Entropic gravity is back in the news. Various science blogs again carry headlines dealing with entropic gravity. This time round, the reports are less favorable towards the idea of gravity being entropic, with headlines like
Experiments Show Gravity Is Not an Emergent Phenomenon screaming for attention.
Sounds like a death stab to Erik Verlinde's brainchild, right?
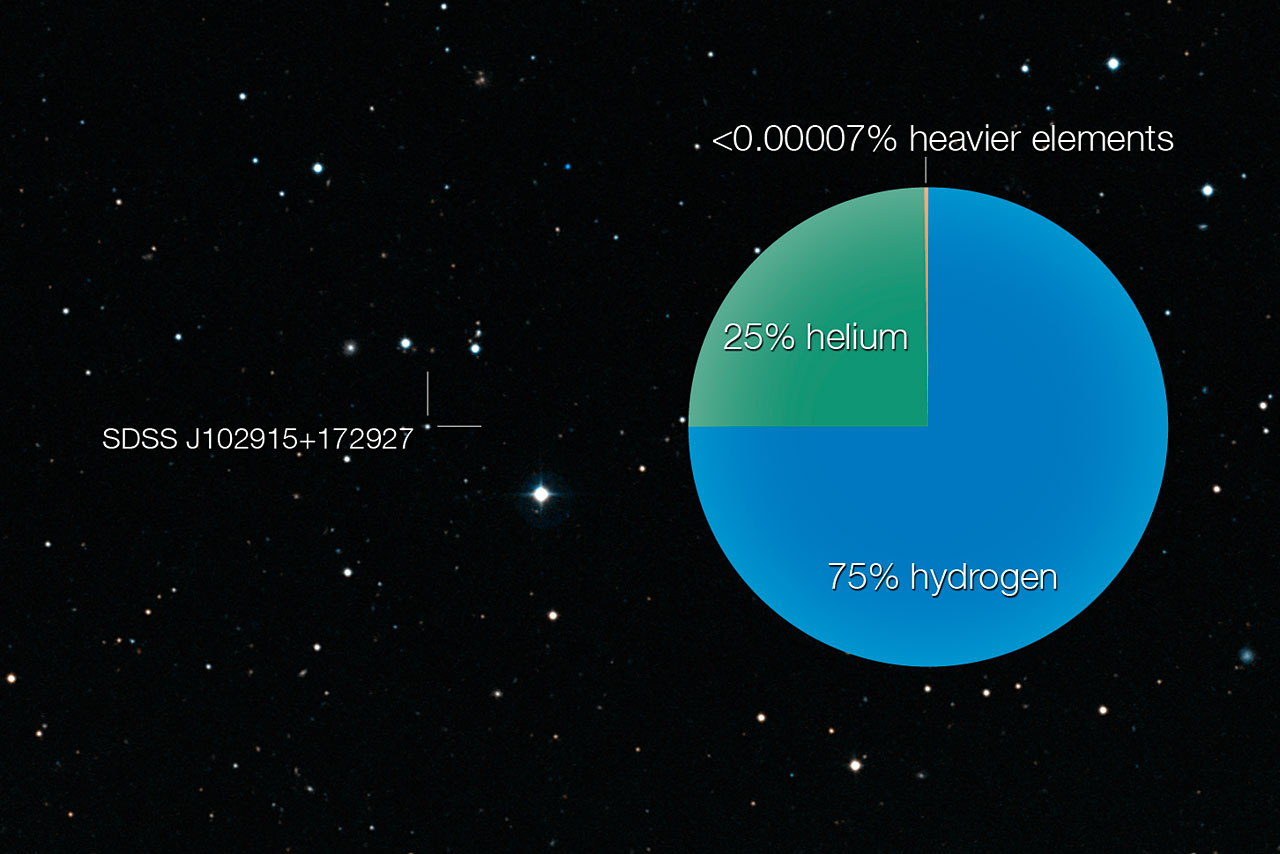
SDSS J102915+172927 is in the constellation of Leo. It has a mass smaller than that of the Sun and is probably more than 13 billion years old and has been found to have the lowest amount of elements heavier than helium (what astronomers call "metals") of all stars yet studied.
The mystery? It shouldn't exist.
The Moon And The Telephone
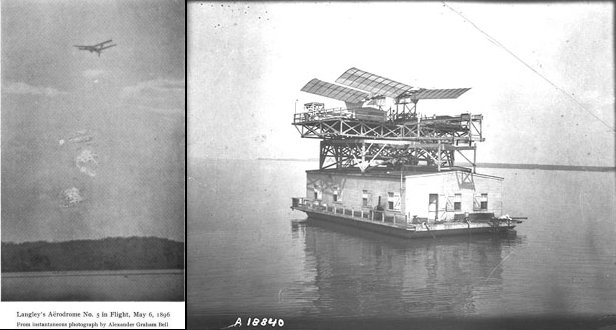
In the history of the discovery of climate change and its causes, there are many pioneers whose work in relevant areas is all but forgotten. Some of these people are not widely known. Others are widely known, but their climate-related work tends to lie forgotten in the archives. For example: Edison is famous as an inventor and Langley is famous as an aviation pioneer, but both men made little-known contributions to our knowledge of heat.
Picture the scene: you are about to start in a new school as a science teacher.
The pupils are due back in one week.
You have lessons to plan and resources to prepare.
You walk into your lab for the first time and see, with a sinking feeling, that the display boards are bare.
What on earth do you fill them with?
Planetary waves, named Rossby waves because they were discovered by
Carl-Gustav Rossby in the 1930s,
are intriguing natural phenomena that travel from East to West.
A new NASA study suggests two of the most destructive natural disasters of 2010 were completely natural and closely linked even though they occurred 1,500 miles apart.
