Scientists have known for more than a decade that galaxies in the early universe produced many more stars than galaxies today. But what has remained unknown is why. Now, researchers writing in a recent issue of Nature say they may have an explanation for this astronomical mystery.
"[T]hree to five billion years after the Big Bang...galaxies churned out new stars at a much faster rate than they do now," said Michael Cooper, a postdoctoral Spitzer fellow at the University of Arizona's Steward Observatory.
Badly fitting condoms reduce sexual pleasure for both partners and may discourage men from using protection altogether, suggests a study published in Sexually Transmitted Infections.
The findings are based on a survey of 436 men between the ages of 18 and 67, all of whom were recruited via newspaper ads and a blog on the website of a condom sales company. Participants completed a questionnaire on the Kinsey Institute for Research in Sex, Gender, and Reproduction website about the fit of condom they had most recently used for penetrative sex with a female partner.
A new study by the Oklahoma Tobacco Research Center (OTRC) shows that concentrations of secondhand tobacco smoke inhaled in smoking rooms of restaurants and bars are exceptionally high and hazardous to health. The authors of the report say the findings justify making all public places smoke free - or ignoring private property rights and treating adults like helpless children.
According to the study, the average particulate level measured in restaurant smoking rooms was beyond the hazardous extreme based on levels established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The level found in bars was even worse.
DNA analysis of royal mummies suggest that malaria and bone abnormalities may have contributed to the death of Egyptian pharaoh King Tutankhamun, with other results appearing to identify members of the royal family, including King Tut’s father and mother, according to a new study published in the Journal of The American Medical Association. The findings may lead to a new way of researching the molecular genealogy and pathogen paleogenomics of the Pharaonic era, perhaps even a new field called 'molecular Egyptology.'
The diversity of corals harboring unusual species of symbiotic algae in the warm waters of the Andaman Sea indicates that coral reefs and the ecosystems dependent on them may persist despite climate change, according to a new study in the Journal of Biogeography.
The researchers say the comprehensive survey, which included analysis of the corals and symbiotic algae living in the cooler western Indian Ocean and Great Barrier Reef area of Australia, is unparalleled by any other study.
Human cells contain 46 strands of DNA that code for all our genes. Certain chemicals and UV light can break these strands into pieces, a process that typically leads to cell death or diseases such as cancer if the damage is not repaired quickly. But new research, published in PNAS, shows for the first time that stem cells will intentionally cut and then repair their own DNA as a mechanism of activating genes that promote the development of new tissues.
The discovery could help researchers develop better ways to activate stem cells, so that they can produce new tissues for therapeutic purposes. It also suggests that DNA mutations, which can contribute to a variety of diseases, may initially occur as a result of a normal cellular process.
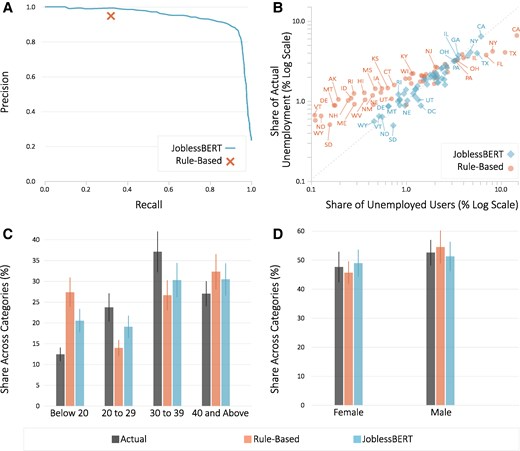 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government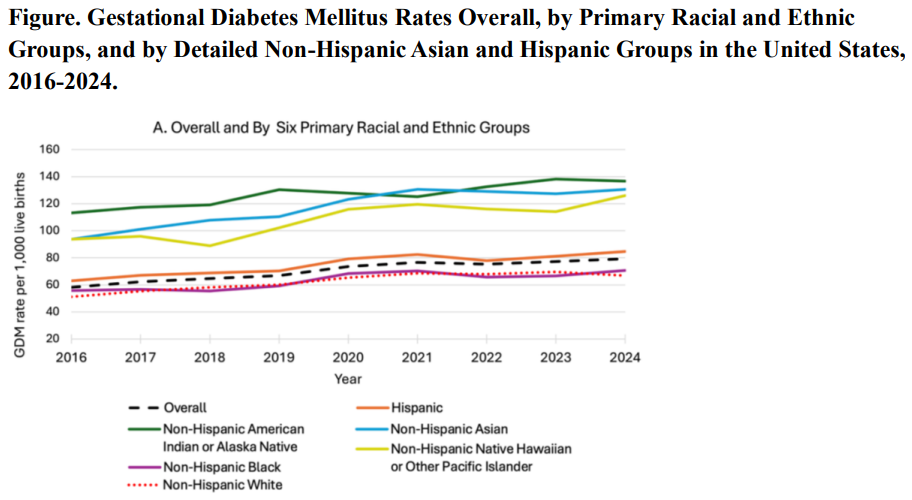 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest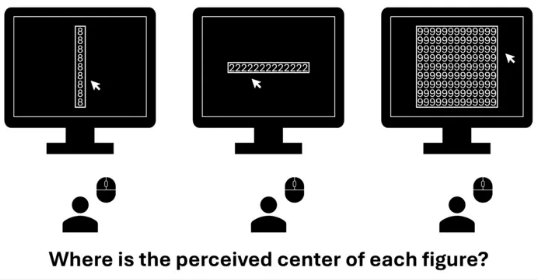 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food







