Research conducted by scientists at the Weizmann Institute and the University of Maryland reveals that bats, which 'see' with beams of sound waves, skew their beams off-center when they want to locate an object. The research, which recently appeared in Science, shows that this strategy is the most efficient for locating objects.
"We think that this tradeoff between detecting a object and determining its location is fundamental to any process that involves tracking an object whether done by a bat, a dog or a human, and whether accomplished through hearing, smell or sight," said co-author Cynthia Moss, a University of Maryland professor of psychology, who directs interdisciplinary bat echolocation research in the university's Auditory Neuroethology Lab.
Despite the endless anti-smoking campaigns and serious health risks associated with tobacco use, many smokers don't give up the habit. Currently, the smoking quit rate remains discouragingly low. Smokers try to quit on average 12 to 14 times before they succeed, and every year about 41% of smokers try to quit but only 10% succeed.
So what, then, is the best to way to convince smokers to stop for good? Giving them information about their individual risk of serious illness may be a good place to start, according to a paper published in the current issue of the Postgraduate Medical Journal.
Quantum biology? Sure, it doesn't get as much attention as its physics counterpart but special proteins called light-harvesting complexes are getting some attention for the field and a team of University of Toronto chemists say they have observed quantum mechanics at work in photosynthesis of marine algae.
Psychologists at the University of Leeds say people who spend a lot of time browsing the internet are more likely to show depressive symptoms.
In a study to be published in the journal Psychopathology next week, researchers documented evidence that some users have developed a compulsive internet habit, whereby they replace real-life social interaction with online chat rooms and social networking sites. The results suggest that this type of addictive surfing can have a serious impact on mental health.
The internet use and depression levels of 1,319 people aged 16-51 were evaluated for the study. Of these, 1.2% were classed as being internet addicted. While small, this figure is larger than the incidence of gambling in the UK, which stands at 0.6%.
The uplifting emotion we experience when watching others perform a virtuous deed--known as "elevation"--may be enough to get us to go out and perform good acts ourselves, say new findings reported in Psychological Science.
During the study, volunteers viewed either a neutral TV clip (showing scenes from a nature documentary) or an uplifting TV clip (a segment from "The Oprah Winfrey Show" showing musicians thanking their mentors) that was designed to induce feelings of elevation and then wrote an essay describing what they watched. As they received their payment and a receipt, they were to indicate if they would be willing to participate in an additional study.
The starburst region NGC 3603 is a cosmic factory where stars form frantically from the nebula's extended clouds of gas and dust. Located 22 000 light-years away from the Sun, it is the closest region of this kind known in our galaxy, providing astronomers with a local test bed for studying intense star formation processes, very common in other galaxies, but hard to observe in detail because of their great distance from us.
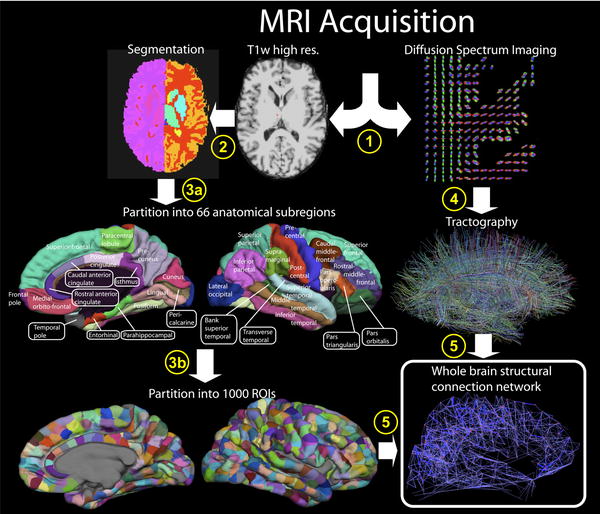
 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
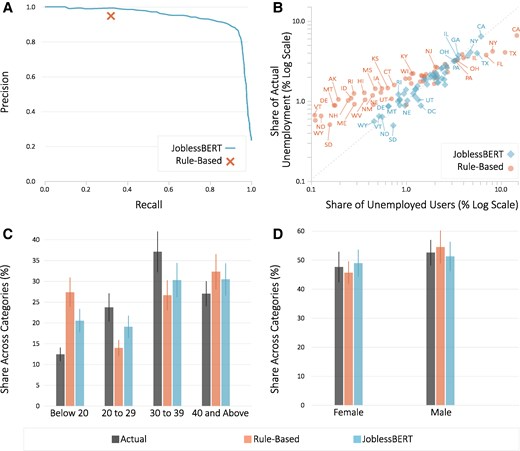
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government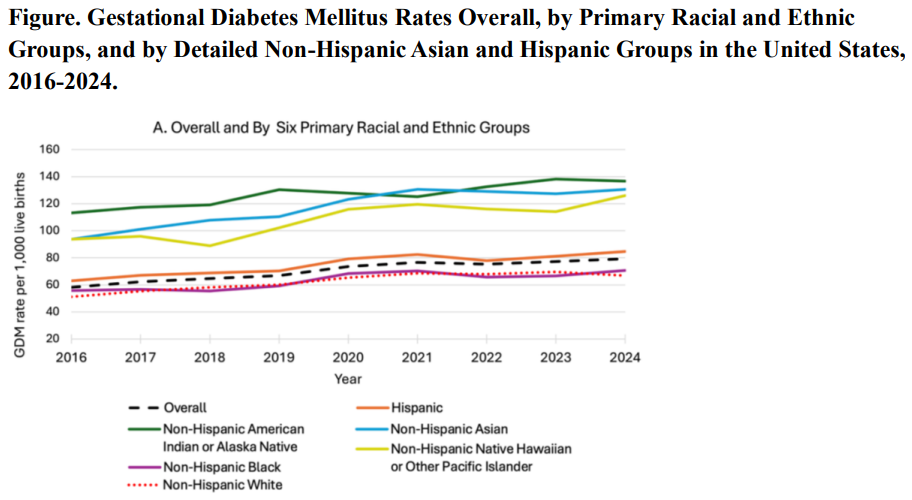 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest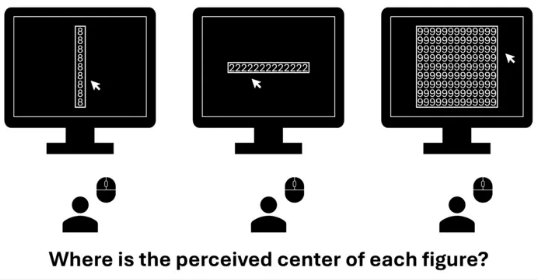 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food