Autism is a complex brain disorder that strikes in early childhood. The condition disrupts a child's ability to communicate and develop social relationships and is often accompanied by acute behavioral challenges. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that one in 150 American children is diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder; the disorder affects four times as many boys as girls. The diagnosis of autism has expanded tenfold in the last decade.
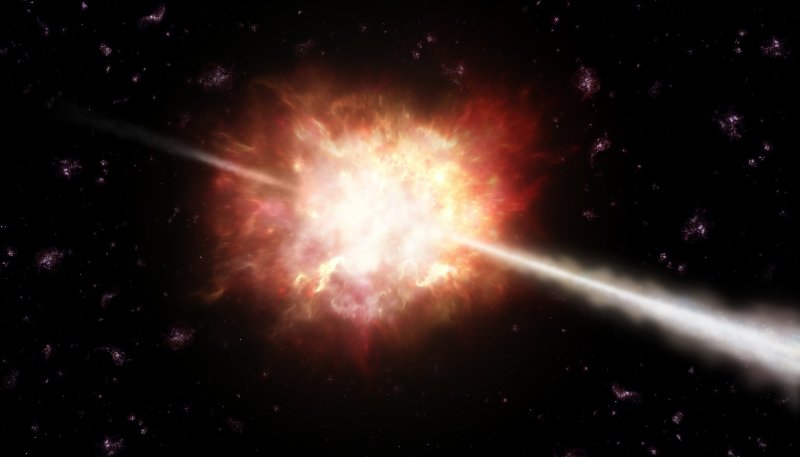
The farthest we have 'seen' in space just got a little farther away, thanks to ESO's Very Large Telescope and GRB (Gamma Ray Burst) 090423.
VLT has shown that a faint gamma-ray burst detected last Thursday is the signature of the explosion of the earliest, most distant known object in the Universe (a redshift of 8.2). The explosion apparently took place more than 13 billion years ago, only about 600 million years after the Big Bang.
An international team of researchers has determined key structural features of the largest known virus -the mimivirus, called by some a possible "missing link" between viruses and living cells. It was discovered accidentally by French scientists in 1992 but wasn't confirmed to be a virus until 2003. The findings may help determine whether the unusual virus causes any human diseases.
The virus infects amoebas, but it is thought to possibly be a human pathogen because antibodies to the virus have been discovered in pneumonia patients. However, many details about the virus remain unknown, said Michael Rossmann, Purdue University's Hanley Distinguished Professor of Biological Sciences.
Facial recognition is not as automatic as it may seem, according to researchers who have identified specific areas in the brain devoted solely to picking out faces among other objects we encounter.
Two specific effects have been established as being critical for facial recognition – holistic processing (in which we view the face as a whole, instead of in various parts) and left-side bias (in which we have a preference for the left side of the face). Psychologists Janet H. Hsiao from the University of Hong Kong and Garrison W. Cottrell from the University of California, San Diego wanted to test if these effects were specific for facial recognition or if they help us to identify other objects as well.
"The Lost World", published in 1912, is not Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's most famous work but his account of an isolated community of dinosaurs that survived the catastrophic extinction event 65 million years ago has lasted into modern times in a way Sherlock Holmes has not -
at least until the new Robert Downey movie comes out with him in the starring role.
In 2004, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) launched experiments designed to combine the H5N1 virus and human flu viruses and then see how the resulting hybrids affected animals so that they could assess the chances that such a "reassortant" virus might emerge and determine how dangerous it would be.
Their reasoning was that the worst fears of infectious disease experts - that the H5N1 avian influenza virus circulating in parts of Asia might combine with a human-adapted flu virus, namely if someone with a flu virus also contracted the avian virus - might result in a deadly new flu virus that could spread around the world. A pandemic of the kind not seen in almost a hundred years.
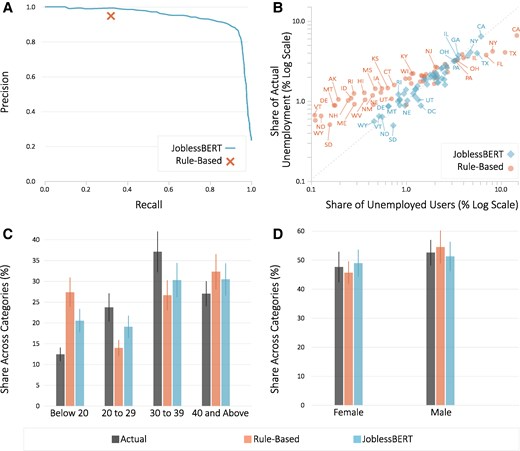 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government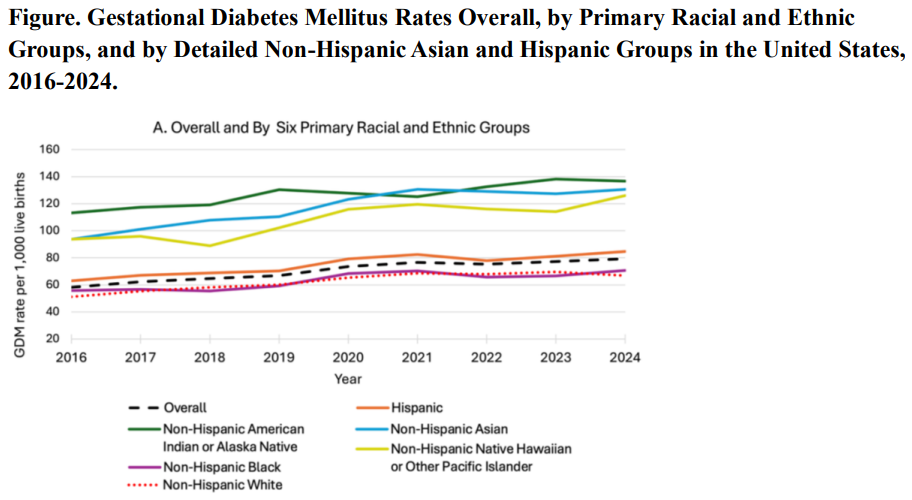 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest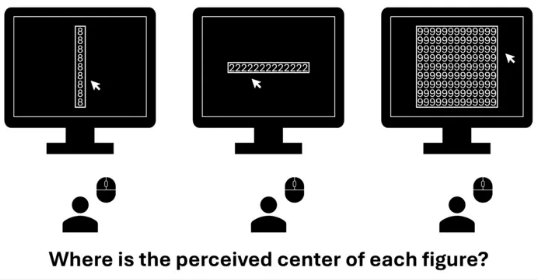 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food