Climate change causing every weather event enjoyed the kind of fallacious media coverage in late 2012 it hadn't gotten since 2006 - it remains bad science. While short-term weather is notoriously volatile, climate is more of an average weather pattern over a long period of time. This dichotomy provides the analytical framework for scientific thinking about atmospheric variability, including climate change.
But even the weather-climate dichotomy paints an incomplete picture.one that may be complicating efforts to untangle natural variations in climate from man-made effects, according to a paper published recently in the journal Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union.
Lovejoy argues that statistical analysis shows there is a period between short-term weather and long-term climate that should be recognized as distinct.
Using the three-part atmospheric regime also makes the challenge of climate modeling more precise, and could open up a new set of approaches for modeling and predicting the climate, says McGill University physics professor Shaun Lovejoy Lovejoy, whose statistical analysis shows there is a period between short-term weather and long-term climate that should be recognized as distinct.
Lovejoy used what he calls a new kind of "fluctuation analysis" to show that there are three atmospheric regimes, each with different types of variability. Between the weather (periods less than 10 days) and the climate (30 to 100 years), there is an intermediate "macroweather" regime.
The chart below shows examples from weather (one-hour resolution, bottom), macroweather (20 days, middle) and climate (one century, top). The daily and annual cycles were removed and 720 consecutive points from each resolution are shown so that the differences in the characters of each regime are visually obvious.
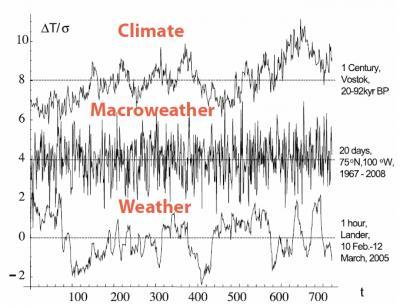
Lovejoy and his research team used 'fluctuation analysis' to state that there are three atmospheric regimes, each with different types of variability. Between the weather (periods less than 10 days) and the climate (periods longer than about 30 to 100 years), there is an intermediate 'macroweather' regime. Credit: S. Lovejoy
At the bottom, the weather curve "wanders" up or down in a path resembling a drunkard's walk. In the middle, the macroweather curve has a markedly different character: upward fluctuations are typically followed by nearly cancelling downward ones. "The longer the period over which we average it, the smaller the variations become," Lovejoy says.
By contrast, the century scale climate curve (top) displays again a weather-like, wandering variability. (While this plot shows temperatures, other atmospheric fields – including wind, humidity and precipitation -- are similar.)
Although the ultimate implications of macroweather may not be known for some time, a basic change in our understanding of what climate is will surely have repercussions, Lovejoy notes.
"Macroweather clarifies the distinction between natural and anthropogenic types of variability and allows us to separate the two with more confidence."
The old saying that "climate is what you expect, weather is what you get," also needs to be reconsidered, he adds. "Macroweather is what we expect."






Comments