Streptococcus mutans and other harmful bacteria get their own holiday feast and S. mutans gets to launch one of its biggest assaults of the year on your tooth enamel. But you have soldiers on your side too, namely cranberries and even wine, say dental researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center
Cookies, pies and other sweets common on Thanksgiving contain mountains of sugar, but it's not the sugar itself that causes tooth decay. Instead, S. mutans and other bacteria in our mouths feast on the sugars, stick on your teeth and then churn out acid that eats away at tooth enamel. Hyun "Michel" Koo, D.D.S, Ph.D., is a dentist turned food scientist and microbiologist who is studies the destructive power of S. mutans and scouring foods and natural substances to harness their ability to prevent cavities.
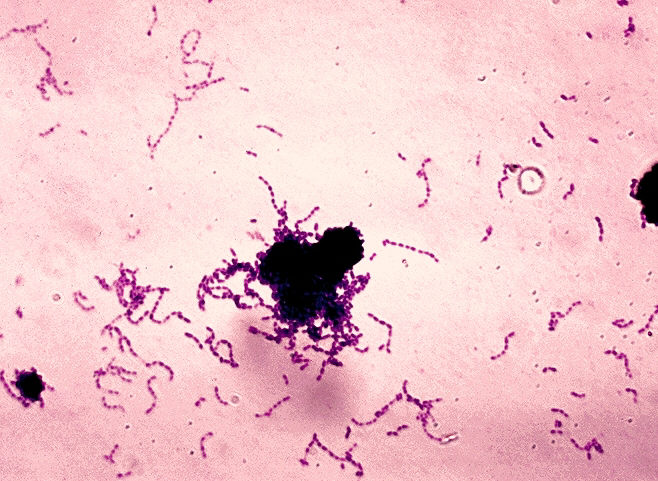
Credit: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Public Health Image Library (PHIL), identification number #1043
"Natural substances offer tremendous possibilities for stopping tooth decay," said Koo. "Our time spent in the laboratory is aimed at harnessing the potential of some of these compounds, perhaps eventually incorporating them into a toothpaste or mouth rinse to stop dental decay."
Koo says cranberry is a potential ally in the fight against S. mutans, which is a threat to our teeth primarily because of its ability to form plaque. What appears to us as sticky white gunk along our teeth is actually a formidable fortress of molecules known as glucans – building blocks of plaque, stacked like bricks in a wall, rife with bacteria. It's a gunky fortress that covers the tooth and gives bacteria a safe haven to munch on sugar, thrive, and churn out acid.
Koo has discovered that compounds within the cranberry disrupt enzymes known as glucosyltransferases that bacteria use to build glucans. Without its glucans, S. mutans and other bad bacteria in plaque becomes vulnerable.
Together with Nicholi Vorsa, Ph.D., director of the Philip E. Marucci Center for Blueberry and Cranberry Research and Extension at Rutgers University, Koo is working to isolate the compounds within the cranberry that are most protective. The pair has identified molecules known as A-type proanthocyanidins as having potential to reduce cavities dramatically. Earlier this year in the journal Caries Research, the team reported that when the molecules were applied, glucan and acid production by S. mutans was reduced by up to 70 percent, and cavity formation in rats was slashed by up to 45 percent.
"Maintaining the natural balance of resident flora in the oral cavity is important for keeping opportunistic pathogens in check," said Koo, a researcher in the Center for Oral Biology and an associate professor in the Eastman Institute for Oral Health and the Department of Microbiology and Immunology. "These molecules don't outright kill S. mutans. Instead, they disrupt the two most harmful actions of this pathogenic organism, acid production and glucan production."
More good news about red wine
It's been a good decade for red wine and health benefits and 2010 will end it no different. With funding from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Koo began a research project with Olga I. Padilla-Zakour, Ph.D., associate professor of Food Processing at the New York Agricultural Experiment Station of Cornell University. They found that the abundant waste from the red-wine-making process – materials such as fermented seeds and skins collectively known as pomace that are cast away after grapes are pressed – contains compounds that fight S. mutans. In particular, some polyphenols can inhibit the activity of S. mutans' crucial enzymes by as much as 85 percent and also reduce the amount of acid the bacteria produce.
Last month, a study showed that S. mutans is even more powerful than scientists have realized (PLoS ONE 5(10): e13478. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013478), responding readily to changing environmental conditions in the presence of starch and sucrose to thrive in the mouth.
In work led by Marlise Klein, D.D.S., Ph.D., research assistant professor, the team analyzed the activity of more than 300 genes in S. mutans under changing conditions. The team found that certain key proteins boost their activity dramatically in the presence not only of sugar but also complex carbohydrates derived from starch digestion. Once the body's own amylase enzymes naturally present in saliva break down starches, S. mutans kicks its glucan-forming machinery into high gear.
"The new research shows how two pillars of the modern diet, starch and sugar, can work cooperatively to bring about tooth decay," said Koo. "A cookie, sugar-covered doughnut, or a piece of pie filled with both sugar and starch provide the perfect recipe for the bacteria that destroy teeth."
Even when the amount of sugar was slashed in half, certain genes central to the ability of S. mutans to create its formidable glucan fortress boosted their activity five-fold in the presence of starch-derived carbohydrates. That enabled the bacteria to create plaque that is hardier, stickier, and capable of producing more acid than plaque created without significant starch present.
So what to do on Thanksgiving Day
Eating more cranberry sauce or drinking more wine is the fun way to try and prevent cavities but the high levels of acidity or the added sugar that cranberry products include are not great. Instead, everything your dentist keeps telling you remains the best advice to prevent cavities.
"On Thanksgiving Day, like any day, brush your teeth, avoid foods filled with sugars as best you can, and don't snack often – and if you do, brush your teeth again," said Koo. "Consider using a mouth rinse, get some fluoride in there – and be sure to see a dentist regularly."






Comments