserved and has not been modified by farming, or modern development."
According to research presented on Monday, June 8 at SLEEP 2009, in the presence of free access to food, sleep restricted subjects reported decrease in appetite, food cravings and food consumption; however, they gained weight over the course of the study. Thus, the finding suggests that energy intake exceeded energy expenditure during the sleep restriction
Results indicate that people whose sleep was restricted experienced an average weight gain of 1.31 kilograms over the 11 days of the study. Of the subjects with restricted sleep who reported a change in their appetite and food consumption, more than 70 percent said that it decreased by day 5 of the study. A group of well rested control subjects did not experience the weight gain.
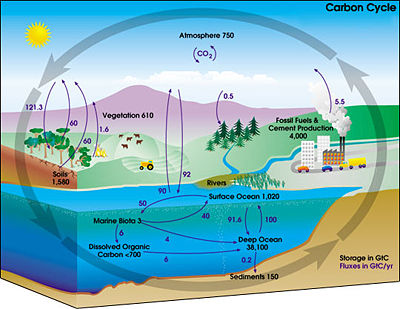
Trains, planes, buses and automobiles are more than just exhaust, when it comes to the full scope of environmental damage. There is a full life-cycle of processes associated with getting from Point A to Point B that we have difficult quantifying but in an article published today in Environmental Research Letters, researchers from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of California, Berkeley, say they have created a framework to help us calculate the true environmental cost of travel.
 The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science Look
The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science Look $0.50 Pantoprazole For Stomach Bleeding In ICU Patients Could Save Families Thousands Of Dollars
$0.50 Pantoprazole For Stomach Bleeding In ICU Patients Could Save Families Thousands Of Dollars Metformin Diabetes Drug Used Off-Label Also Reduces Irregular Heartbeats
Metformin Diabetes Drug Used Off-Label Also Reduces Irregular Heartbeats  Your Predator: Badlands Future - Optical Camouflage, Now Made By Bacteria
Your Predator: Badlands Future - Optical Camouflage, Now Made By Bacteria