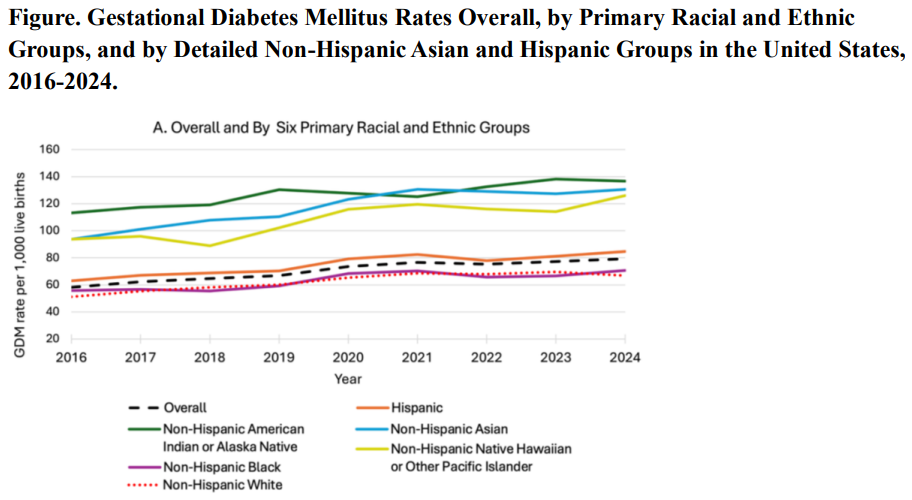
 Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are Healthiest
Gestational Diabetes Up 36% In The Last Decade - But Black Women Are HealthiestGestational diabetes, a form of glucose intolerance during pregnancy, occurs primarily in women...
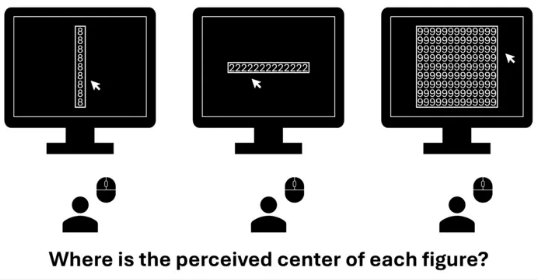 Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive Spaces
Object-Based Processing: Numbers Confuse How We Perceive SpacesResearchers recently studied the relationship between numerical information in our vision, and...
 Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For Food
Males Are Genetically Wired To Beg Females For FoodBees have the reputation of being incredibly organized and spending their days making sure our...
 The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science Look
The Scorched Cherry Twig And Other Christmas Miracles Get A Science LookBleeding hosts and stigmatizations are the best-known medieval miracles but less known ones, like ...