For quantum physicists working on future systems, entangling quantum systems is a key resource for upcoming quantum computers and simulators.
Physicists have crafted a new, reliable method to verify entanglement in the laboratory using a minimal number of assumptions about the system and measuring devices - it witnesses the presence of useful entanglement, a ‘verification without knowledge’.
Quantum computation, quantum communication and quantum cryptography often require entanglement. For many of these upcoming quantum technologies, entanglement – this hard to grasp, counter-intuitive aspect in the quantum world – is a key ingredient. Therefore, experimental physicists often need to verify entanglement in their systems.
Antioxidants have been hyped by marketing and mainstream media claims as cure-alls for almost anything, but a systematic review has likely eliminated one - there is no quality evidence that antioxidant supplements help to increase a woman's chances of having a baby and information is still too limited to know if it has potential harms.
The paper says around 25% of couples planning a baby may have 'difficulty' conceiving. Women undergoing fertility treatment often take dietary supplements, including antioxidants, to try to increase their chances of becoming pregnant. Antioxidant supplements taken to improve fertility are unregulated and there is limited evidence on their safety and effects.
In 2011, a paper revealed that Dictyostelium discoideum, a single-celled organism, picks up edible bacteria, carries them to new locations and harvests them like crops - basically, it is the world's smallest farmer. (Nature 469, 393-396 doi:10.1038/nature09668)
There is lots of speculation about the impact of climate change on polar bears but little data. Society needs to understand the potential impact of sea ice retreats but polar bears are difficult to study in the wild.
"Direct behavioral observations are nearly impossible," says Amy Cutting, Oregon Zoo curator.
Enter Tasul, an Oregon Zoo polar bear, who is now wearing a high-tech collar to help get some climate change answers. Within the collar is an accelerometer, like the one found in most smart phones the NSA is monitoring you with, and it detects minute changes in motion and direction of movement.
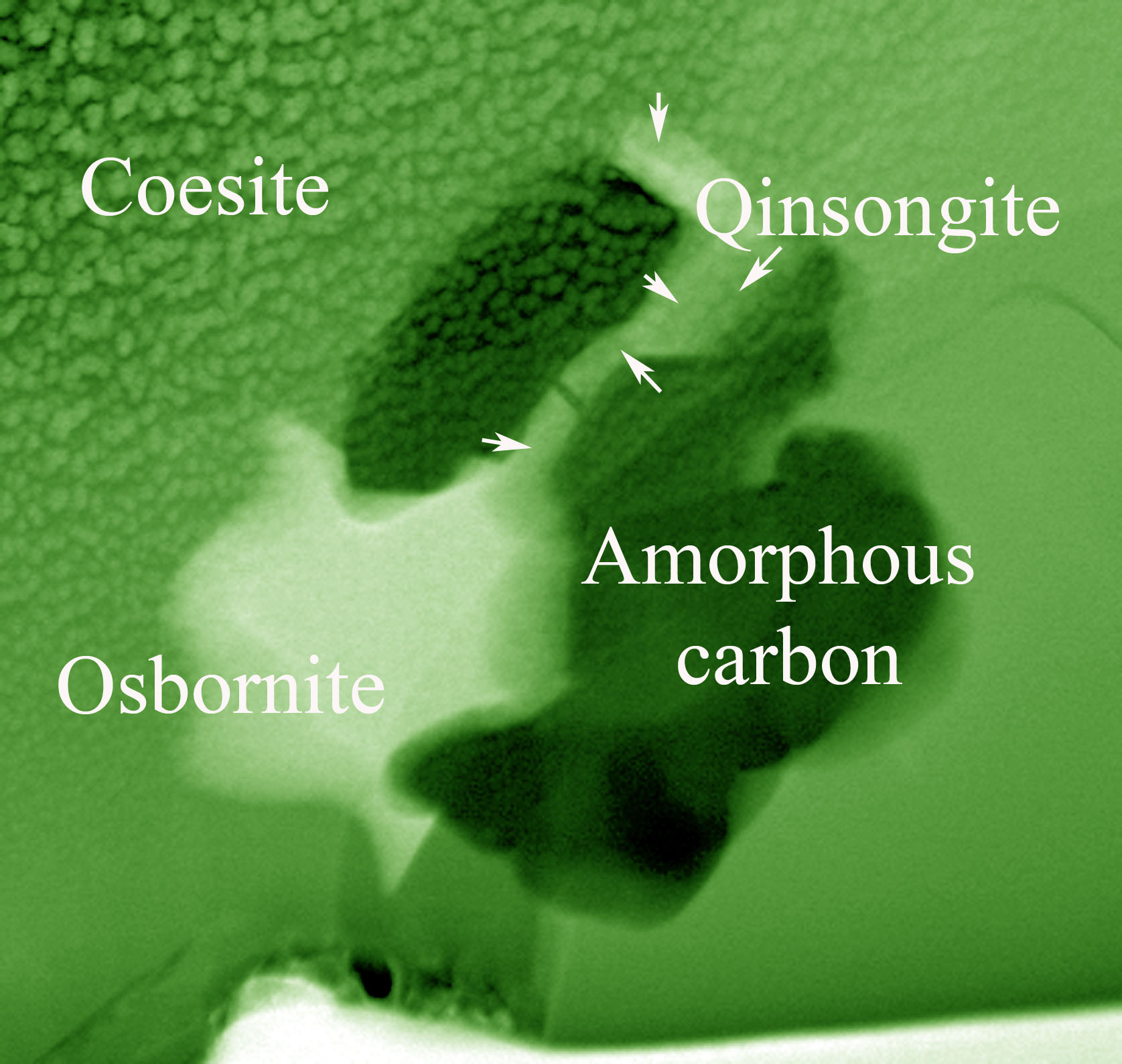
A new mineral, cubic boron nitride, has been officially approved by the International Mineralogical Association as “qingsongite.” You'd think there aren't a lot of mineral discoveries happening every day but this had been in committee since 2009. Geology paces itself and perhaps so do naming conventions. But it turns out there are at least 100 proposals for new minerals and their names submitted each year. To-date, more than 4700 species of minerals have been recognized.
