Asiaticoside is the main saponin constituent of Centella asiatica, a plant long used in the Ayurvedic system of medicine that has become popular for human collagen synthesis applications, like anti-wrinkle treatments.
In the central nervous system, Asiaticoside has been found by some studies to attenuate in vitro neuronal damage caused by exposure to β-amyloid. However, any potential neuroprotective properties in glutamate-induced excitotoxicity have not been fully studied.
Researchers from Fourth Military Medical University of Chinese PLA in China are now reporting that pretreatment with Asiaticoside decreased neuronal cell loss in a concentration-dependent manner and restored changes in expression of apoptotic-related proteins Bcl-2 and Bax. They authors say Asiaticoside pretreatment also attenuated the upregulation of NR2B expression, a subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors but did not affect expression of NR2A subunits.
Additionally, in cultured neurons, they report that Asiaticoside significantly inhibited Ca2+ influx induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate. They believe their results provide confirmation and some new insight into the possible neuroprotective effects of Asiaticoside.
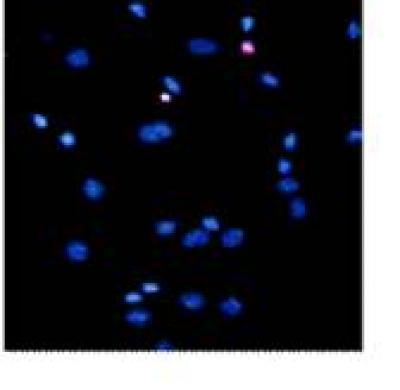
Pretreatment with Asiaticoside reduced cortical neuron apoptosis induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate - Hoechst 33258 and propidium iodide double staining. Credit: Neural Regeneration Research
Published in Neural Regeneration Research Vol. 9, No. 13, 2014.
Source: Neural Regeneration Research






Comments