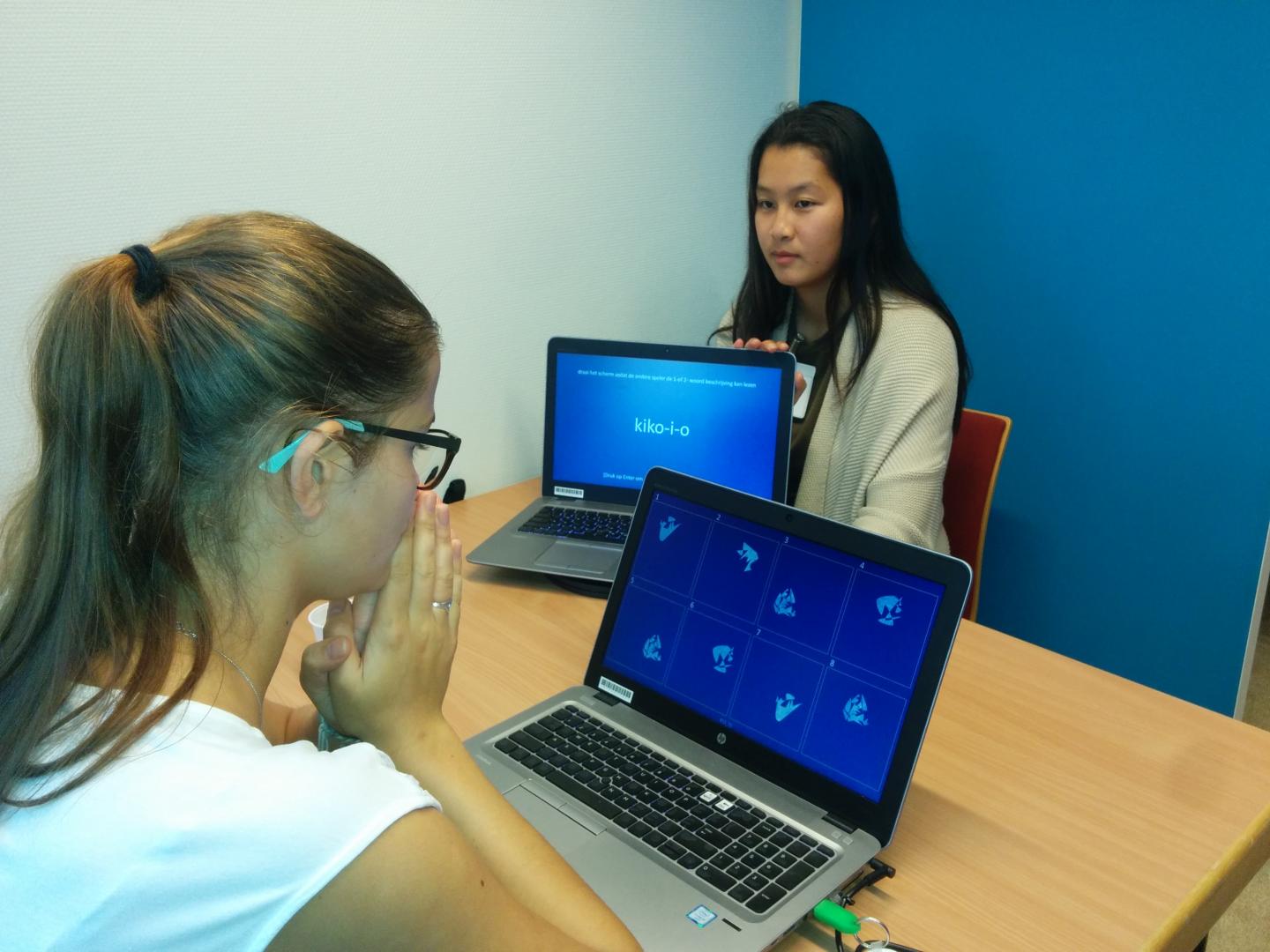
For nearly as long as man has traveled into space, it has been known that it brings a greater risk of fainting upon return; and the longer the time in a gravity-free environment like space, the greater the risk appeared.
Orthostatic hypotension is the technical term for a temporary drop in blood pressure when a person stands up after sitting or lying down because blood rushes to the feet, away from the brain. Dizziness or fainting due to changes in blood flow can occur after lengthy bed rest, among people with certain health disorders or, in the case of astronauts, being in a low-gravity environment.
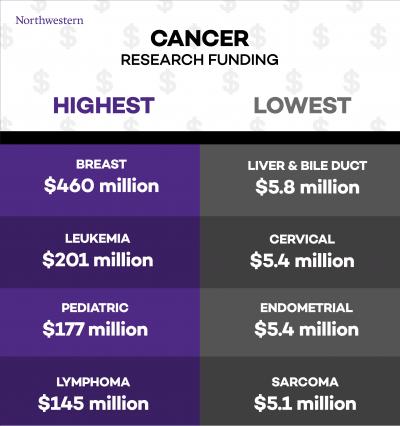
Breast cancer, leukemia, and lymphoma get outsized funding compared to their mortality while pancreatic cancer, colon, liver, and others far deadlier get shorted, at least by government agencies. The private sector obviously wants to make products to save everyone, even if it's only 1,000 people a year.
