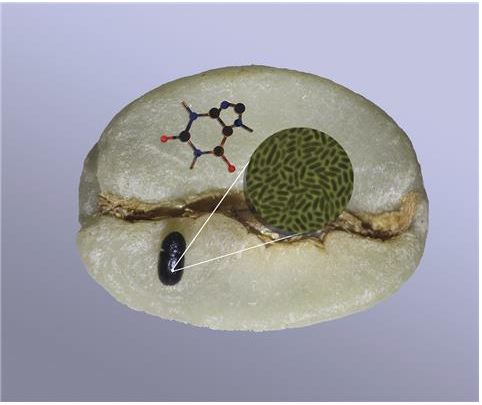
The coffee berry borer (
Hypothenemus hampei) is a plague that affects coffee crops. It has a detoxification system based on microbial communities so it can perform its life cycle in the plant while exposed to high levels of caffeine.
In human terms, the caffeine is equivalent to 500 espressos , which would kill a person.
"The aim was to study which are they and how they are associated with the digestive tract of the insect. For the study we took samples of insects from different locations like Hawaii, Indonesia, Puerto Rico, Mexico, Kenya, India and Guatemala," Javier A. Ceja Navarro of Berkeley National Laboratory told Investigación y Desarrollo.