In the previous post, the two-photons-whirl was introduced in the quite physical and quite rational way.
The two-photons-whirl concept does require deeper/broader analysis, development, investigation, but that simply cannot compromise this concept.
Not only that this concept – that the photons are the basic building blocks for inertial-mass-particles and charged particles, actually, that the elementary particle which has inertial mass and charge is the two-photons-whirl – is both logically and physically completely plausible, but there does not exist any logical, rational, and physical argument against this concept.
The two-photons-whirl enables quite comprehensive reasoning, rational reasoning, about anything that concerns fundamental physical phenomena, and up. And concerning the issues which are still unresolved, it immediately opens the reasonable how-and-why possibilities/directions for solutions.
Let’s make a brief survey:
After introducing the two-photons-whirl, we know what matter
essentially is. Before, each elementary material particle was considered
to be something completely different, something special, a unique kind of
manifestation of existence, and which could mysteriously fall apart into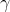 -photons,
and which could also, mysteriously, emerge from
-photons,
and which could also, mysteriously, emerge from 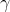 -photons.
After introducing the two-photons-whirl, there is no mystery anymore – just
real science.
-photons.
After introducing the two-photons-whirl, there is no mystery anymore – just
real science.
We do not know the very details of inner ticking of a photon, but we know that it is an elementary EM-oscillation, and we know that it behaves also mechanically, that is, it exchanges momentum/energy with other particles. And now – after introducing the two-photons-whirl concept – we know why other kinds of particles behave in the wave-particle way: the wave-particle behavior of the elementary inertial-mass (the two-photons-whirl) is caused by the wave-particle behavior of the photons which constitute that inertial-mass.
By introducing the two-photons-whirl:
- the spin is the spin, in its original, commonsense meaning,
- the inertia, that is, the inertial mass is explained in unprecedented
and at the same time completely clear, comprehensive way, in
the most explicit way ever. Actually, this is the first time that inertia is at
all explained – so far it was the mysterious property of matter, and
inertia was considered as the synonym for mass. In contemporary physics, the
photon was forbidden to have mass, because it is non-inertial entity. Namely,
since the Einstein’s SR equation for mass shows that mass increases with
velocity and that it cannot reach the velocity c, and photon moves with that
velocity, then the scientists reached the consensus: “photon cannot have mass –
it is massless particle”. That confusion, that is, that inconsistency, is
completely resolved by explanation given in The gem (5), that, essentially, the
mass is the electromagnetic phenomenon::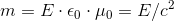 , and that the photon has
the mass, which – in the case of a photon – is just the non-inertial mass. And
then it was explained – by introducing the two-photons-whirl – that the photon’s non-inertial mass is the
origin of inertial mass. And inertia was then finally properly explained. So,
now, everything is consistent. (And later – in the next post – we will also
deal with SR, and make things clear there, too).
, and that the photon has
the mass, which – in the case of a photon – is just the non-inertial mass. And
then it was explained – by introducing the two-photons-whirl – that the photon’s non-inertial mass is the
origin of inertial mass. And inertia was then finally properly explained. So,
now, everything is consistent. (And later – in the next post – we will also
deal with SR, and make things clear there, too).
The two-photons-whirl concept makes the spin --- inertial mass connection/dependence obvious, makes it almost trivial. In current physics, explanation of that dependence was tried through the invention of the whole new imaginary sub-Planck-level world, the new, deeper, undetectable kind of existence, known as the strings, superstrings, …, and then, later, that explanation was replaced with another “explanation”, achieved through visionary upgrade of QM, that is, with QCD. Well, now – with the two-photons-whirl concept, with that completely physical, realistic concept – we have the true explanation (meaning, the explanation in the real sense of the word explanation).
Concerning the stability of the two-photons-whirl, beside its implicit explanation by the fundamental derivation of Gaussian in the previous post, there is another stability enhancing possibility: the two-photons-whirl may be some sort of phase-locked-loop.
The stable photons-whirl is, most probably, some kind of elementary circular standing EM-wave.
An appropriate folding of E and M components of the photons in a photons-whirl would produce an electrically charged particle (the reasonable basis, and also experimental basis for this was given in the previous post).
So, now, we know what the charge actually is. Charge is not some special, separate, axiomatic quality – the special quality is the essential property of existence: electromagnetic duality. It is not the charge which is the source of electric component of that duality. It is opposite – the appropriate superposition of elementary E and M components of two-photons-whirl creates that what we call charge.
Another appropriate folding could produce an electrically neutral particle.
How exactly does that happen? Well, that is something that has to be discovered. But now, we know exactly in what direction we should go with our investigation, what (and why) we have to look for. In other words, we can rationally, reasonably, think about it within the realm of existing, real and known phenomena (we do not need to invent some “higher/deeper” over-rational principles, “higher/deeper” realities, …).
