A mummy dating from 3700-3500 B.C. housed in the Egyptian Museum in Turin since 1901 has never undergone any conservation treatments - and that provided a unique opportunity for some science.
And the results were a surprise. It was assumed the Turin mummy had been naturally mummified by the desiccating action of the hot, dry desert sand but
chemical analysis showed that the mummy had undergone an embalming process, with a plant oil, heated conifer resin, an aromatic plant extract and a plant gum/sugar mixed together and used to impregnate the funerary textiles in which the body was wrapped.
Secondhand smoke remains controversial because it takes statistical manipulation to link it to any deaths. Yes, it can be harmful to asthmatics, just like perfume or a wine cellar, but a whole advocacy industry has not been built up talking about how wine cellars must be killing people. And
the most comprehensive study ever done on secondhand smoke and mortality has never been shown to be flawed.
About 1 billion years after the Big Bang, the gas in deep space was highly opaque to ultraviolet light and its transparency varied widely from place to place, obscuring much of the light emitted by distant galaxies. This opaque quality contains tantalizing mysteries about the universe.
That's because now the gas between galaxies is almost totally transparent thanks to being kept ionized-- electrons detached from their atoms--by an energetic bath of ultraviolet radiation.
Young religious Americans are more concerned about the environment than older parishioners, and that may be thanks to religious leaders. They talk about caring for the world given to them and avoid the political activism.
Historically, large atmospheric events like fires and volcanic eruptions have had cooling effects. It is the 200th anniversary of Mary Shelley's "Frankenstein", for example, part of which was inspired by the gloom from a volcanic eruption that
led to 'a year without a summer' in Europe of 1816.
Fires and other events cause the release of soot and other aerosols to be released which can cool the planet by reflecting sunlight back into space and increasing cloud brightness. A new study finda that such a cooling effect on the planet may have been significantly underestimated by previous researchers.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) is part of the World Health Organisation, which is part of the United Nations, but it is really its own agency that shares little in common with WHO. Whereas WHO wants to save lives, IARC has taken to using statistics to scaremonger trace chemicals by conflating hazard and risk. So if high doses, 10,000 exposures of a chemical all at once, might be linked to cancer by looking at statistics, their flawed methodology, where five orders of magnitude are considered equal, will cause them to declare even 1 exposure a hazard.
And though they do not calculate risk, they frequently talk about risk in their media kits for journalists, which leads to confusion in media and therefore the public.
 El Niño Climate Effects Shaped By Ocean Salt
El Niño Climate Effects Shaped By Ocean Salt Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?
Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?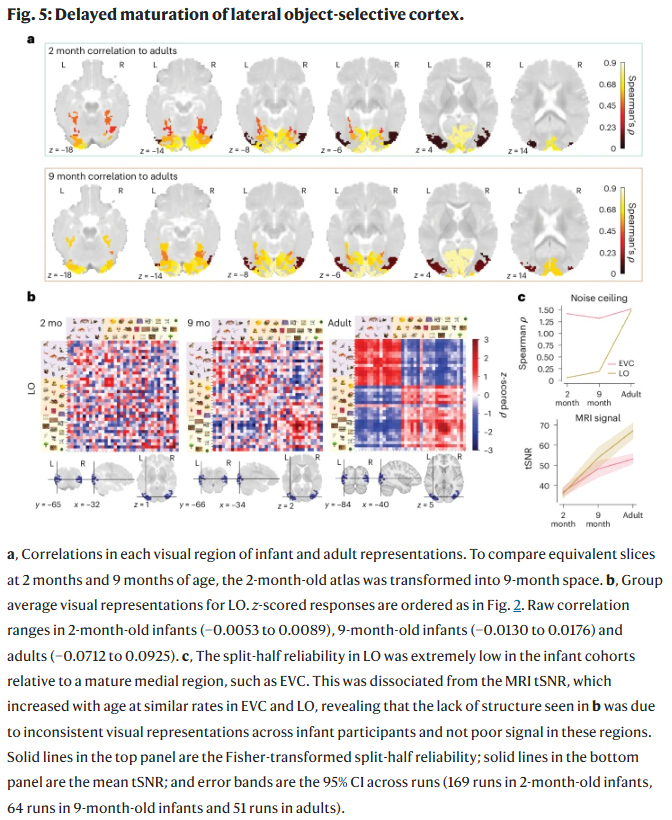 At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize Objects
At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize Objects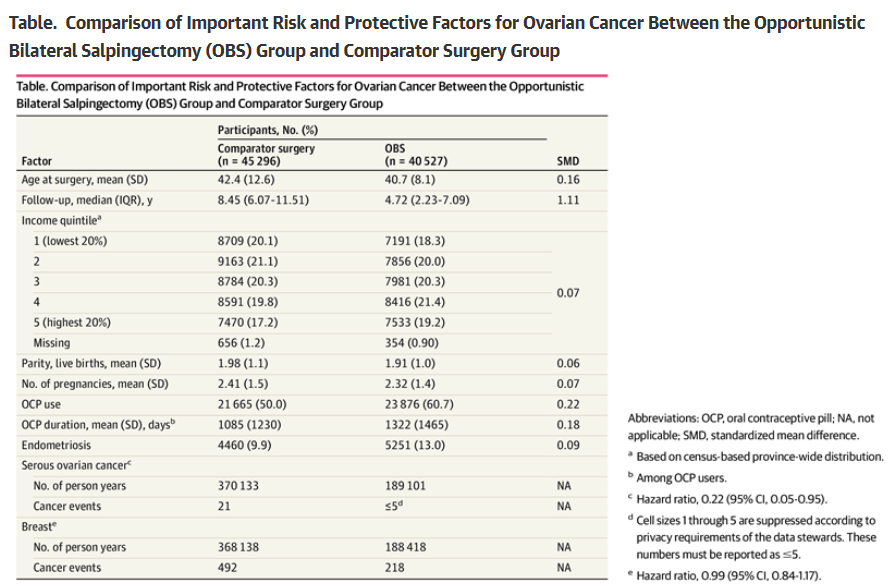 Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%
Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%