They even look similar to ones from the Jurassic period some 200 million years ago.
A new study find that it's due to a 'stop-start' pattern of evolution, governed by environmental change. This pattern of evolution known as "punctuated equilibrium" is generally slow, but occasionally means faster evolution because the environment has changed. This new research suggests that their evolution speeds up when the climate is warmer, and that their body size increases.
"Our analysis used a machine learning algorithm to estimate rates of evolution," said lead author Dr. Max Stockdale from the University of Bristol. "Evolutionary rate is the amount of change that has taken place over a given amount of time, which we can work out by comparing measurements from fossils and taking into account how old they are. For our study we measured body size, which is important because it interacts with how fast animals grow, how much food they need, how big their populations are and how likely they are to become extinct."
This also explains why there are only 25 species of crocodile today while animals such as lizards and birds have achieved a diversity of many thousands of species in the same amount of time or less. Crocodiles arrived at a body plan that was very efficient and versatile enough that they didn't need to change it in order to survive.
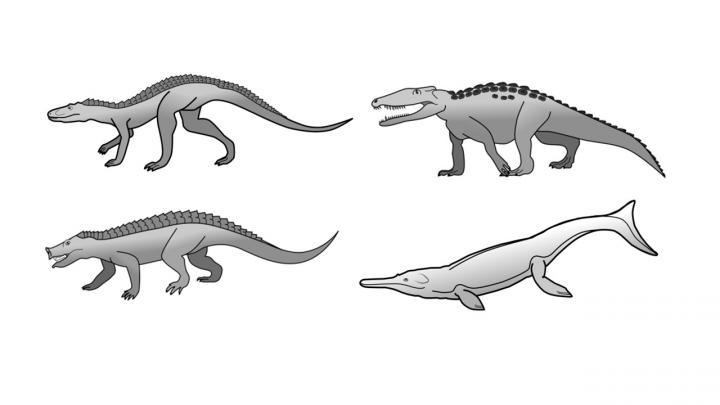
Crocodiles had a much greater diversity of forms in the past. Examples include fast runners, digging and burrowing forms, herbivores, and ocean-going species. Image: University of Bristol
So why did prehistoric dinosaurs die out? The climate during the age of dinosaurs was warmer than it is today, and that may explain why there were many more varieties of crocodile than we see now. Being able to draw energy from the sun means they do not need to eat as much as a warm-blooded animal like a bird or a mammal. Which means they should not have been as impacted by the meteor impact that set off the daisy chain of events that led to mass extinction. But there is no certain answer.






Comments