If someone would argue that the „annihilation“ of a slow
electron and a slow positron results with just two 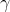 -photons, that would be easy to explain:
-photons, that would be easy to explain:
- it is the resonant, perfect (precise, accurate) match, whose result is:
one photon of the electron and one photon of the positron merge into one photon, and the rest two photons merge into the other photon. These new photons have higher energy (bigger mass), which affects their lengths. Also, the allowed-velocities-distribution is affected. Also, the whirl-radius is affected. All of these changes together disturb the geometry and balance of whirling enough to cause that these new photons – two of them – fly away.
In other words, the reasonable and the easiest explanation of the fact that the result of “annihilation” are two photons, actually requires (demands) the two-photons-whirl concept.
The energy exchange between a photons-whirl, that is, between the elementary inertial-(charged)-mass, and some other such particle manifests itself as the classical kinetic energy exchange, as long as that exchange does not become so intensive, or resonant to cause the transformation or dispersion of the photons-whirl.
The „annihilation“, the nuclear processes (fission, fusion, radioactive decay), the electron-positron pair generation are, respectively, the processes of unformation (dispersion), reformation (transformation), formation of the photons-whirls.
Etc.
Actually, the only thing that is hard to comprehend and/or hard to accept concerning the concept „an elementary particle is the two-photons-whirl“, is that it was never considered in physics so far.
Unification of physics
What is the simplest way possible to mathematically model the presence of something, or, in other words, what is the basic, the essential potential for influence of some object?
The
more energy some object has, the more influence on another object it may exert,
i.e., when they collide. So, the basic mathematical model should contain the
direct proportionality to the energy 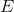 of an object.
of an object.
In order to collide, the objects have to approach each other. The more near they are, the “danger” (or the expectation) of collision rises. So, the basic mathematical model should contain the reciprocal proportionality to the distance from the object.
In other words: if there is more of something (and the measure for that is the energy of that something), and if that something is more near to us, then that something will/can/does affect us more. This is what we experience every day.
So,
the very basic mathematical model of the
presence of something (of the
essential potential for influence of something) would be the ratio 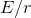 (where
(where 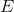 is the energy of
the object, and
is the energy of
the object, and  is the
distance from that object).
is the
distance from that object).
Beside
that this was quite reasonable and understandable establishment and
interpretation of 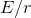 ,
this ratio is also something what
appears on the fundamental level, on the photon-level: on several places in
this post-series, we have already derived the equation
,
this ratio is also something what
appears on the fundamental level, on the photon-level: on several places in
this post-series, we have already derived the equation
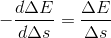
which may/could/should be interpreted like this: the force (influence) which a photon may exert is equal to the ratio of its current energy and its current length. So, the ratio of photon’s current energy and current length is the potential for influence of a photon.
With respect to the previous introduction/presentation of the measure of presence (of the potential to influence), this presentation is spatially constrained, to the size of a photon. This one is the most elementary one. The previous one contains the generalization of the spatial part: there, it is not the size of the object, but it is the distance from the object.
Though
that ratio has the dimension of force, it is not the force. The force is the
change of energy along length  – it stops acting as soon as there is no change of energy any more (as soon
as energy distribution becomes constant along length),
and the
– it stops acting as soon as there is no change of energy any more (as soon
as energy distribution becomes constant along length),
and the 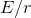 is the measure of presence, or, the potential to influence.
is the measure of presence, or, the potential to influence.
Starting with the two-photons-whirl and up, the measure of presence describes, so to say, external behavior of inertial-mass bodies, which implies action at a distance.
What about the apparent singularity at 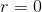 of the model
of the model 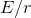 ? Well, for that
we’d have to know the inner details of the two photons whirl, which are still
unknown, but it is immediately noticeable that there should not be problems
with that, since the center of any real whirl tends to be empty. And this
should be also seen as one more argument in favor of the two-photons-whirl
concept.
? Well, for that
we’d have to know the inner details of the two photons whirl, which are still
unknown, but it is immediately noticeable that there should not be problems
with that, since the center of any real whirl tends to be empty. And this
should be also seen as one more argument in favor of the two-photons-whirl
concept.
According
to the definition of space, introduced in “The gem (5)” (and based on the
physical facts, real facts, detectable/measurable facts), the only physically
possible way for occurrence of the action
at a distance is that the presence of matter does cause the change of  and
and  properties of
space. And, we know that the presence of matter affects
properties of
space. And, we know that the presence of matter affects  and
and  properties of
space:
properties of
space:  and
and  properties
have higher values within an optical prism (or within any other material body),
than they have in the free space.
properties
have higher values within an optical prism (or within any other material body),
than they have in the free space.