Qingsongite was named after Qingsong Fang (1939–2010), a professor at the Institute of Geology, the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, who found the first diamond in the Tibetan chromium-rich rocks in the late 1970s, and contributed to the discovery of four new mineral species.
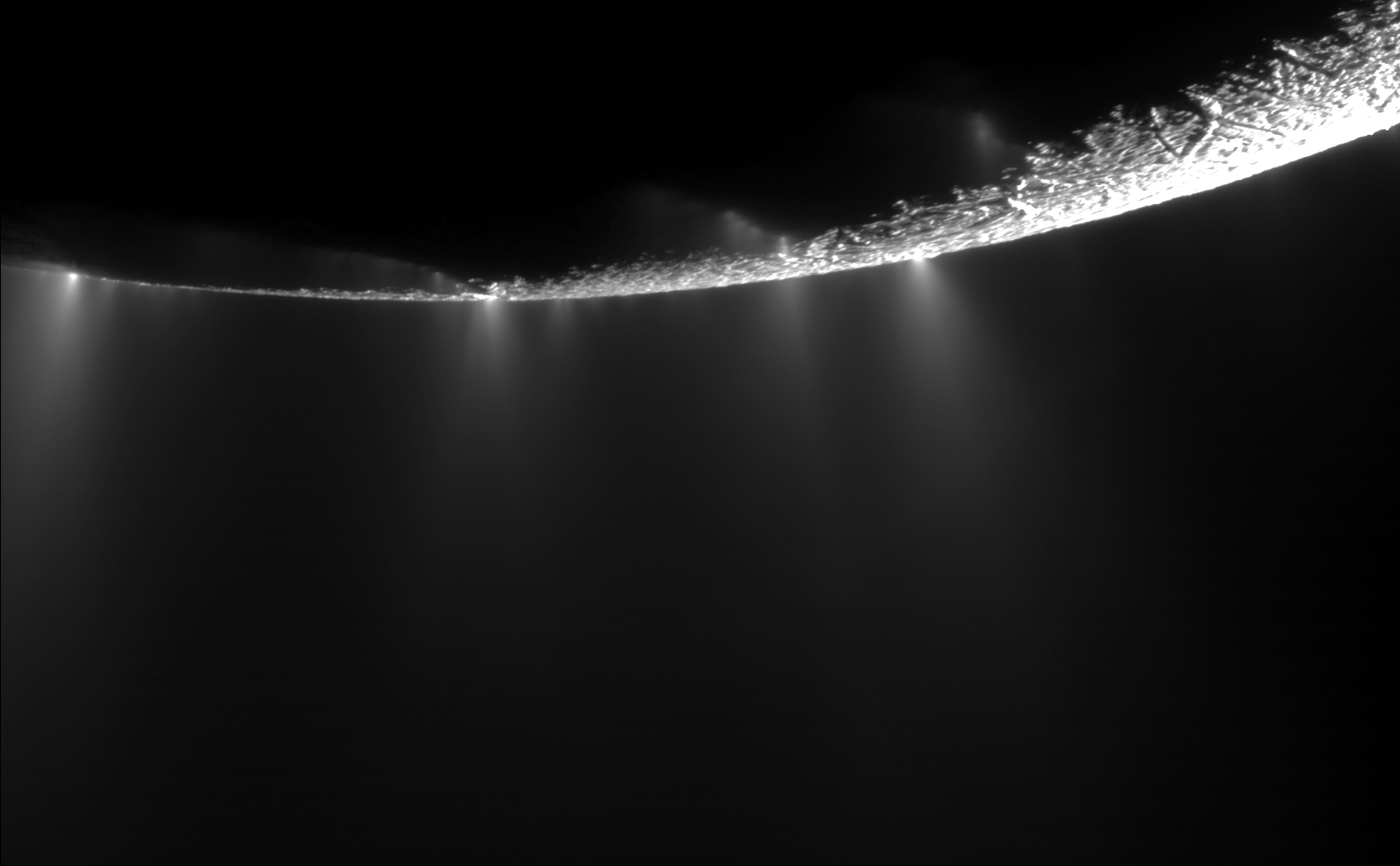
The intensity of the jets of water ice and organic particles that shoot out from Enceladus, a moon orbiting Saturn, depends on its proximity to the ringed planet, according to data obtained by NASA's Cassini spacecraft.
