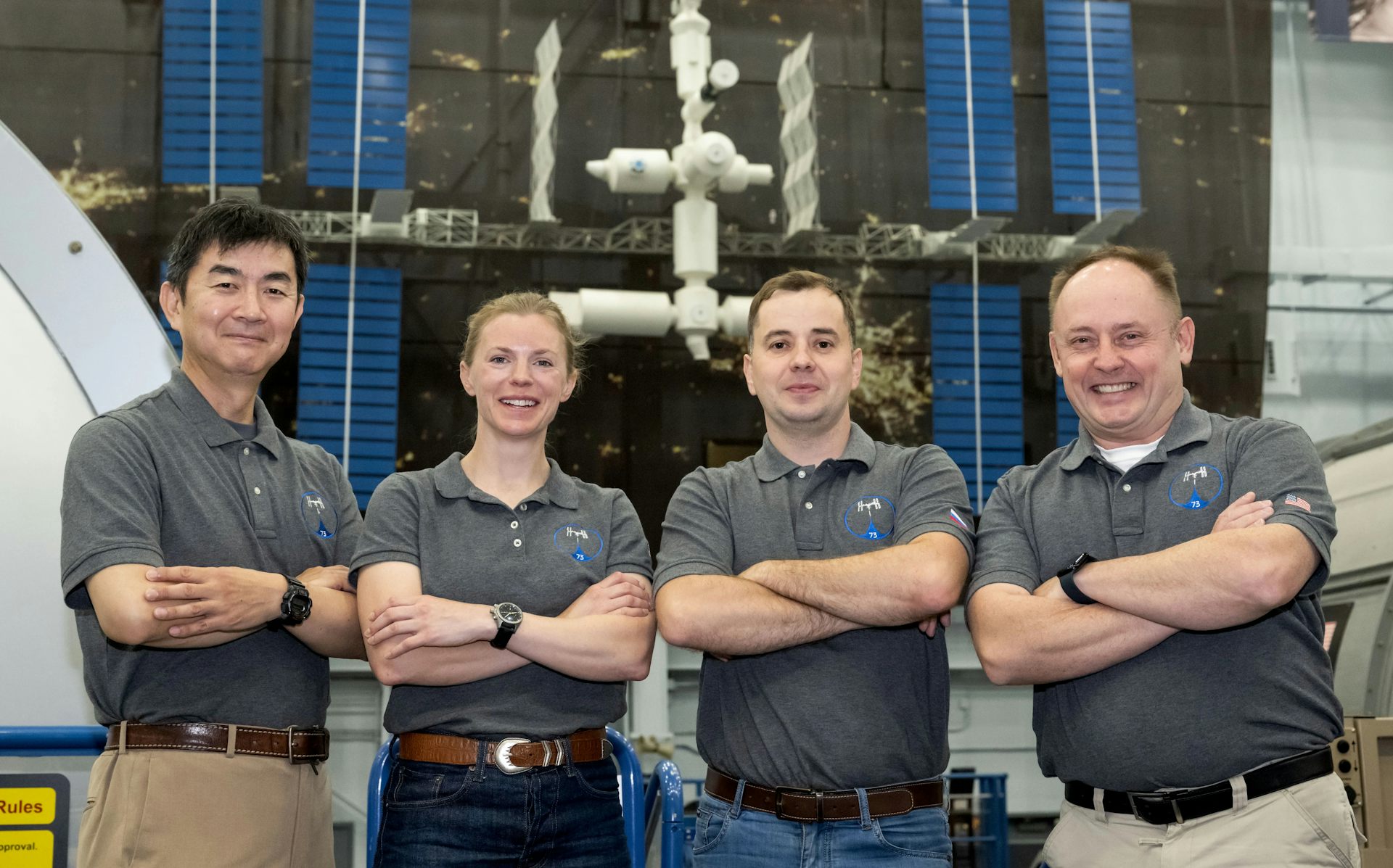
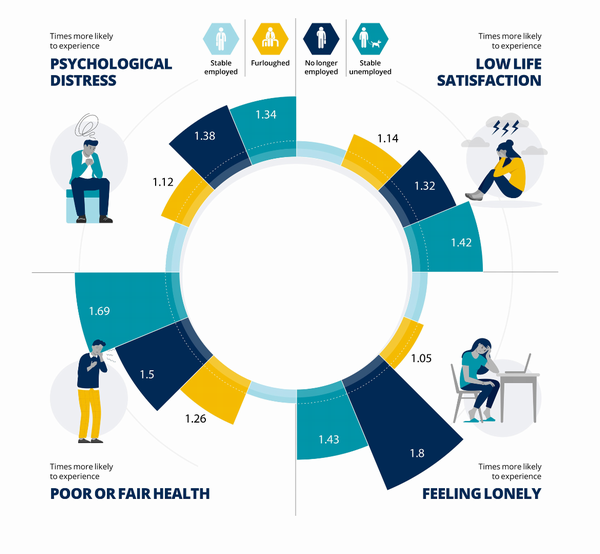
Healthcare In Space - The First Medical Evacuation From The ISS
Healthcare In Space - The First Medical Evacuation From The ISSFor the first time in 25 years of continuous crewed operations, an astronaut has been medically...
 I Earned It, You're Privileged - The Paradox In How We View Achievement
I Earned It, You're Privileged - The Paradox In How We View AchievementThe concept of “hard work v privilege”, and what either one says about someone’s social status...
 Not Just The Holidays: The Hormonal Shift Of Perimenopause Could Be Causing Weight Gain
Not Just The Holidays: The Hormonal Shift Of Perimenopause Could Be Causing Weight GainYou’re in your mid-40s, eating healthy and exercising regularly. It’s the same routine that...
 Anxiety For Christmas: How To Cope
Anxiety For Christmas: How To CopeChristmas can be hard. For some people, it increases loneliness, grief, hopelessness and family...