Human evolution and culture have been shaped by our increasing ability to communicate.
A new
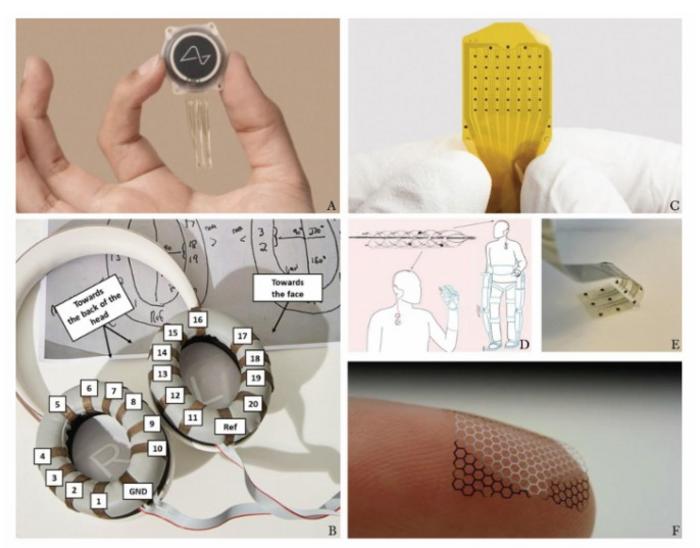
review from China believes that brain-computer interfaces mark the next leap: a direct connection between mind and machine. They note breakthroughs in neural signal decoding, AI, and bioengineering but what should really worry residents of a communist dictatorship is how they believe it will shape autonomy, identity, and mental privacy.
Applications for MSCA Post-doctoral fellowships are on, and will be so until September 10 this year. What that means is that if you have less than 8 years of experience after your Ph.D., you can pair up with a research institute in Europe to present a research plan, and the European Commission may decide to fund it for two years (plus 6 months in industry in some cases).
In order for your application to have a chance to win funding, you need to:
- have a great research topic in mind,
- be ready to invest some time in writing a great application, and
- pair up with an outstanding supervisor at a renowned research institute.
University of Southern Denmark recently demonstrated a soft robot capable of navigating complex terrains using a combination of inflatable actuators and a patterned "kirigami" skin, all moving via rectilinear motion.
You probably think it looks like a worm and it can certainly go places only small things could go.
It's not very fast, only 11 millimeters per second, but it can twist, turn, and navigate through tight spots thanks to its anisotropic anchoring and flexible skin.
 Credit: SDU Soft Robotics
Credit: SDU Soft Robotics
When most people think of hurricanes, they imagine winds gusting over 100 miler per hour, but water has been responsible for 86 percent of all direct hurricane and tropical storm fatalities in the United States for almost this entire century.
Floods, rip currents, and storm surges are the big risk, with freshwater flooding inland accounting for over half of drownings. To help with real-time, the Southeast Atlantic (SEA) Econet network of atmospheric and hydrological monitoring stations provide the real-time data used by the National Weather Service.
An old adage goes that 'if life gives you lemons, make lemonade', which basically means turn something negative into something positive.
Pollution is bad but a new study shows that it may some day be a net win for energy.
Processed and
Ultra-Processed™
foods have been heavy-rotation buzzwords in the food activist community since the Obama administration but gained increased attention once the Trump administration came into power and a chief evangelist against modern food, former Natural Resources Defense Council lawyer Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., was placed in charge of the world's most important government science agency, the National Institutes of Health.
Now, epidemiology has become a Supreme Court over science and instead of evidence-based decision-making, the default has become that if a harm or benefit can be suggested using food or chemical surveys, government will ban it and then tell scientists to figure out why.
Diets high in phytosterols, such as vegetarian diets, have long been linked to lower risk of heart disease and diabetes by lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol but food surveys, questionnaires, and diaries are not reliable enough to make clinical determinations while in mouse experiments the doses were too human to be relevant in the real world.
The organic process is neither viable nor sustainable but a new
paper would like to change that. By allowing modern gene editing. The only way Europe can reach the goal of 25% Organic™ farmland that its government-funded environmental groups demand, a 250% increase, is by moving into the 21st century, they argue.
When the organic process was the only thing available, the food-rich were rich and the poor were poor and the only difference was being born into a natural breadbasket. Cycles of famine were common.