The finding adds to evidence that a liquid water reservoir or ocean lurks under the icy surface of the moon. This is the first clear observation the bright plume emanating from Enceladus' south pole varies predictably.
Cassini, which has been orbiting Saturn since 2004, discovered the jets that form the plume in 2005. The water ice and organic particles spray out from several narrow fissures nicknamed "tiger stripes."
Ann Finkbeiner, author of 2007's
The Jasons: The Secret History of Science's Postwar Elite
(among other things)
and contributor to The Last Word On Nothing, recently had a fascinating exchange with one of my favorite journalists,
USA Today's
Dan Vergano.
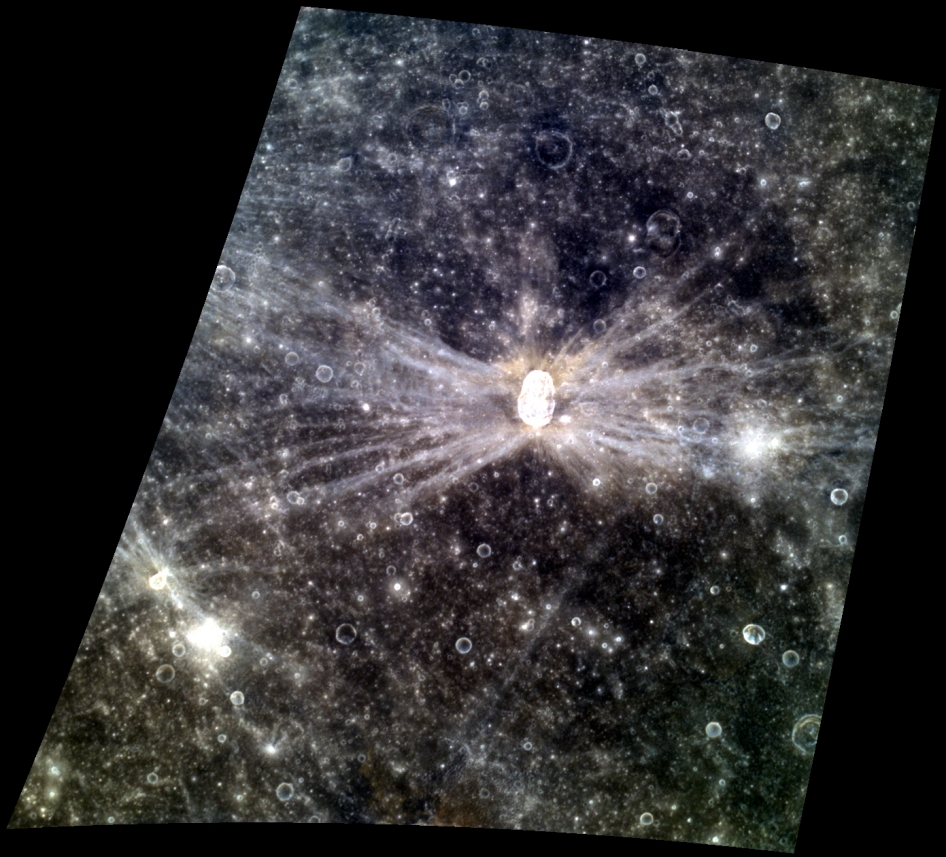
A color image, taken on May 1st, 2013 by the Wide Angle Camera (WAC) instrument aboard NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft orbiting Mercury, features the Hovnatanian crater, named for Armenian painter Hakop Hovnatanian.
The crater's elliptical shape and the bright rays' butterfly pattern indicate that a very oblique impact produced the crater. The brightness of the rays indicate that they are relatively young features on Mercury's surface.
Two days ago I showed how the measurements produced in the course of the last decade have allowed us to "zoom into" the parameter space of the Standard Model, pinpointing the W boson, top quark, and Higgs boson masses to a very narrow 3-D volume of phase space.
It didn't take long before the Netflix dramedy hit "Orange Is The New Black" made its way into Psychology of Women Quarterly, a publication devoted to peer-reviewing the feminist science.
With all that humor and girl kissing and talk of beatdowns, you know an editor was excited about the chance to link a paper to the show in a press release - things have been rather tame, culturally, for readers and contributors there since "The L Word" went off the air. The American Psychological Association is, as always, happy to ride a cultural wave.(1)