The Kepler spacecraft and its Delta II rocket have been cleared to launch into space at 10:49 p.m. EST Friday night. Its mission; watch a patch of space (see image below) for the next 3.5 years and look for signs of Earth-sized planets moving around stars similar to the sun. The area that Kepler will watch contains around 100,000 stars like the sun and Kepler will look for slight dimming in the stars as planets pass between the star and Kepler. Unlike observatories like Hubble, Kepler will be able to watch the same stars constantly throughout its mission.
Here are 5 quick facts, courtesy of JPL:
Not only have horses been domesticated longer than we thought but they were also milked, says an article in Science.
The researchers have traced the origins of horse domestication back to the Botai Culture of Kazakhstan circa 5,500 years ago, about 1,000 years earlier than thought and about 2,000 years earlier than domestic horses are known to have been in Europe. Their findings strongly suggest that horses were originally domesticated, not just for riding, but also to provide food, including milk.
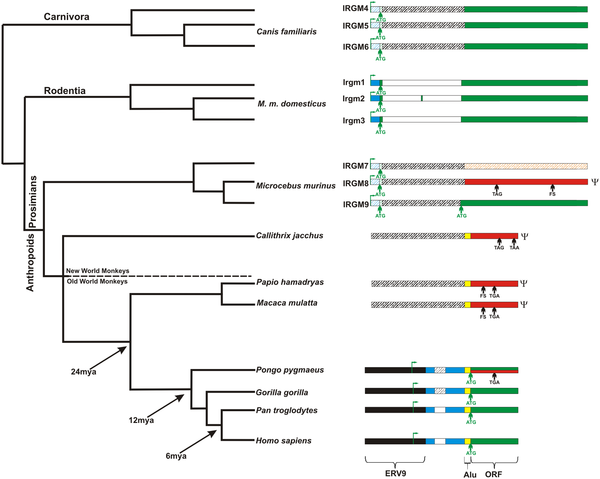
Researchers have discovered that a long-defunct gene was resurrected during the course of human evolution. This is believed to be the first evidence of a doomed gene – infection-fighting human IRGM – making a comeback in the human/great ape lineage.
The truncated IRGM gene is one of only two genes of its type remaining in humans. The genes are Immune-Related GTPases, a kind of gene that helps mammals resist germs like tuberculosis and salmonella that try to invade cells. Unlike humans, most other mammals have several genes of this type. Mice, for example, have 21 Immune-Related GTPases. Medical interest in this gene ignited recently, when scientists associated specific IRGM mutations with the risk of Crohn's disease, an inflammatory digestive disorder.
We know that lifespan can be extended in some animals by restricting calories such as sugar intake shortly after birth. Université de Montréal scientists now say that it's not sugar itself that is important in this process but the ability of cells to sense its presence.
Aging is a complex phenomenon and the mechanisms underlying aging are yet to be explained. What researchers do know is that there is a clear relationship between aging and calorie intake. For example, mice fed with half the calories they usually eat can live 40 percent longer. How does this work?
Dual catalysts may be the key to efficiently turning carbon dioxide and water vapor into methane and other hydrocarbons using titania nanotubes and solar power, according to Penn State researchers.
Burning fossil fuels like oil, gas and coal release large amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. Rather than contribute to global climate change, producers could convert carbon dioxide to a wide variety of hydrocarbons, but this makes sense to do only when using solar energy.
Two highly lethal viruses that have emerged in recent outbreaks are susceptible to chloroquine, an established drug used to prevent and treat malaria, according to a new basic science study by researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College in the Journal of Virology.
The two henipaviruses that are the subject of the study -- Hendra Virus (HeV) and Nipah Virus (NiV) -- emerged during the 1990s in Australia and Southeast Asia. Harbored by fruit bats, they cause potentially fatal encephalitis and respiratory disease in humans, with a devastating 75 percent fatality rate. More recently, NiV outbreaks in Bangladesh involving human-to-human transmission have focused attention on NiV as a global health concern.
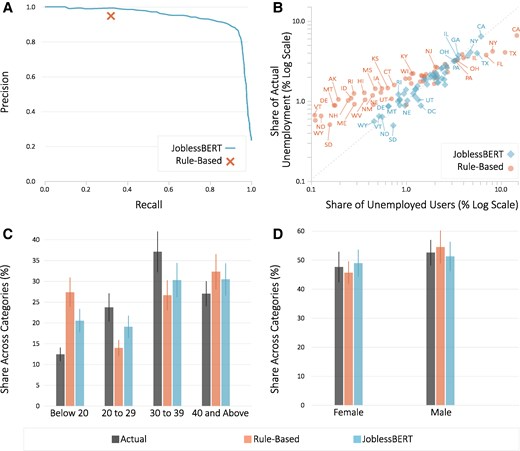 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government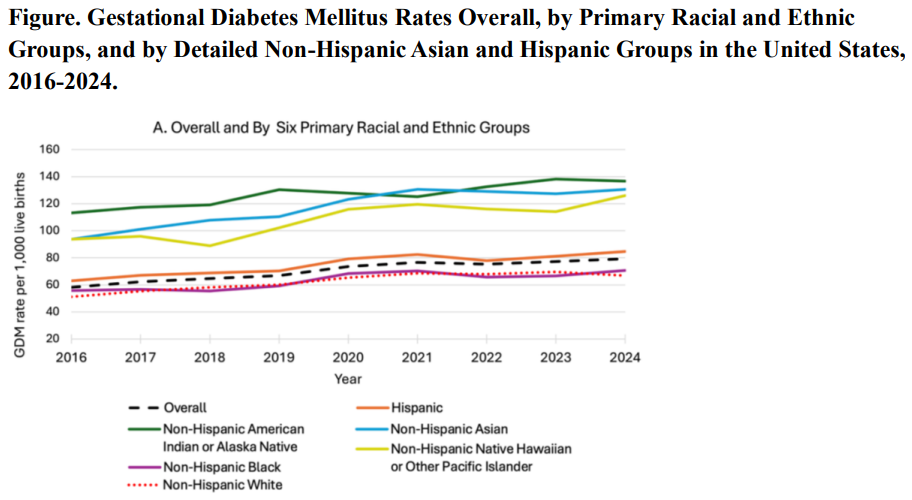 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest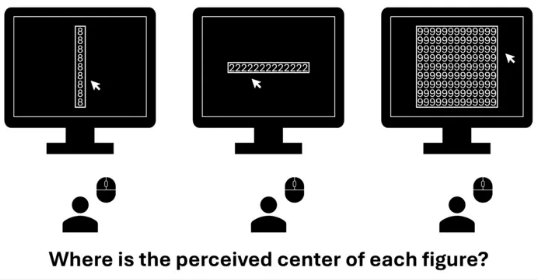 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food