The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science Look
The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science LookBleeding hosts and stigmatizations are the best-known medieval miracles but less known ones, like ...
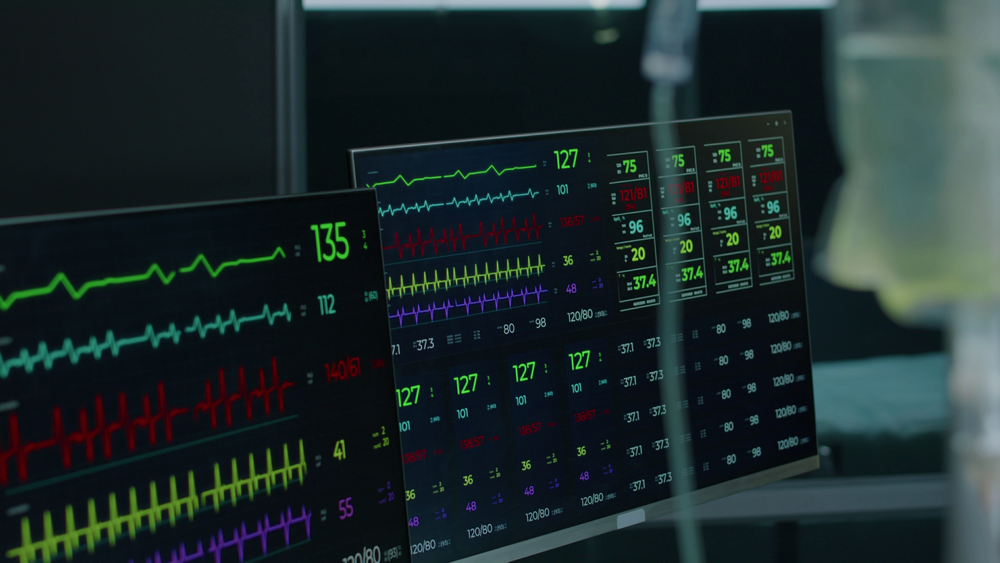 $0.50 Pantoprazole For Stomach Bleeding In ICU Patients Could Save Families Thousands Of Dollars
$0.50 Pantoprazole For Stomach Bleeding In ICU Patients Could Save Families Thousands Of DollarsThe inexpensive medication pantoprazole prevents potentially serious stomach bleeding in critically...
 Metformin Diabetes Drug Used Off-Label Also Reduces Irregular Heartbeats
Metformin Diabetes Drug Used Off-Label Also Reduces Irregular Heartbeats Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who are not diabetic but are overweight and took the diabetes...
 Your Predator: Badlands Future - Optical Camouflage, Now Made By Bacteria
Your Predator: Badlands Future - Optical Camouflage, Now Made By BacteriaIn the various 'Predator' films, the alien hunter can see across various spectra while enabling...