Scientists at the University of California San Francisco say a majority of published studies analyzing the relationship between Alzheimer's disease and smoking indicates that the habit is a significant risk factor for the disease. Researchers also found that studies funded by the tobacco industry tended to conclude that smoking protects against the development of AD, while independent studies showed that smoking increased the risk of developing the disease. The findings were published online today in the January issue of the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
Assuming good health, older adults can expect to have a reduced "sleep need" and to be less tired during the day compared to healthy young adults, according to a new study published in Sleep.
Proapoptotic Peptides that target blood vessels in White adipose (fat) tissue and cause them to go undergo programmed cell death could become a model for future weight-loss therapies, says a study published online in Diabetes. The study found that obese animal models treated with proapoptotic peptides experienced decreased food intake and significant fat loss.
Fat tissue is vascularized, much like a tumor, and growth of fat tissue is highly dependent on the tissue's ability to build new blood vessels—a phenomenon called angiogenesis. Inhibiting adipose angiogenesis—essentially "starving" fat tissue—can reverse the effects of a high-fat diet in mice and rats.
Scientists from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden say they have discovered how aged yeast cells manage to form new and undamaged daughter cells. In a study published in Cell, two collaborating research groups at the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology have been able to show how newly formed yeast cells transport damaged and aged proteins back to the mother cell, guaranteeing that the new cell is born young and healthy.
The authors of a new study reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology say they know how much smoking affects cardiac health before and after a heart attack and have determined whether cutting back instead of completely kicking the habit will have a positive effect as well.
A new study analyzing mixed hardwood forest plots in Maryland indicates that forests in the Eastern United States may be growing faster than they have in the past 225 years. On average, the forest is growing an additional 2 tons per acre annually--the equivalent of a tree with a diameter of 2 feet sprouting up over a year.
Forests and their soils store the majority of the Earth's terrestrial carbon stock. Small changes in their growth rate can have significant ramifications in weather patterns, nutrient cycles, climate change and biodiversity. Exactly how these systems will be affected remains to be studied.
Individuals who suffer memory loss may face a higher risk of stroke, regardless of whether they have been diagnosed with dementia, according to a new study published in Neurology.
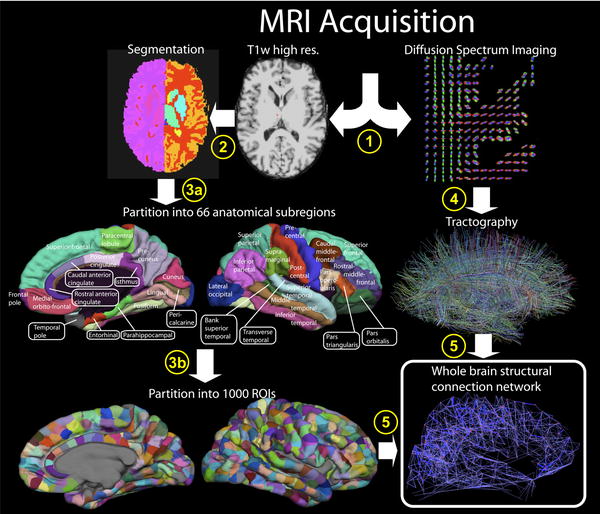
For the study, 930 men in Sweden around the age of 70 without a history of stroke participated in three mental tests. The first test, called the Trail Making Test A, measures attention and visual-motor abilities. The second, the Trail Making Test B, measures the ability to execute and modify a plan. The third, the Mini Mental State Examination, is commonly used by doctors to measure cognitive decline.