Yet they can be thrown out of balance by nature. Coenzyme Q is entirely natural, and a lack of it leads to mitochondrial diseases like Leigh syndrome. But short of experimentally replacing mitochondrial DNA, it is hard to modify. For anything to change it must pass through the watery cell interior called cytoplasm to the surface of the cells in order to neutralize oxidized lipid species.
A new study found that an enzyme called STARD7 helps transport the coenzyme. This protein is not only localized in the mitochondria, but also inside the cytoplasm, and it is involved in coenzyme Q transport from the mitochondria to the cell surface.
A deficiency of coenzyme Q is a hallmark of aging, studies have been done on healthy centenarians and found they have the mitochondria of 'younger' people, but declines can occur in people as early as their early 20s. Yet that co-evolutionary protective mechanism - the cell provides defense while mitochondria provide energy, are why even eating 50 pounds of spinach per day won't help. Coenzyme Q is not water soluble.
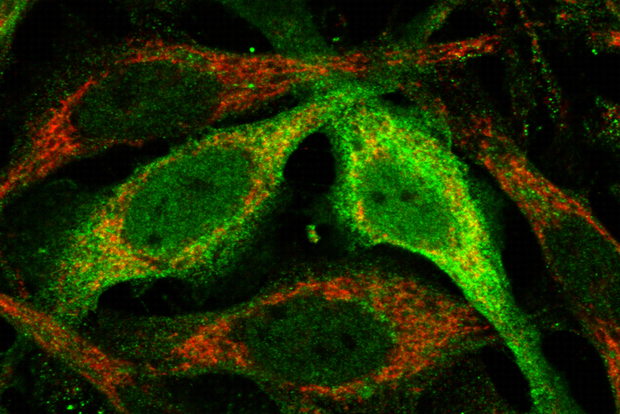
The enzyme STARD7 (green) helps mitochondria (red) to transport Coenzyme Q to protect cells from cell death. Credit: MPI f. Biology of Ageing/ S. Deshwal
“With our research, we have now been able to identify the proteins involved in coenzyme Q transport from the mitochondria to the cell surface”, says Deshwal. The researchers found that an enzyme called STARD7 helps transport the coenzyme. This protein is not only localized in the mitochondria, but also inside the cytoplasm," explains Soni Deshwal, scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Aging and lead author of the study. “The mitochondria actively transport coenzyme Q to the cell surface to protect cells from cell death. It is as if the mitochondria deliver band-aids to the surface to protect the cell.”




Comments