Sinkholes are depressions that occur when soil or bedrock has been removed and only air remains - commonly when the rock below the land surface is limestone, carbonate rock or salt beds that have been naturally dissolved by ground water circulating through them and then the water dries up.
As the rock is dissolved by water(dissolution), spaces are created (suffosion) and typically sinkholes happen suddenly because the surface stays intact until the weight becomes too much.
Sinkholes occur more often in places like Florida and Alabama because they have more underground rivers than most other states. When sinkholes form it is commonly because the ground has simply collapsed over underground rivers that were once filled with water.
So if you want to look for signs of a major drought in the making, disgruntled skiers at Lake Tahoe are not going to be as accurate as sinkholes.
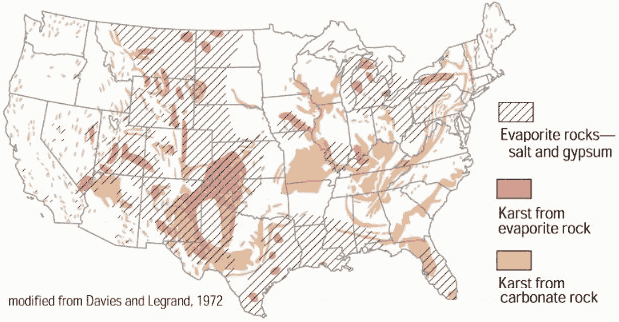
This map from the USGS shows where underground cavities have more frequently occurred and resulted in sinkholes. As they note, these susceptible types of rock are called evaporites, such as salt, gypsum, and anhydrite, and carbonates, such as limestone and dolomite. Evaporite rocks are in 35-40% of the US, but at various depths, which is why not all areas are equally affected.
Can sinkholes be caused by man?
Land-use practices have also been implicated in sinkholes. When natural water drainage patterns are changed or water is otherwise diverted, the upward pressure of water is no longer keeping the surface stable. Likewise, heavy industrial building or artificial lakes can cause weight issues that result in sinkholes.
Obviously if underground mining has occurred plain ol' gravity can cause sinkholes.
3 types of sinkholes
Dissolution sinkholes - where water first contacts the rock surface and also in joints and fractures.
Cover-subsidence sinkholes - usually when the covering is permeable and contain sand.
Cover-collapse sinkholes - usually when the covering contains a large amount of clay and surface erosion and drainage cause the 'bowl' people commonly see.





Comments