And
the deepest possible rational reason for the fact that  and
and  behave in this
way, was explained in “The gem (8)”, and what can be summarized like this:
behave in this
way, was explained in “The gem (8)”, and what can be summarized like this:
The fundamental EM-properties of space are  and
and  . These properties are variable (they have some minimal possible value:
. These properties are variable (they have some minimal possible value: 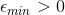 and
and 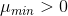 , and they can have values which are greter than these minimal values). The
most fundamental physical cause of increase of
, and they can have values which are greter than these minimal values). The
most fundamental physical cause of increase of and
and  is an appropriate confrontation of two photons which have
sufficiently high energies. In other words: two fundamental
EM-energy-entities, by their appropriate confrontation,
cause the increase of two fundamental EM-properties of space, and that increase
can be such to enable the two-photons-whirl formation, that is, the formation
of elementary constituents of that what we call matter. (The fundamental constituents of matter are electrons and
quarks).
is an appropriate confrontation of two photons which have
sufficiently high energies. In other words: two fundamental
EM-energy-entities, by their appropriate confrontation,
cause the increase of two fundamental EM-properties of space, and that increase
can be such to enable the two-photons-whirl formation, that is, the formation
of elementary constituents of that what we call matter. (The fundamental constituents of matter are electrons and
quarks).
So, the confrontation of two
photons is the primary cause for increase of  and
and  .
When the confrontation is such that the conditions for formation of a
steady two-photons-whirl are fulfilled, then these conditions remain unchanged,
that is, the
.
When the confrontation is such that the conditions for formation of a
steady two-photons-whirl are fulfilled, then these conditions remain unchanged,
that is, the  and
and  remain increased – the stable whirl is the
continuous (ongoing, lasting) non-direct (almost-direct) confrontation – in
other words – it is the continuously confronting flow.
remain increased – the stable whirl is the
continuous (ongoing, lasting) non-direct (almost-direct) confrontation – in
other words – it is the continuously confronting flow.
And, the  and
and  can be also affected further, outside the
two-photons-whirls, by superposition of influences of many two-photons-whirls.
Actually, that would be the basic explanation of the increased values of
can be also affected further, outside the
two-photons-whirls, by superposition of influences of many two-photons-whirls.
Actually, that would be the basic explanation of the increased values of  and
and  within
material objects. And, we also have another level of that superposition, the
weakest one: the superposition of influences of many material objects.
within
material objects. And, we also have another level of that superposition, the
weakest one: the superposition of influences of many material objects.
Let us, briefly, recall the gravitational equations which were derived in „The gem (1)“, and let us pay attention to that what is the essential cause of change of time and length.
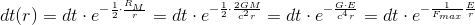
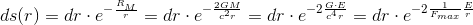
So, that
essential cause, that influencer, is
the ratio 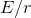
By the way, even the actual GR equations, i.e. the Schwarzschild's solution for gravitational time:
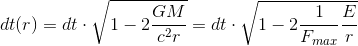
contain the same influencer.
Hence, according to all
this, whatever the inner
distribution of energy and  and
and  of a two-photons-whirl may be, it
has the external residual
of a two-photons-whirl may be, it
has the external residual
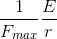
So, the influences of the two-photons-whirl on  and
and  properties of space, outside
the two-photons whirl, should be some fuctions of the type
properties of space, outside
the two-photons whirl, should be some fuctions of the type
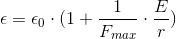
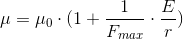
where 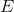 is
the energy of the two-photons-whirl,
is
the energy of the two-photons-whirl,  is
the distance from the center of the two-photons-whirl.
is
the distance from the center of the two-photons-whirl.
This is
the most basic way to model the behavior of  and
and  . And there are all indications that
this is the way we should start that modeling.
. And there are all indications that
this is the way we should start that modeling.
At some observed point in space, which is at a
distance r from a particle of type a, we’d have that the
values of  and
and  in that point are:
in that point are:

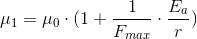
If we now bring another
particle of type a, and set it to be at the
same distance,  , from the observed point in
space, we’d have that the values of
, from the observed point in
space, we’d have that the values of  and
and  in that point are:
in that point are:
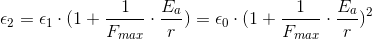
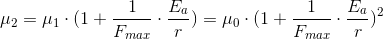
We will continue to add particles, assuming that they are all equally distant from the observed point. We could derive this in a completely proper way, namely to pile-up the particles in the spherical cluster, and to observe some arbitrary point outside that cluster, and to take the real distance of each particle in such cluster from the observed point. But, we won't do that now – we will just continue to add particles, taking that each of them is equally distant from the observed point. We could think of this as if we pile-up the particles in the spherical cluster, and take that their distance from the observed point is the distance among the observed point and the center of the mass of that cluster. We could consider that the observed point is far enough from the cluster, so that the error that we make is acceptably small. And later in this text, we will do the calculation for the real cluster, and show that the i.e. gravitational-time-equation-graph of that cluster, as we go away from the center, flows smoothly into the equation-graph which we will get using this, idealized approach. The finer the granularity of the cluster (the smaller the cluster-elements (which keep to be next to each other), so better the fit in the area near the center. Farther from the center (but not very far – it happens in the vicinity of the Schwarzschild radius) we have the perfect overlap.
