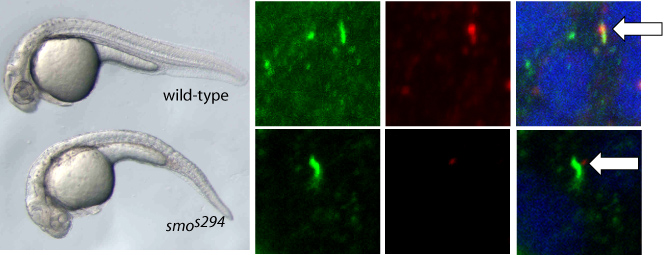
It is the concentration of a few signaling molecules that determines the fate of individual cells during the early development of organisms, say a team of molecular biologists writing in Current Biology. Pia Aanstad of the University of Innsbruck and colleagues report that a variety of molecular mechanisms accounts for the interpretation of the concentration of the signaling molecule Hedgehog.
The development of an organism is a complex process to which a dozen or hundreds of signaling molecules contribute. Some of these molecules have dozens of functions in the fruit fly and in humans alike.
Pulsars are superdense neutron stars, the remnants left after massive stars have exploded as supernovae. Their powerful magnetic fields generate lighthouse-like beams of light and radio waves that sweep around as the star rotates. Most rotate a few to tens of times a second, slowing down over thousands of years.
The Mars rover, Opportunity, surveyed the rim and interior of Victoria Crater on the Red Planet from September 2006 through August 2008. Key findings from that work, reported in the May 22 edition of Science, reinforce and expand what researchers learned from Opportunity's exploration of two smaller craters after landing on Mars in 2004.
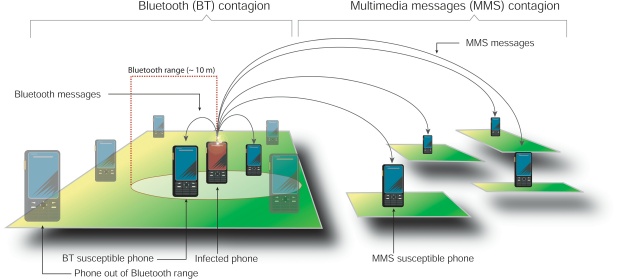
If you own a computer you have probably gotten a 'virus' but there have been no major outbreaks of mobile phone viral infection despite the fact that over 80 percent of Americans now use these devices. A team headed by Albert-Laszlo Barabasi, director of the Center for Complex Network Research at Northeastern University, set out to explain why this is true.
A class of drugs already approved as cancer treatments might also help to beat alcohol addiction. That's the conclusion of a discovery in flies of a gene, dubbed happyhour, that has an important and previously unknown role in controlling the insects' response to alcohol.
Animals with a mutant version of the gene grow increasingly resistant to alcohol's sedative effects, the research shows. The researchers report further evidence that the gene normally does its work by blocking the so-called Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) pathway. That EGF pathway is best known for its role in cancer, and drugs designed to inhibit the EGF receptor, including erlotinib (trade name Tarceva) and gefitinib (trade name Iressa), are FDA-approved for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
New research provides exciting genetic insight into a rare syndrome that first appeared in the medical literature in the mid 1800s with the case of Julia Pastrana, the world's most notorious bearded lady. The study, published by Cell Press in the May 21st issue of the American Journal of Human Genetics, reveals intriguing molecular clues about the pathogenesis of this mysterious condition that has captured the attention of the public since the Middle Ages.
 Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science Look
The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science Look $0.50 Pantoprazole For Stomach Bleeding In ICU Patients Could Save Families Thousands Of Dollars
$0.50 Pantoprazole For Stomach Bleeding In ICU Patients Could Save Families Thousands Of Dollars Metformin Diabetes Drug Used Off-Label Also Reduces Irregular Heartbeats
Metformin Diabetes Drug Used Off-Label Also Reduces Irregular Heartbeats