We usually associate smell with bad things, like body odors or fire or a gas leak, but a keen sense of smell helps us enjoy food and other pleasures in life.
Many things cause loss of smell; aging is number one, but also brain injuries and loss of smell was a common complaint about COVID-19 infections. It's not a life-threatening condition, which may be why there are very few effective treatments.
In all racket sports, a well-executed serve can establish a real advantage. Badminton is played by around 220 million people across the globe and a“spin serve” took badminton by storm when a Danish player at the Polish Open 2023 badminton tournament used it to dominant effect.
Like in table tennis, a spin-serve in badminton adds pre-spin before the racket touches the shuttlecock and the natural spin determined by its feathers’ inclination angles plus the pre-spin makes the flight trajectory even more unpredictable.
Naturally, instead of expecting players to adjust and improve, the community demanded the Badminton World Federation ban it. Coaches and players said extended rallies were more exciting for fans than good serves.
The most common cancer-causing strain of human papillomavirus, HPV16, can reprogram immune cells surrounding the tumor to help cancer grow, and new work in mice blocking this process helped treatments prevent the spread of cancer.
HPV is common in humans and in most cases clears naturally but HPV16 is linked to over half of cervical cancer cases and roughly 90% of HPV throat cancers. The HPV vaccine can prevent those cancers if vaccination occurs prior to HPV exposure but young people are the first generation to have the vaccine readily available.
The El Niño climate phenomenon is consistently inconsistent, which plays havoc with computer models hoping to anticipate the effects of increased emissions from large polluting countries like China.
It may even be causing
periodic booms and busts in spiders and overall insects.
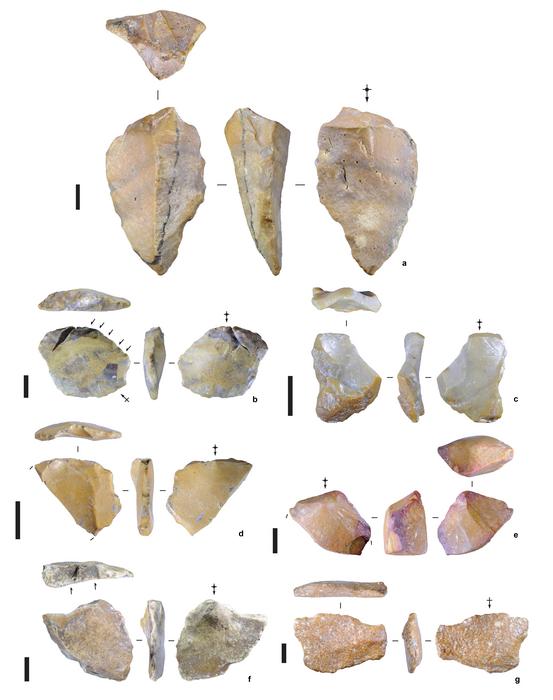
Over 1 million years ago, early hominims made a treacherous deep sea crossing to reach the Indonesian island of Sulawesi and in a modern corn field local people discovered what looked like stone tools in the sedimentary layers and called in archaeologists.
What they found in the Early Pleistocene site of Calio reset the date for colonization of the island; seven stone artifacts. Because this was near a river channel, the researchers believe this would have been the hub for hominin tool-making and other activities such as hunting.
Methanetetrol, the only alcohol which has four hydroxyl groups (OH) at a single carbon atom, is out of this world.
Scientists meant that literally, it had been only theorized because it cannot occur naturally in Earth's everyday conditions but in extreme conditions of space it was assumed to exist. Now after a century of hypothetical existence, ultra-cold temperatures, near-perfect vacuum and high-energy radiation to simulate the environment inside interstellar clouds have combined to make it real.
The scientists from institutions in Russia, communist China, Hawaii, and Mississippi, believe their work could reshape our understanding of chemistry in the universe and shed light on the complex reactions happening in deep space.
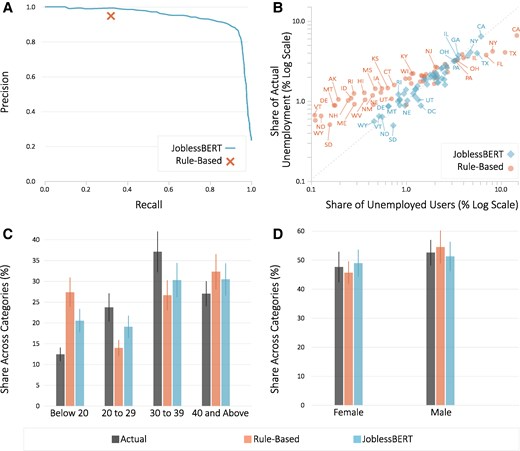 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government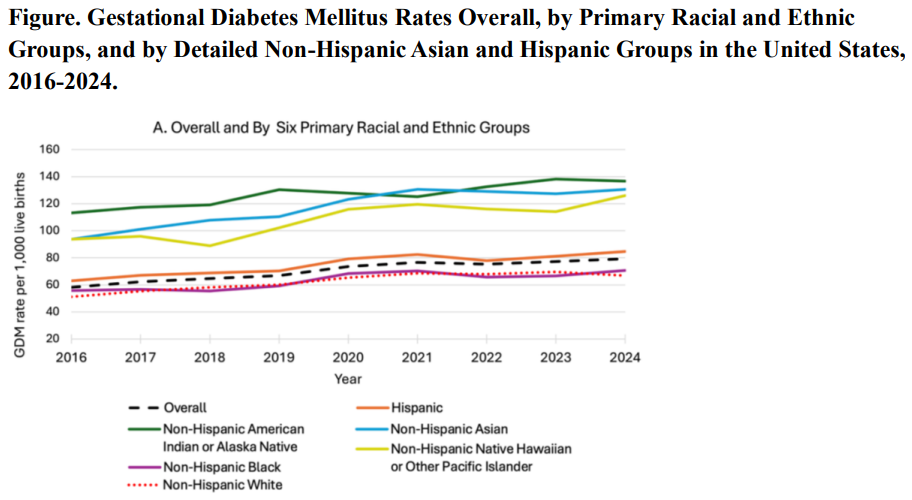 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest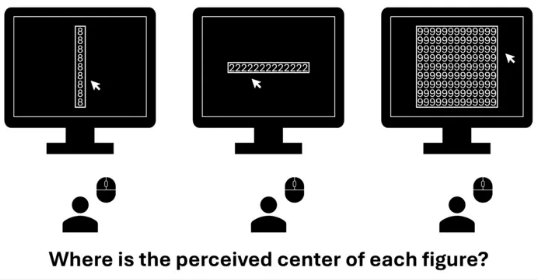 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food









