The more heterogeneous the community of an online chat channel, the more chances the channel has to survive over time, according to a study conducted by researchers at the University of Haifa and the New Jersey Institute of Technology.
Previous research focused on group size and activity suggested that there are too many variables influencing the lifespan of such channels and there is, therefore no way of testing how long they will survive.
Insulin resistance, high cholesterol, fatty liver, greater risk for diabetes, heart disease, and stroke are all related to obesity, but are likely not caused by it, according to a review in Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism.
In fact, obesity is the body's way of storing lipids where they belong, in fat tissue, in an effort to protect our other organs from lipids' toxic effects. It's when the surplus of calories coming in gets to be too much for our fat tissue to handle that those lipids wind up in other places they shouldn't be, and the cascade of symptoms known as metabolic syndrome sets in.
A team of researchers has discovered how to efficiently turn carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide using visible light. The discovery opens the doors for scientists to explore what organism is out there – or could be created – to chemically break down the greenhouse gas into a useful form. The results are reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Alcohol consumption has been suspected of contributing to weight gain in the United States, but among normal-weight women moderate alcohol consumption is associated with a reduced risk for obesity, according a new study by researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Harvard School of Public Health.
When it comes to wine, 'green' labels just don't pack the same financial wallop that they do for low-energy appliances and organically grown produce. A new study has found that organic labels actually decrease the price consumers are willing to pay for their wine.
Wines made with 'organically' grown grapes rate higher on a widely accepted ranking, said Magali Delmas, a UCLA environmental economist and the study's lead author, and these wines can even command a higher price than their conventionally produced counterparts - as long as wineries don't use the word "organic" on their labels.
When wineries do use eco-labels, prices plummet.
According to a new study of 504 death penalty cases in Harris County, Texas between 1992 and 1999, a defendant is much more likely to be sentenced to death if he or she kills a "high-status" victim - a white or Hispanic victim who is married with a clean criminal record and a college degree. The study appears in a recent issue of Law and Society Review
"The concept of arbitrariness suggests that the relevant legal facts of a capital case cannot fully explain the outcome: irrelevant social facts also shape the ultimate state sanction" says Scott Phillips, associate professor of sociology and criminology at the University of Denver (DU). "In the capital of capital punishment, death is more apt to be sought and imposed on behalf of high status victims."
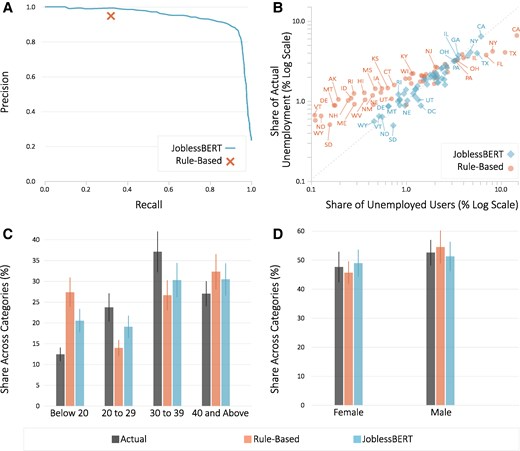 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government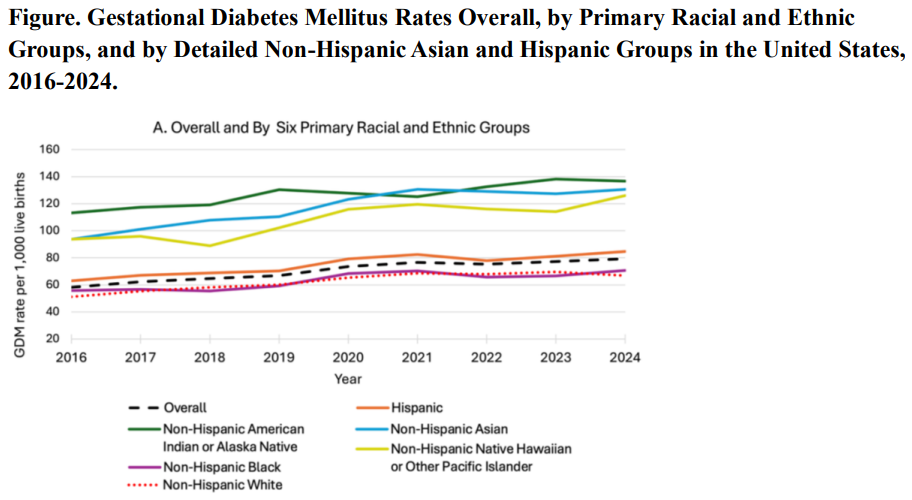 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest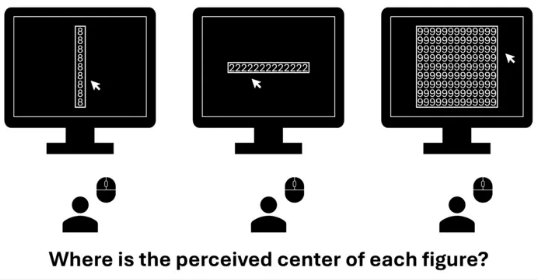 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food