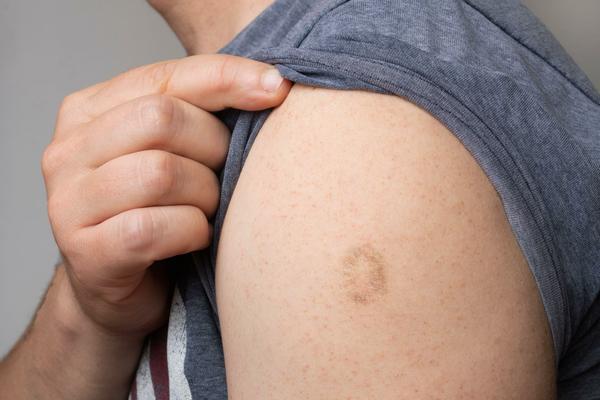
 At 3 Cases In 6 Months, Monkeypox In The US Is Effectively Contained
At 3 Cases In 6 Months, Monkeypox In The US Is Effectively ContainedMonkeypox (Mpox) is an infection transmitted by skin-to-skin contact and causes fever and painful...
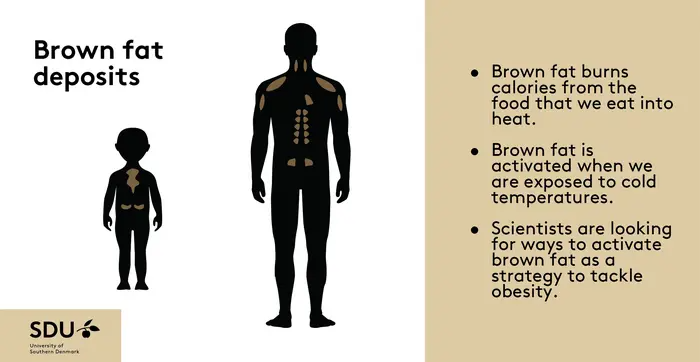 Brown Fat’s “Off-Switch” Isn't A New Ozempic Diet Exploit
Brown Fat’s “Off-Switch” Isn't A New Ozempic Diet ExploitBrown adipose tissue is different from the white fat around human belly and thighs. Brown fat helps...
 Opioid Addicts Are Less Likely To Use Legal Opioids At The End Of Their Lives
Opioid Addicts Are Less Likely To Use Legal Opioids At The End Of Their LivesWith a porous southern border, street fentanyl continues to enter the United States and be purchased...
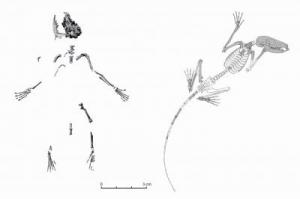
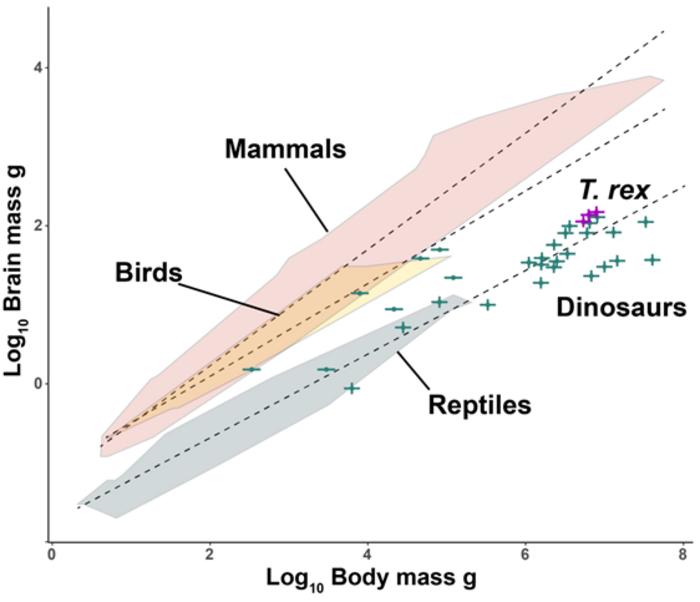 More Like Lizards: Claim That T. Rex Was As Smart As Monkeys Refuted
More Like Lizards: Claim That T. Rex Was As Smart As Monkeys RefutedA year ago, corporate media promoted the provocative claim that dinosaurs like Tyrannorsaurus rex...