For  particles of the type a, we’d have
particles of the type a, we’d have
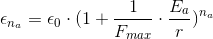
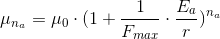
If we now involve one particle of a type b, we’d have
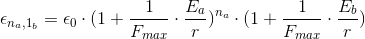
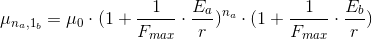
For  particles of type a, and
particles of type a, and 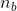 particles of type b, we’d have
particles of type b, we’d have
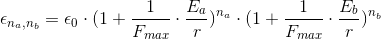
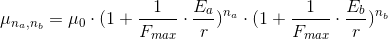
It should be now clear how would these equations look like if we’d have one more particle type: type c.
And that is enough – the, so to say, standard matter is composed of three types of particles: electrons, up-quarks, down-quarks.
Actually, it would had been sufficient if we’d used just one particle type, but we did it this way in order to prove exactly that – that we could had used just one particle type. And that proof will become obvious near the end of this derivation (where the energies of all different particles simply add up).
In the case of bodies of i.e.
cannon-balls-size, the numbers  ,
, 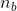 ,
, 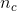 are huge (they are multiples of Avogadro-number).
are huge (they are multiples of Avogadro-number).
So, for i.e.
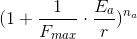
we have
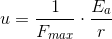
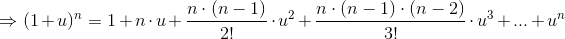
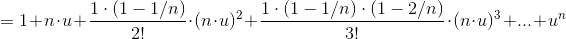
Since 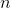 is
huge number, we have
is
huge number, we have
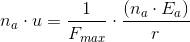
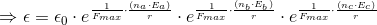
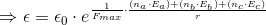
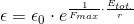
and also,
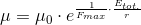
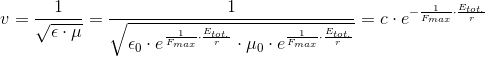
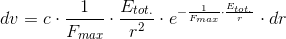
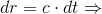
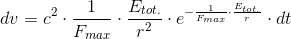
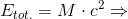
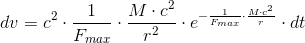
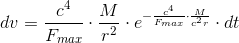
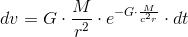
So, if we accept the experimentally confirmed fact that the gravitational acceleration is
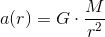
then,
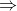
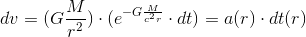
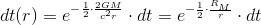
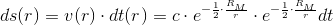
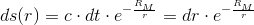
So, the gravitation is essentially an electromagnetic phenomenon.
Namely:
the radially variable gravitational acceleration 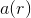 is the consequence of the radially
variable allowed (determined by
is the consequence of the radially
variable allowed (determined by 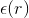 and
and 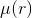 )
velocity
)
velocity 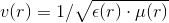 , so, which is the consequence of the
radially variable lengthwise capacitance (electric permittivity) of space
, so, which is the consequence of the
radially variable lengthwise capacitance (electric permittivity) of space 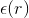 and lengthwise inductance (magnetic
permeability) of space
and lengthwise inductance (magnetic
permeability) of space 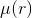 . And radially
variable
. And radially
variable  and
and  are the consequence of the superimposed
influences of two-photons-whirls on
are the consequence of the superimposed
influences of two-photons-whirls on  and
and  . And the primary influence on
. And the primary influence on  and
and  is the adequate confrontation of two
photons, which causes the change (increase)
of
is the adequate confrontation of two
photons, which causes the change (increase)
of  and
and  in the area of confrontation, and that change enables the two-photons-whirl
formation.
in the area of confrontation, and that change enables the two-photons-whirl
formation.
Well, this was the proper unification of physics
(derivation of gravitation from the quantum-level up, that is, from the photons-confrontation
which causes the increase of  and
and  , which enables two-photons-whirl formation,
and derivation of gravitation as the consequence of superposition of influences
of two-photons-whirls on
, which enables two-photons-whirl formation,
and derivation of gravitation as the consequence of superposition of influences
of two-photons-whirls on  and
and  )
)
So, we have just 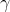 -photons,
-photons,  and
and  , shortly
, shortly 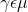 , or,
written with English alphabet, gem.
That is why this post series in named “The gem”. And it has quite appropriate
meaning (in English).
, or,
written with English alphabet, gem.
That is why this post series in named “The gem”. And it has quite appropriate
meaning (in English).
(to be continued)