Why? In the case of lung cancer, it may be because over half of lung cancers are caused by smoking and even more are statistically linked to smokers (second-hand smoke) but it still carries a stigma. Liver cancer may be associated with alcoholics. Both of those are lifestyle diseases and not genetic bad luck.
As government control of science funding increased, and government spent billions convincing young scholars that only government-funded academia was a fulfilling science career, competition grew at a rapid pace. And collaboration declined.
In 1965, 42.4% of U.S. adults admitted to smoking on surveys. By 2017 that has dropped to 14% and that is due in large part to awareness efforts and to modern smoking cessation efforts. In 1965, quitting meant going "cold turkey" and sucking on candy to mimic the behavioral aspects of smoking addiction. Then came gums and patches created by Big Pharma to replace the nicotine cravings. Finally, a grassroots consumer effort took hold in the form of nicotine vaping.
On this morning’s edition of AMHQ, The Weather Channel’s morning show, meteorologists Jim Cantore&Tevin Wooten gave viewers an in-depth look at what it would have been like to land on the moon - using The Weather Channel's’s proprietary Immersive Mixed Reality technology.
You may have seen it in the past, during coverage of a flood,
when they had everything from televisions to fish floating as their pundits exaggerated the effects of water rising. While the hyperbolic claims they made were ridiculous, they were no more ridiculous than what other media outlets did to grab viewers, and the technology was outstanding.
German was once the language of engineering and science, but as the world became more scientific, English became the common tongue. The reason may be German's notoriously irregular nouns.
 El Niño Climate Effects Shaped By Ocean Salt
El Niño Climate Effects Shaped By Ocean Salt Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?
Could Niacin Be Added To Glioblastoma Treatment?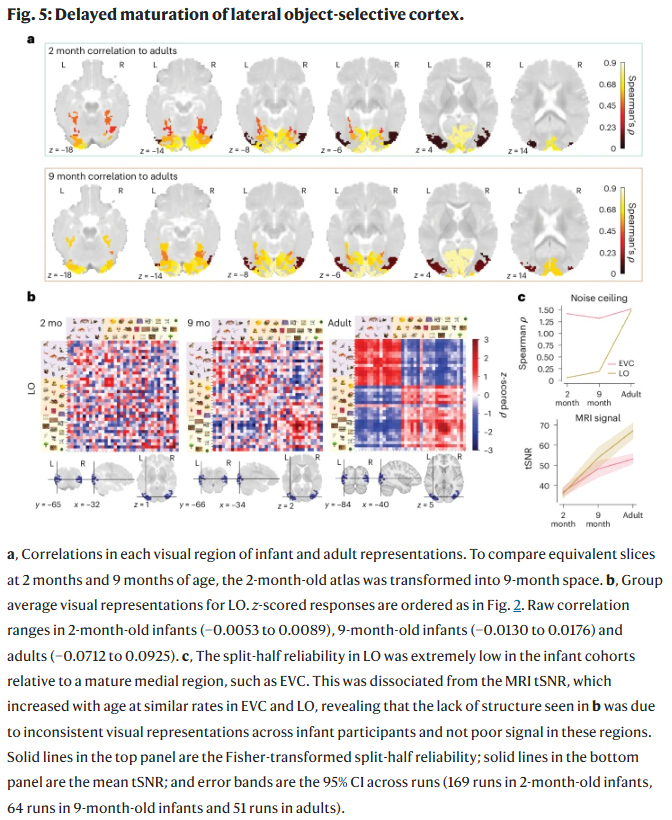 At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize Objects
At 2 Months, Babies Can Categorize Objects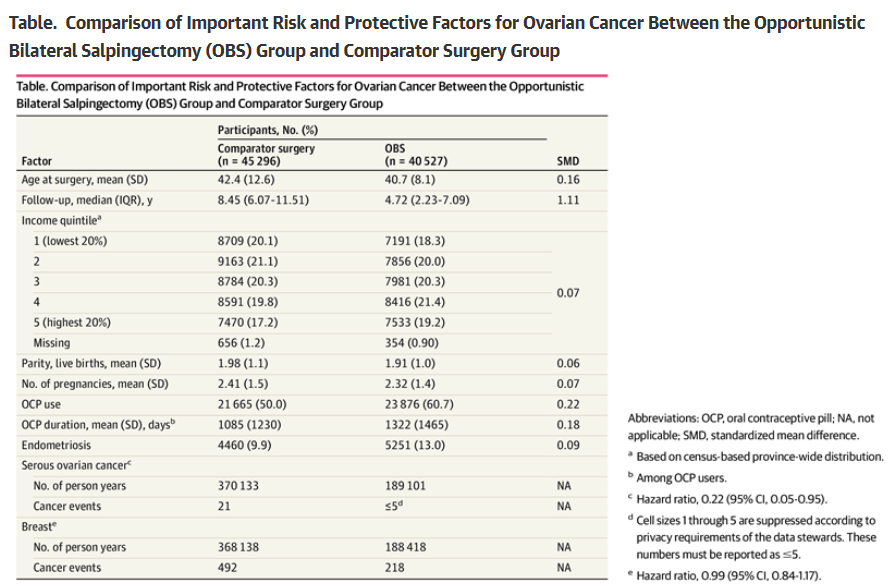 Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%
Opportunistic Salpingectomy Reduces Ovarian Cancer Risk By 78%