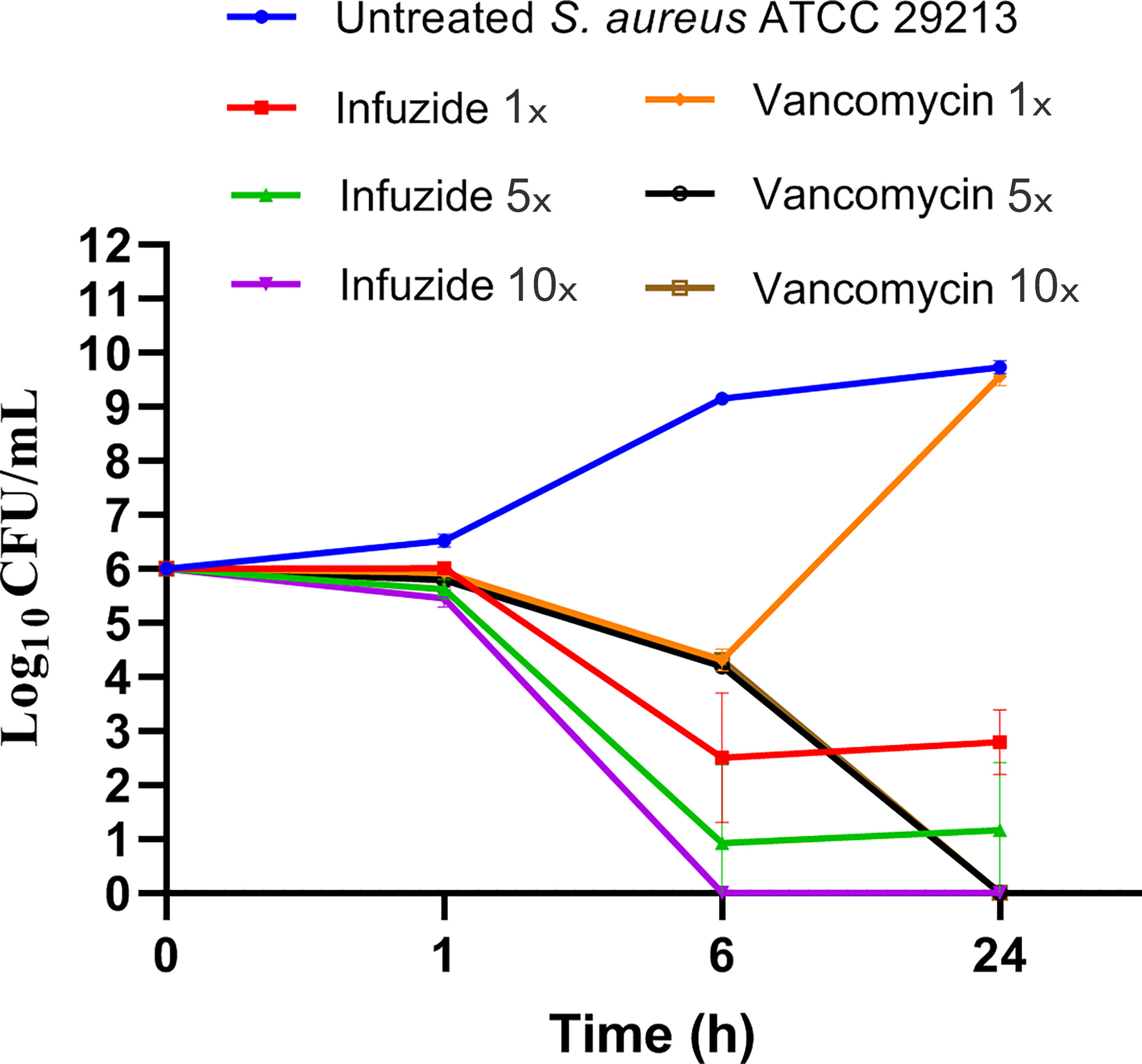
There is no balance of nature and never has been, the universe is always looking for new ways to kill and create, which is why pathogens evolve resistance to drugs over time. It is estimated that antimicrobial resistance causes over 1,000,000 deaths each year and is involved in 35,000,000 more, if estimates by the United Nations World Health Organisation are accurate. Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus sp., two gram-positive pathogens highly likely to develop resistance to known treatments, can cause dangerous hospital-acquired and community-acquired infections.