The strength of gravity at Earth’s surface varies subtly from place to place owing to factors such as the planet’s rotation and the position of mountains and ocean trenches. Changes in the mass of large ice sheets can also cause small local variations in gravity.
Recently, the high-resolution measurements from GOCE over Antarctica between November 2009 and June 2012 have been analyzed by scientists and they found that the decrease in the mass of ice during this period was mirrored in GOCE’s measurements, even though the mission was not designed to detect changes over time. Using gravity data to assess changes in ice mass is not new. The NASA–German Grace satellite, which was designed to measure change, has been providing this information for over 10 years.
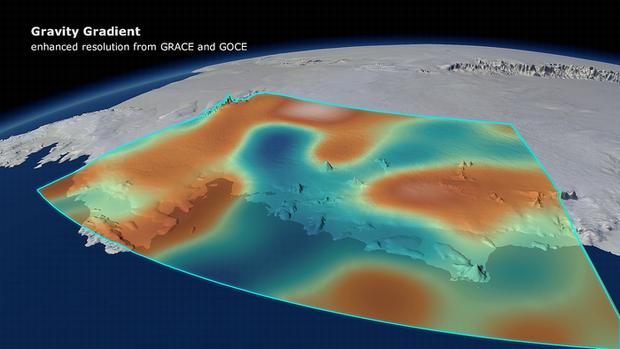
Changes in Earth’s gravity field resulting from loss of ice from West Antarctica between November 2009 and June 2012 (mE = 10–12 s–2). A combination of data from ESA’s GOCE mission and NASA’s Grace satellites shows the ‘vertical gravity gradient change’. Credit: DGFI/Planetary Visions
However, measurements from Grace are much coarser than those of GOCE, so they cannot be used to look at features such as Antarctica’s smaller ‘catchment basins’. For scientific purposes, the Antarctic ice sheet is often divided into catchment basins so that comparative measurements can be taken to work out how the ice in each basin is changing and discharging ice to the oceans. Some basins are much bigger than others.
By combining GOCE’s high-resolution measurements with information from Grace, scientists can now look at changes in ice mass in small glacial systems – offering even greater insight into the dynamics of Antarctica’s different basins.
Credit: ESA/DGFI/Planetary visions
They have found that that the loss of ice from West Antarctica between 2009 and 2012 caused a dip in the gravity field over the region. ESA’s CryoSat satellite, which carries a radar altimeter, has recently shown that since 2009 the rate at which ice is been lost from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet every year has increased by a factor of three.
And, between 2011 and 2014, Antarctica as a whole has been shrinking in volume by 125 cubic kilometers a year. Johannes Bouman from the German Geodetic Research Institute said, “We are now working in an interdisciplinary team to extend the analysis of GOCE’s data to all of Antarctica. This will help us gain further comparison with results from CryoSat for an even more reliable picture of actual changes in ice mass.”
Source: ESA




Comments