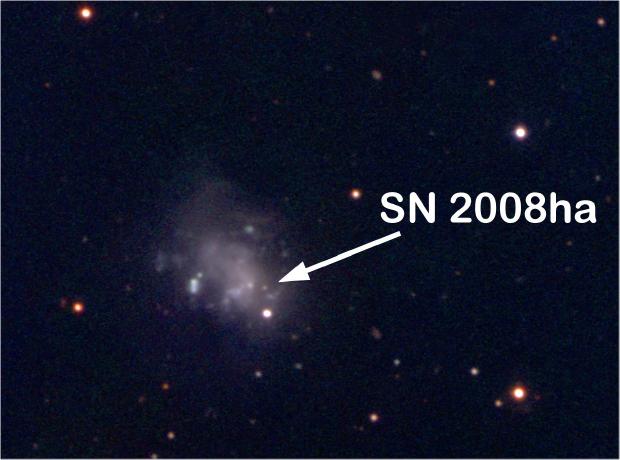
Core-collapse (or gravitational) supernovae are among the most energetic and violent events in the universe and constitute the final tremendous explosions in the life cycles of stars 8 times more massive than our Sun.
After running out of fuel, the core of such a star collapses and forms a neutron star or a black hole. At the same time, the outer layers are ejected at high velocity (up to 10% of the speed of light) and shine as brightly as billions of stars together.
To provide some perspective, the total energy suddenly released by such a supernova exceeds the total energy release by our Sun to-date; and also in the next 10 billion years.
Want to know how gravestones will weather due to pollution? Can you help measure hailstones? If so, or you are wondering what else one person can contribute to solving global climate issues, controlling the spread of invasive plant species or managing severe weather risk, EarthTrek is for you.
EarthTrek is a new worldwide program developed by the Geological Society of America and an array of national and international partners to provide a new tool allowing concerned citizens to collect data that will provide answers in understanding our planet
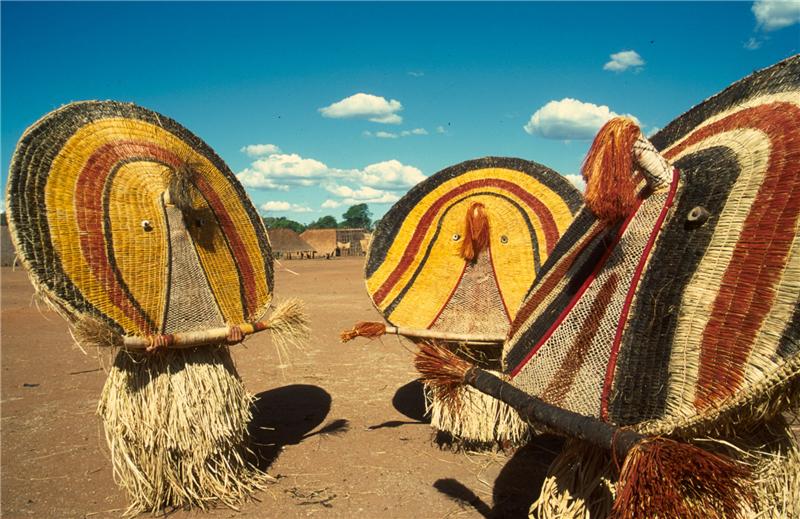
Did animals teach us one of the oldest forms of human technology, basketry? Did that help us learn to count? These are just two of the themes due to be explored at a University of East Anglia event which takes place June 5-6) is part of Beyond the Basket, a new research project led by the university exploring the development and use of basketry in human culture over 10,000 years.
Basketry has been practiced for millennia and ranges from mats for sitting on, containers and traps for hunting, to partitions and walls - all of which have been central to advancing our culture.
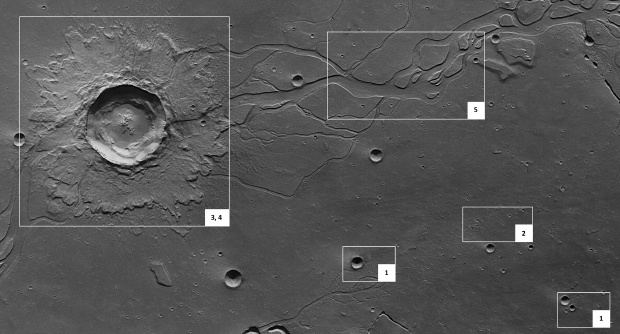
ESA’s Mars Express orbiter has obtained images of Hephaestus Fossae, , which lies at about 21° North and 126° East on Mars. Named after the Greek god of fire, Hephaestus Fossae extends for more than 600 km on the western flank of Elysium Mons in the Utopia Planitia region.
The images have a ground resolution of about 16 m/pixel. They show that the region has channel systems of unknown origin. The images cover 170 x 80 sq km, an area almost as large as Montenegro. The surface is mostly smooth, and is covered by several small impact craters 800-2800 m in diameter. Smaller craters are scattered across the entire region.
Research scientists at the Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB in Stuttgart working in conjunction with their colleagues from the company Logos Innovationen have found a way of converting this air humidity autonomously and decentrally into drinkable water.
Even in deserts the air contains water and the research scientists have found a way of obtaining drinking water from air humidity using a system is based completely on renewable energy, making it autonomous.
Even in places with no lakes, rivers or groundwater, considerable quantities of water are stored in the air. In the Negev desert in Israel, for example, annual average relative air humidity is 64 percent – in every cubic meter of air there are 11.5 milliliters of water.
The thinking, talking robots of Isaac Asimov science fiction are nothing like what we actually have - programmed machines that do the simplest things. European researchers in robotics, psychology and cognitive sciences say they have developed a robot that can predict the intentions of its human partner; this ability to anticipate (or even question) actions could make human-robot interactions more natural.
You cannot make human-robot interaction more natural unless you understand what 'natural' actually means. But few studies have investigated the cognitive mechanisms that are the basis of joint activity (i.e. where two people are working together to achieve a common goal).
 Study: Caloric Restriction In Humans And Aging
Study: Caloric Restriction In Humans And Aging Science Podcast Or Perish?
Science Podcast Or Perish? Type 2 Diabetes Medication Tirzepatide May Help Obese Type 1 Diabetics Also
Type 2 Diabetes Medication Tirzepatide May Help Obese Type 1 Diabetics Also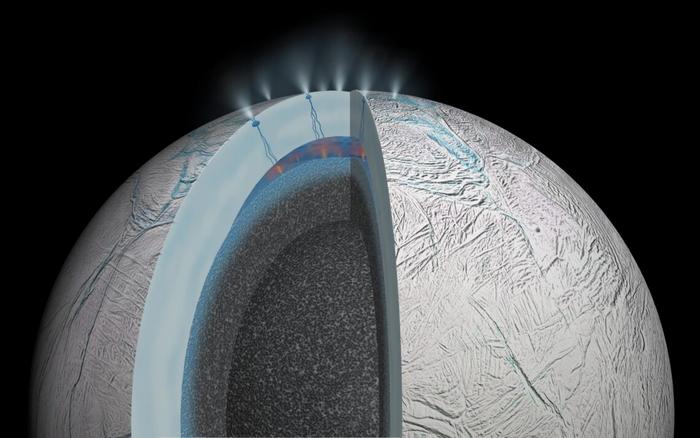 Life May Be Found In Sea Spray Of Moons Orbiting Saturn Or Jupiter Next Year
Life May Be Found In Sea Spray Of Moons Orbiting Saturn Or Jupiter Next Year