Writing in the latest issue of JAMA, Alec B. O'Connor, associate professor at the University of Rochester Medical Center, says the federal guidelines governing the approval of potential new drugs should be much more stringent. The FDA, according to the commentary, should require studies comparing the effectiveness and safety of a new drug to an established first-line drug when considering a drug for approval.
Currently the agency does not require such studies, known as "active comparator trials," though some large studies of new drugs do include them. In many cases, to gain approval, the main criterion besides safety is that a new drug must be shown to be more effective than placebo.
A team of astronomers writing in Astrophysical Journal Letters has shown that the two stars in the binary HM Cancri revolve around each other in a mere 5.4 minutes, making HM Cancri the binary star with by far the shortest known orbital period. It is also the smallest known binary; The system is no larger than 8 times the diameter of the Earth.
The team was able to prove the short binary period of the system by detecting the velocity variations in the spectral lines in the light of HM Cancri. These velocity variations are induced by the Doppler effect, caused by the orbital motion of the two stars revolving around each other. The Doppler effect causes the lines to periodically shift from blue to red and back.
Researchers at Yale School of Medicine have discovered that exposure during pregnancy to Bisphenol A (BPA), a common component of plastics, causes permanent abnormalities in the uterus of offspring, including alteration in their DNA. The findings were reported the Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB J.).
The authors say the study is the first to show that BPA exposure permanently affects sensitivity to estrogen.
Scientists from the U.S. department of Agriculture have discovered how The Aedes aegypti mosquito detects the chemical structure of a compound called octenol as one way to find a mammalian host for a blood meal.
Scientists have long known that mosquitoes can detect octenol, but this most recent finding, published in PLoS One, explains in greater detail how Ae. aegypti--and possibly other mosquito species--detect the compound.
Using data from two recent national surveys, University of Toronto sociologist Scott Schieman has found that most Americans believe God is concerned with their well-being and is directly involved in their personal affairs.
The research, he says, uncovered the ways these beliefs about divine intervention differ across education and income levels. The results are published in Sociology of Religion.
Traditionally, scientists believed that nicotine inhaled in a puff of cigarette smoke took a mere seven seconds to be taken up by the brain, but new evidence indicates that nicotine takes much longer to reach peak levels in the brains of cigarette smokers, according to a new study in PNAS.
Using PET imaging, Duke investigators found for the first time that cigarette smokers actually experience a steady rise of brain nicotine levels during the course of smoking a whole cigarette.
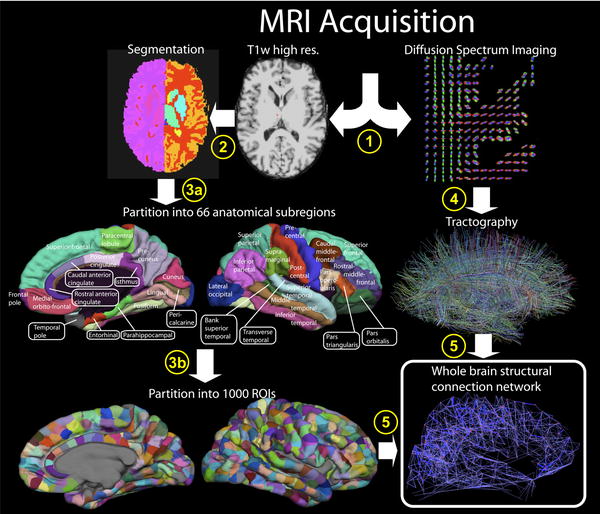
 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
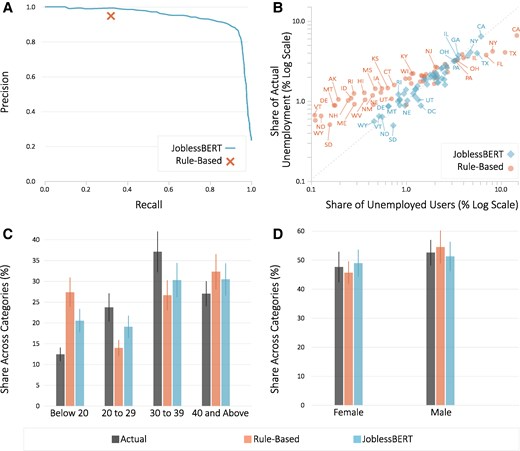
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government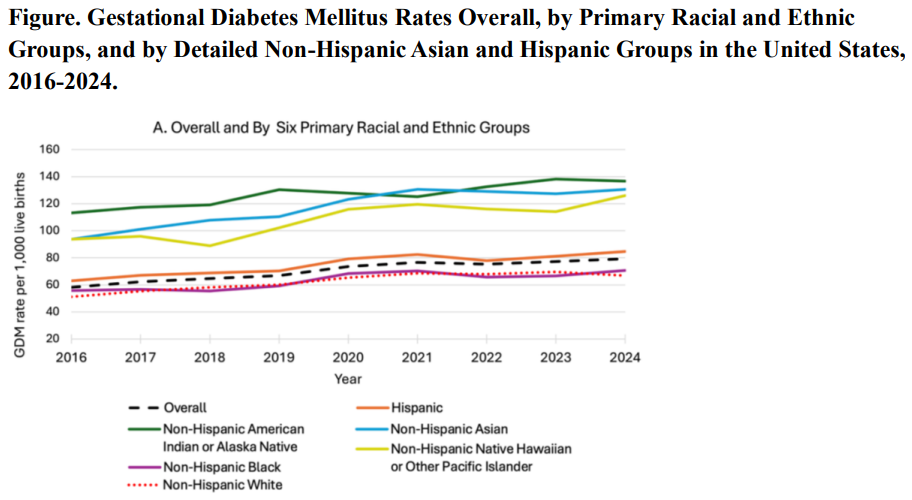 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest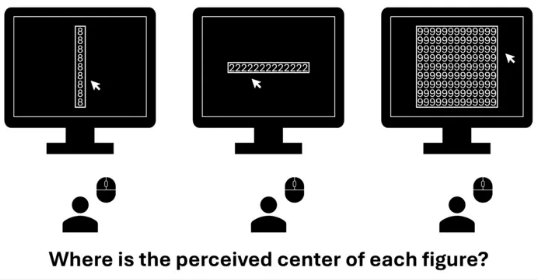 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food