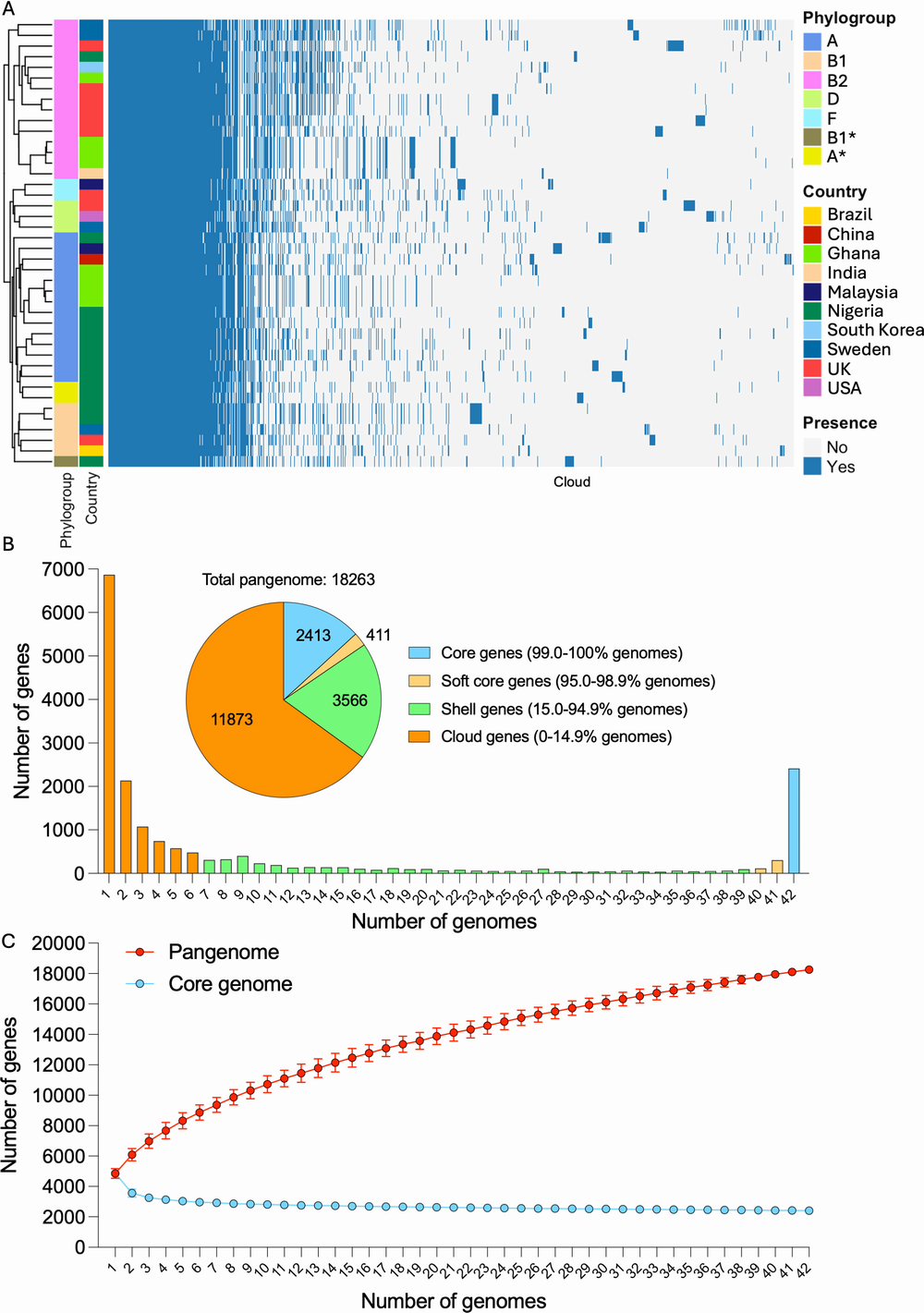
 E. Coli Linked To Diabetic Foot Infections Gets Worldwide Analysis
E. Coli Linked To Diabetic Foot Infections Gets Worldwide AnalysisDiabetic foot infections are a serious complications of diabetes and a leading cause of lower-limb...
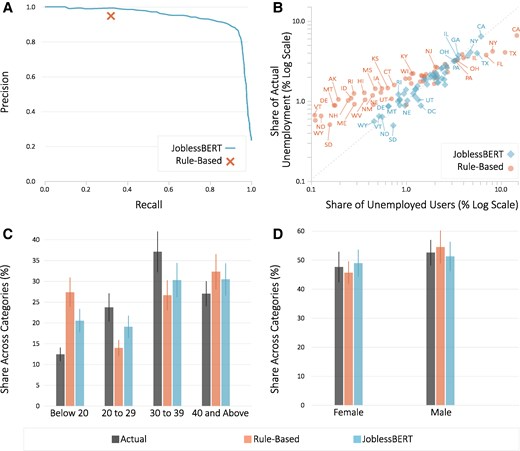 Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than Government
Social Media Is A Faster Source For Unemployment Data Than GovernmentGovernment unemployment data today are what Nielsen TV ratings were decades ago - a flawed metric...
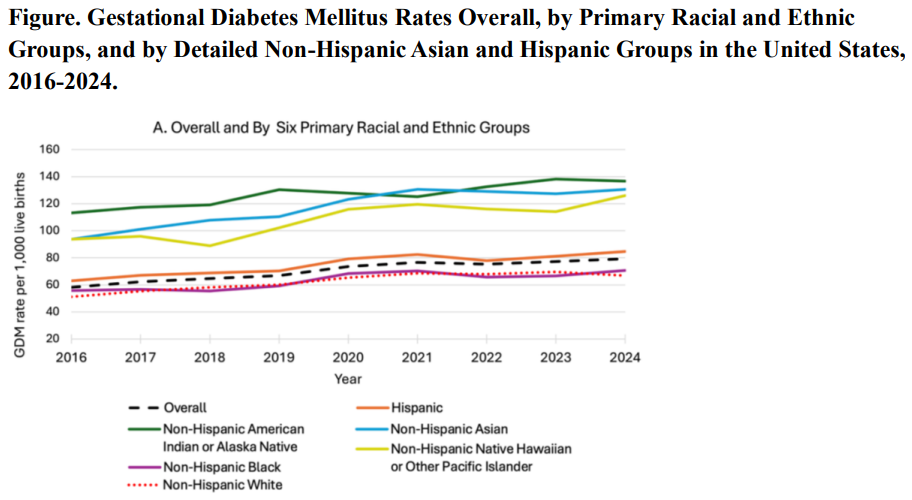 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are HealthiestGestational diabetes, a form of glucose intolerance during pregnancy, occurs primarily in women...
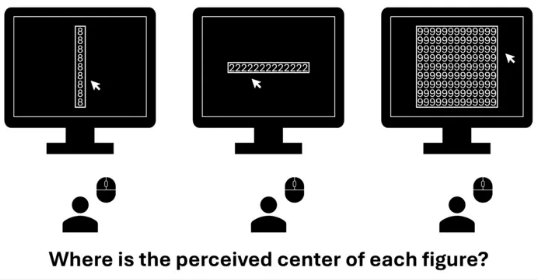 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive SpacesResearchers recently studied the relationship between numerical information in our vision, and...







