Scientists in Italy have found bacteria in the root of a tropical grass whose oils have been used in the cosmetic and perfumery industries. These bacteria seem to promote the production of essential oils, but also they change the molecular structure of the oil, giving it different flavours and properties: termicidal, insecticidal, antimicrobial and antioxidant.
A research study carried out by the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) proves that administering natural antioxidants can reduce the effects of lead poisoning in animals during the gestation and lactation periods. The study suggests that it could also be effective in humans.
In this study, published in the magazine Food and Chemical Toxicology, the researchers aimed to prove that since the principal toxicity mechanism of lead poisoning is that it creates free radicals that lead to cellular destruction; administrating natural antioxidants could reverse this process and re-establish the organism's lost balance. The results of the study are preliminary but they could be the beginning of a possible therapeutic treatment to cure the disease.
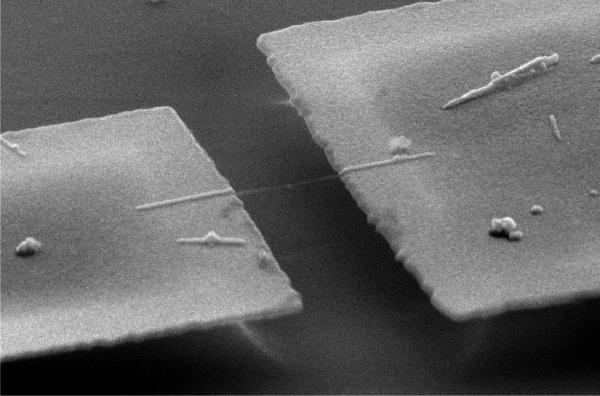
A group of researchers led by Adrian Bachtold of the CIN2 laboratory in Spain has developed an ultrasensitive mass sensor, which can measure tiny amounts of mass with atomic precision, and with an unprecedented resolution to date.
The CIN2 (Research Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology), is a joint centre belonging to the Spanish National Council for Scientific Research (CSIC) and the Nanotechnology Catalonian Institute (ICN).
Consuming foods rich in polyphenols from grapes, including red wine, helps reduce the risk of heart disease, according to a review article in the November issue of Nutrition Research.
The authors review the accumulating evidence that grape polyphenols work in many different ways to prevent cardiovascular and other "inflammatory-mediated" diseases. Polyphenols are natural antioxidants found in grapes and some other plant foods. Their types and actions vary, depending on where in the grape they are found. Grape seeds, grape skin, and grape juice contain several types of polyphenols, including resveratrol, phenolic acids, anthocyanins, and flavonoids.
A group of researchers have created a biodegradable 'scaffold' and living heart cells or stem cells seeded onto such a scaffold could develop into a patch of cardiac tissue to treat congenital heart defects, or aid the recovery of tissue damaged by a heart attack. The biodegradable scaffold would be gradually absorbed into the body, leaving behind new tissue.
The accordion-like honeycomb scaffold, to be reported in the Nov. 2 online edition of Nature Materials, is the first to be explicitly designed to match the structural and mechanical properties of native heart tissue. As a result, it has several advantages over previous cardiac tissue engineering scaffolds.
Industry analysts suggest that the recent financial crisis is starting to have an effect on the growth of the biotechnology industry, once thought to be a recession-proof sector. They contend that the lack of available institutional cash and venture money is causing extant biotechnology companies to “tighten their belts.” And, if the trend continues, this lack of capital will stifle innovation, which in turn, will threaten and undermine the stability and future of the entire biotechnology sector. While times are certainly tough, the biotechnology industry, in my opinion, is alive and well and will continue to expand well into the 21st century.
BASEL, Switzerland, November 1 /PRNewswire/ --
- Three New Studies Presented at AASLD Demonstrate Efficacy and Safety of Extended Treatment in Non-Responders, Relapsers and Slow-Responders
Cure rates for certain groups of difficult-to-treat hepatitis C patients can be improved significantly by extending the treatment period with PEGASYS(R) (peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD)) and COPEGUS(R) (ribavirin) to 72 weeks, according to new studies being presented at AASLD this week in San Francisco.
BASEL, Switzerland, November 1 /PRNewswire/ -- A new, independently-conducted study being presented at AASLD shows that PEGASYS(R) (peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD)) regimens result in higher cure rates for hepatitis C patients compared to regimens with another pegylated interferon.(1)
Comparing Today's Standard Treatment Regimens: The Milan Safety Tolerability Study
A system of presumed consent for organ donation - where people have to opt out of donating their organs when they die - is the best way to tackle a growing waiting list for transplant, according to Dr John Troyer, an expert in organ donation and the illegal trade of body parts, who has recently joined the University of Bath’s Centre for Death&Society. Yes, that is a real department and not a Halloween trick. We checked.
There are more than 7,500 patients in the UK currently on the waiting list for organ donations.
A study in the Nov. 1 issue of the journal Sleep is the first demonstration of a specific neurochemical abnormality in adults with primary insomnia, providing greater insight to the limited understanding of the condition's pathology.
Results indicate that gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the most common inhibitory transmitter in the brain, is reduced by nearly 30 percent in individuals who have been suffering from primary insomnia for more than six months. These findings suggest that primary insomnia is a manifestation of a neurobiological state of hyperarousal, which is present during both waking and sleep at physiological and cognitive levels.