A study by UC Davis researchers published in Archives of Pediatric&Adolescent Medicine has found that most of the healthy children and teenagers in the United States who are taking daily vitamin and mineral supplements probably don't need them. The study also found that the children who most need to take vitamins aren't getting them.
The idea of ecosystem services is a promising conservation concept but has been rarely put into practice. In Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, researchers have created a tool they say can report some of the first quantifiable results that place values on nature's services to humans.
Some of the best-described ecosystem services include pollination of crops, flood and storm protection, water filtration and recreation. The challenging part is translating these services into something with a measurable value. Economic valuation methods take changes in the supply of ecosystem services and translate these into changes in human welfare.
If you care about the environment, you probably have become familiar with the phrase 'food miles' - along with production methods, it has become a key factor in what environmentally conscious people do to get quality food with less impact on the ecosystem.
But they may be negating it, according to new research by the University of Exeter (UK) p ublished in the journal Food Policy. Shopping locally may not be as good for the environment as having food delivered - on average, lower carbon emissions result even from having food delivered right to your house than driving to a local farm.
Most animals, like humans, have separate sexes. We are born, live out our lives and reproduce as one sex or the other, but some animals live as one sex in part of their lifetime and then switch to the other sex, a phenomenon called sequential hermaphroditism. Yale scientists believe the bigger puzzle is why the phenomenon is so rare, since their analysis shows the biological “costs” of changing sexes rarely outweigh the advantages.
This process is even evolutionarily favored, they say, so its rarity cannot be explained by an analysis of the biological costs vs benefits.
Sliced light is how we communicate now. Millions of phone calls and cable television shows per second are dispatched through fibers in the form of digital zeros and ones formed by chopping laser pulses into bits. This slicing and dicing is generally done with an electro-optic modulator, a device for allowing an electric signal to switch a laser beam on and off at high speeds (the equivalent of putting your hand in front of a flashlight). Reading that fast data stream with a compact and reliable receiver is another matter. A new error-free speed-reading record using a compact ultra-fast component—640 Gbits/second (Gbps, or billion bits per second)—has now been established by a collaboration of scientists from Denmark and Australia.
Whenever humans create a new antibiotic, deadly bacteria can counter it by turning into new, indestructible super-bugs. That's why bacterial infection is the number one killer in hospitals today. But new research from Tel Aviv University may give drug developers the upper hand in outsmarting bacteria once and for all.
The secret weapon against a colony of bacteria may be to stress it with its own protection system, which forces it to reduce its population through ... cannibalism.
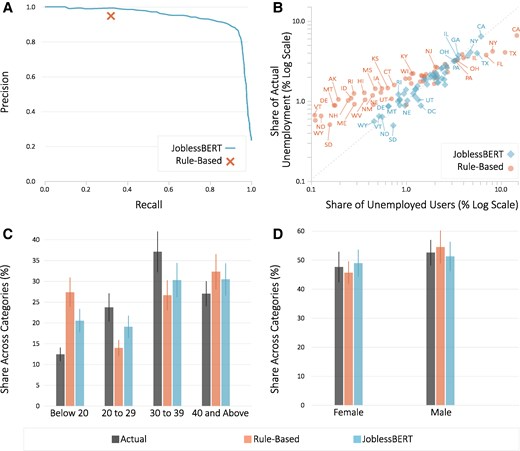 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government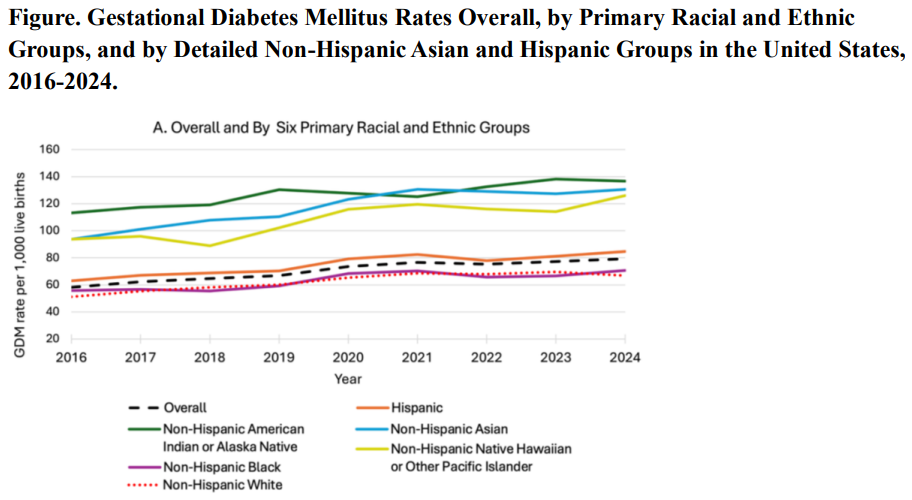 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest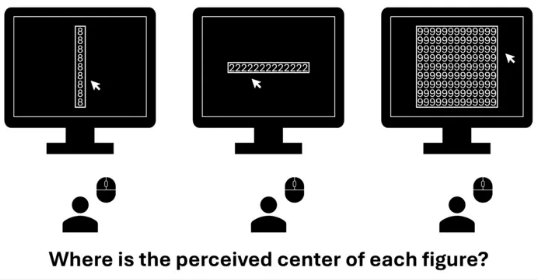 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food