America never migrated to nuclear energy the way the French did so today up to 75 percent of electricity used in the United States is instead produced by coal-burning power plants and that means carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere and increased risk of global warming. To reduce the impact of current power generation, researchers are searching for porous materials to filter out the CO2 generated by those plants before it reaches the atmosphere, a process commonly known as carbon capture.
Identifying realistic materials is easier said than done. In just the category of zeolites, which are crystalline porous materials, there are around 200 known materials and 2.5 million structures predicted by computational methods. That's why Maciej Haranczyk, a scientist in the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's Computational Research Division, and colleagues have developed a computational tool that can help researchers sort through vast databases of porous materials to identify promising carbon capture candidates—and at record speeds. They call it Zeo++.
By using Zeo++ researchers have already sifted through one such database of millions of materials and have identified a few that could outperform current technologies. The tool works not by simulating each atom of a material, but by mapping what isn't there: The voids in the materials.
Porous materials like zeolites or metal organic frameworks come in a variety of shapes and have a range of pore sizes. It is actually the shape and pore sizes that determine which molecules get absorbed into the material and which ones pass through.
Like molecular sponges, porous materials can also be reused in a cycle of capture and release. For instance, in the case of carbon capture, once the material is saturated and cannot absorb any more CO2, the gas can be extracted, and the cycle repeated.
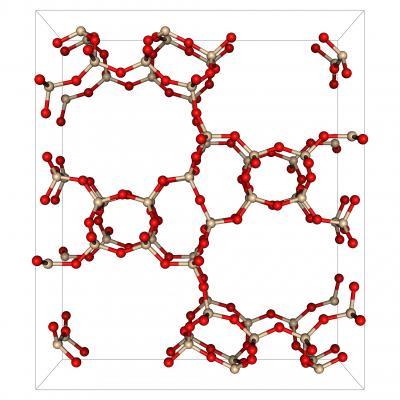
Porous structure from Michael Deem's database of predicted zeolites, which consist of silicon (tan) and oxygen (red) atoms. Credit: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
"Understanding how all of these factors combine to effectively capture carbon is a challenge," says Richard Luis Martin, a member of the Zeo++ development team and a postdoctoral researcher in Berkeley Lab's Computational Research Division. "Until Zeo++, there were no easy methods for analyzing such large numbers of material structures and identifying what makes a material an outstanding carbon catcher."
He notes that silicious zeolites, to take one example, are composed of the same tetrahedral blocks of silicon and oxygen atoms, but the geometric arrangement of these blocks differs from one zeolite to the next, and this configuration is what determines how CO2 or any other molecule will interact with the porous material.
Before Zeo++, scientists would typically characterize a porous structure based on a single feature, like the size of its largest pore or its total volume of empty space, then compare and categorize it based on this single observation.
"The problem with this one-dimensional description is that it does not tell you anything about how a molecule like CO2 will move through the material," says Martin. "To identify the most effective materials for absorbing CO2, we need to understand the porous structure from the perspective of the penetrating molecule."
This is precisely why Zeo++ characterizes these structures by mapping the empty spaces between their atoms. Drawing from a database of the coordinates of all the atoms in each porous structure, Zeo++ generates a 3D map of the voids in each material. This 3D network allows researchers to see where the channels between atoms intersect to create cavities. The size and shape of these cavities determine whether a molecule will pass through the system or be absorbed.
Using a tool called Voronoi Holograms, also developed by the Berkeley Lab team, researchers can automatically compare these 3D maps to identify materials with similar pore sizes and structures.
"Using this technique we can examine the pathways between atoms and see how these paths connect to create a larger network," Martin says.
Since researchers already know the positions of atoms in materials being considered, the tool can chart these empty channels relatively quickly. And because researchers are not dealing with all of the atoms in a structure, but a more simple representation of the material's empty space, Zeo++ can run its analysis much faster and with a lot less computing power than a typical simulation based on physical models.
For their first project, the team analyzed a database of millions of predicted porous material structures compiled by Rice University Professor Michael Deem and his research group to identify which would be most effective for trapping molecules like CO2.
Narrowing the Field Faster
Searching vast sets of materials for desired characteristics is a problem that is not unique to the quest for carbon capture. In fact, the pharmaceutical industry faces similar challenges in the search for new drugs, and uses informatics approaches to explore large databases of drug candidates. Haranczyk and his Berkeley Lab colleagues applied some of these industry concepts combined with state-of-the-art advances in mathematics and computational algorithms to create Zeo++.
According to Berend Smit, who leads the Energy Frontier Research Center for Gas Separations Relevant to Clean Energy Technologies at the University of California at Berkeley, it used to take weeks to manually characterize and compare the porous structures of a mere 20 materials. With Zeo++, researchers can analyze an entire database, containing information on hundreds-of-thousands to millions of porous structures, in a few days.
"Zeo++ allows us to do things that would otherwise be physically impossible," says Smit, whose group is developing laboratory and computational methods for identifying carbon dioxide-absorbing nanomaterials.






Comments