Researchers have discovered that the protein resistin, which is secreted by fat tissue, causes high levels of "bad" cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein or LDL), increasing the risk of heart disease.
High blood cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It can lead to a buildup of plaque in the artery walls and narrowing of the arteries, causing atherosclerosis, which can make it more difficult for blood to flow through the heart and body.
Watching single strands of DNA being prepped for repair may help researchers understand the origins of breast cancer.
In a new study, graduate student Jason Bell imaged individual strands of bacterial DNA as they were coated with a protein called RecA. Studying how this process works gives insights into the "mediator" proteins responsible that facilitate it. In humans, one of those mediators is the protein BRCA2, which is strongly associated with breast cancer. RecA, called Rad51 in humans, helps the single strand of DNA find its complementary, matching strand elsewhere in the chromosome. The RecA protein has to displace another protein, imaginatively named single-strand DNA-binding protein, to get to the DNA.
Professor Marie-Pierre Laborie of the University of Freiburg and professors Antonio Pizzi and Alain Celzard from the French Université de Lorraine bagged almost $20,000 in prize money and the distinction of being a "German High Tech Champion" for developing "Biofoambark", a hard foam derived from bark extract that can be used as insulating material for homes.
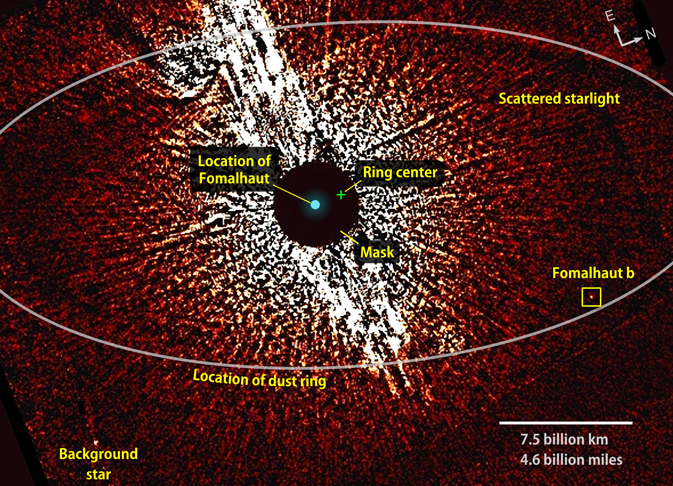
Does the nearby star Fomalhaut host a massive exoplanet? It depends on who you ask.
A new paper says that the planet, named Fomalhaut b, is a rare and possibly unique object that is completely shrouded by dust. Wasn't it already a planet?
Researchers have successfully created a human heart cell model of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), an inherited heart muscle disorder that puts carriers at high risk of developing life-threatening arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.
1.8 million years ago, giant German hippopotamuses wallowed on the banks of the Elbe.
Hippos were all over Europe then, along with other megafauna like woolly mammoths and giant cave bears. What went wrong? Palaeontologists blame global cooling during the Pleistocene Era, which may have forced Europe’s hippos to shrink to pygmy sizes before finally driving them to warmer climes.
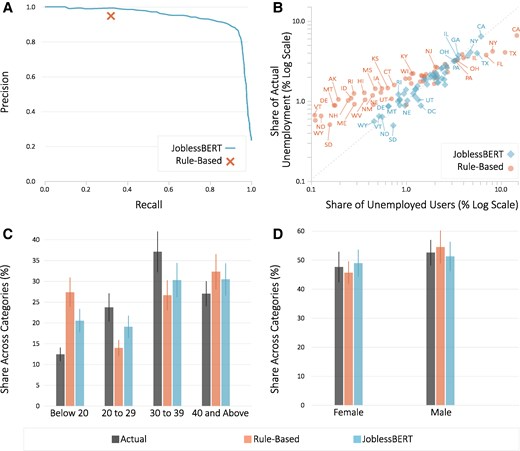 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government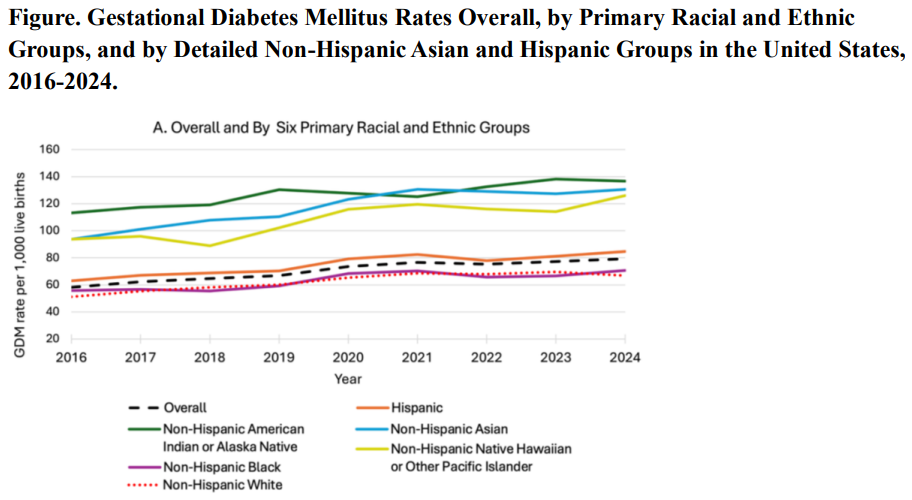 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest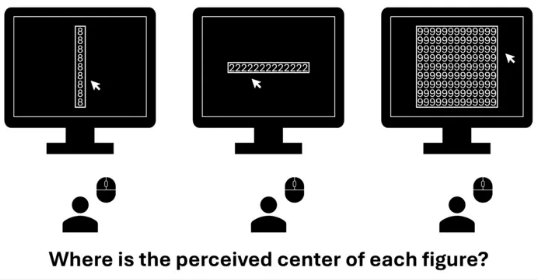 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food