As solar power continues to grow in popularity, science issues like pollution are being swept under the rug in hopes future technology will solve it before it becomes a crisis, much like with ethanol, MTBE, PBDEs and other once-popular efforts environmental lobbyists spent millions promoting.
Chris Cherry, assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering at University of Tennessee-Knoxville, says solar power's reliance s on lead batteries has the potential to release more than 2.4 million tons of lead pollution in China and India, a pattern likely to be repeated throughout much of the developing world, such as in Africa.
It seems trees have the ability to tap into nitrogen found in rocks, boosting the trees’
growth and their ability to pull more carbon dioxide from the
atmosphere.
That's good news in the short term. Carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas most are worried about so that means nitrogen in rocks can significantly affect how rapidly the earth will warm in
the future, the U.C. Davis researchers say.
Nitrogen, found in such vital molecules as DNA and protein, is necessary for all life and is used worldwide as a fertilizer for food crops. It is the nutrient that most often limits plant growth in natural ecosystems.
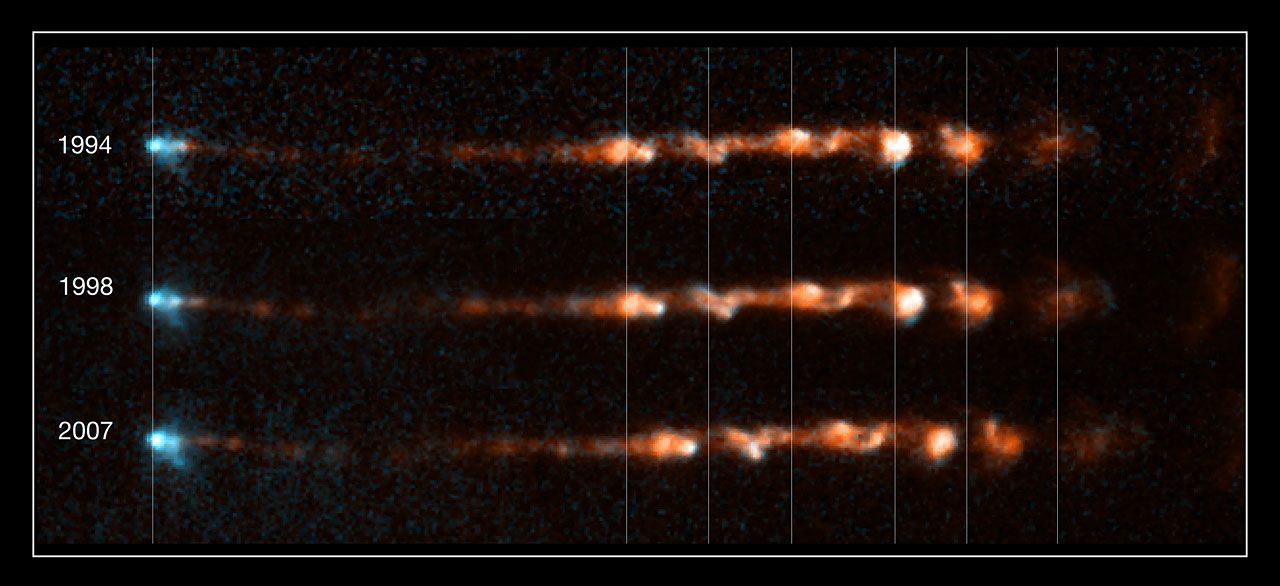
1350 light-years from Earth, near the Orion Nebula, a bright, clumpy jet called called Herbig-Haro 34 (HH 34) ejected from a young star has changed over time - a signpost of star birth.
Stars aren't shy about sending out birth announcements. They fire off energetic jets of glowing gas travellng at supersonic speeds in opposite directions through space. Although astronomers have looked at still pictures of stellar jets for decades, now they can watch movies, thanks to the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
Increasing resistance of pathogens to antibiotics is an important issue. The hunt for new antibiotics/antimicrobials is on. For example, the 10X’20 Initiative aims to develop 10 new antimicrobial drugs by 2020. But where will these new drugs come from?
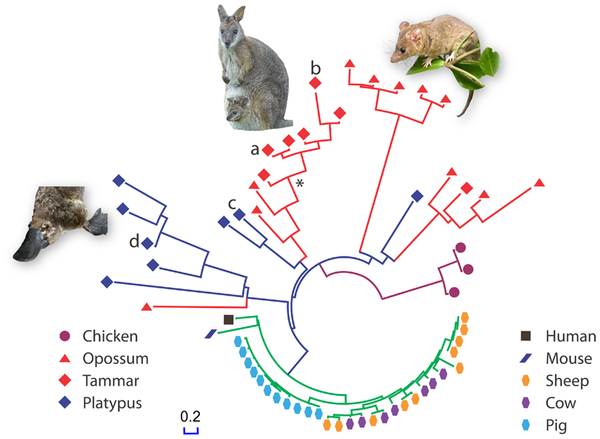
The recent efforts in sequencing marsupial genomes might prove helpful. Since the young of marsupials and monotremes are relatively little developed at birth, and have to survive outside of the sterile environment of the uterus, their immune system has to be capable of dealing with potential pathogens in their environment.
When I saw some preliminary results in Nature about CERN's CLOUD experiment a while ago, I didn't regard it as interesting enough to write about.
Seriously, does anyone not think the Sun impacts the climate by now?
I know, I know, in the 1990s it was all carbon dioxide, but it's no longer 2006 - anyone gullible enough to believe the French and the Germans insisted on a 1990 date in the Kyoto protocol based on science, rather than the fact that Germany simply had to close a few post-unification Soviet-era factories from World War II and France had already brought more nuclear plants online to more easily meet their goals, well, they were too stupid to keep their money anyway.