From 2000-2013 the global ocean surface temperature did not rise in spite of increasing greenhouse gas concentrations. This Global Warming Hiatus generated a lot of public and scientific interest and no small amount of skepticism about the accuracy of the numerical models created by climate scientists. But data is another matter entirely and as of April 2014 ocean warming has picked up speed again, according to a new analysis of ocean temperature datasets.
"This summer has seen the highest global mean sea surface temperatures ever recorded since their systematic measuring started. Temperatures even exceed those of the record-breaking 1998 El Niño year," says Axel Timmermann, climate scientist and professor, studying variability of the global climate system at the International Pacific Research Center, University of Hawaii at Manoa. "The 2014 global ocean warming is mostly due to the North Pacific, which has warmed far beyond any recorded value (Figure 1a) and has shifted hurricane tracks, weakened trade winds, and produced coral bleaching in the Hawaiian Islands," explains Timmermann.
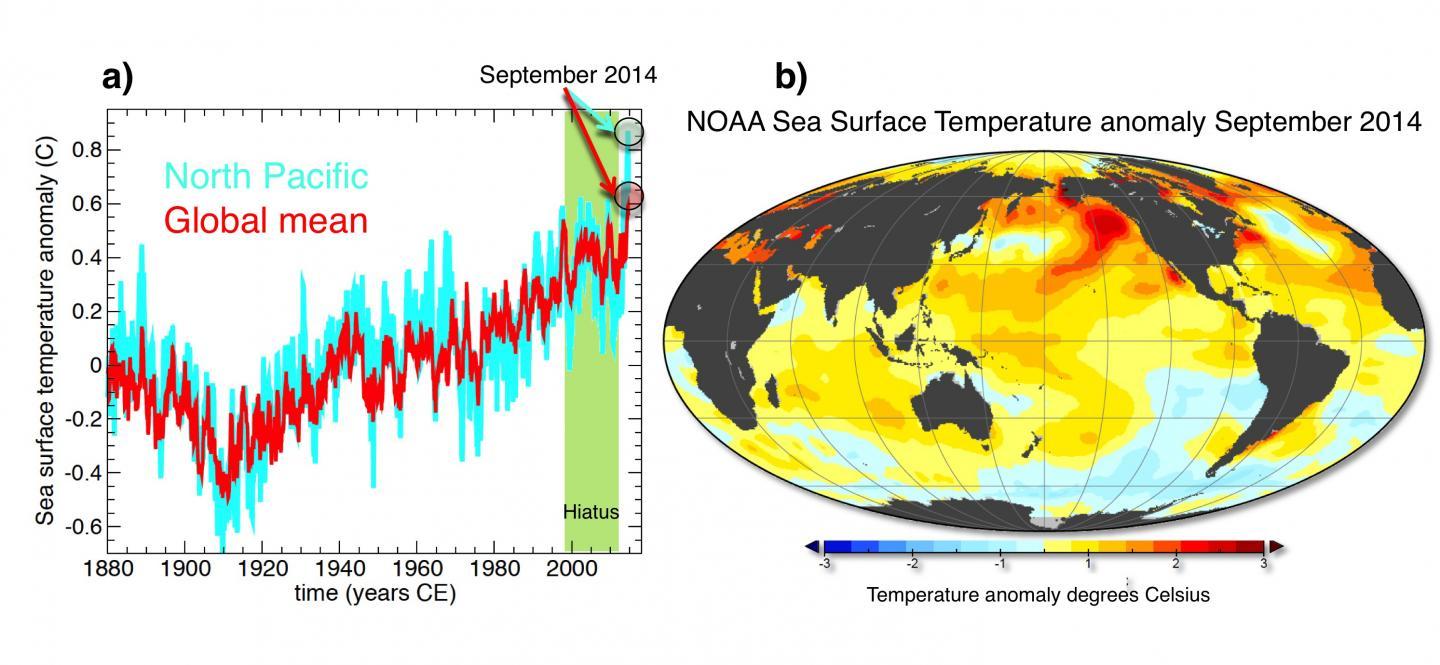
Figure 1: a) NOAA Sea Surface Temperature anomaly (with respect to period 1854-2013) averaged over global oceans (red) and over North Pacific (0-60oN, 110oE-100oW) (cyan). September 2014 temperatures broke the record for both global and North Pacific Sea Surface Temperatures. b) Sea Surface Temperature anomaly of September 2014 from NOAA's ERSST dataset. Credit: Axel Timmermann
He describes the events leading up to this upswing as follows: Sea-surface temperatures started to rise unusually quickly in the extratropical North Pacific already in January 2014. A few months later, in April and May, westerly winds pushed a huge amount of very warm water usually stored in the western Pacific along the equator to the eastern Pacific.
This warm water has spread along the North American Pacific coast, releasing into the atmosphere enormous amounts of heat--heat that had been locked up in the Western tropical Pacific for nearly a decade.
"Record-breaking greenhouse gas concentrations and anomalously weak North Pacific summer trade winds, which usually cool the ocean surface, have contributed further to the rise in sea surface temperatures. The warm temperatures now extend in a wide swath from just north of Papua New Guinea to the Gulf of Alaska (Figure 1b)," says Timmermann.
The current record-breaking temperatures indicate that the 14-year-long pause in ocean warming has come to an end.




Comments