We may now get to think about what it's like for real, though no one lives on the newly discovered cold and gaseous planet, Kepler-16b in the Kepler-16 system, which orbits two stars.
Previous studies have found hints of planets orbiting binary stars, but clear confirmation has been elusive. The Kepler space telescope detects planets through what is known as a planetary transit, in which the brightness of a star dims as a result of a planet crossing in front of it. Scientists detected the new planet in the Kepler-16 system: a pair of orbiting stars that eclipse each other from our point of view on Earth. A primary eclipse occurs when the larger star is partially blocked by the smaller star, and a secondary eclipse occurs when the smaller star is occulted, or completely blocked, by the larger star.
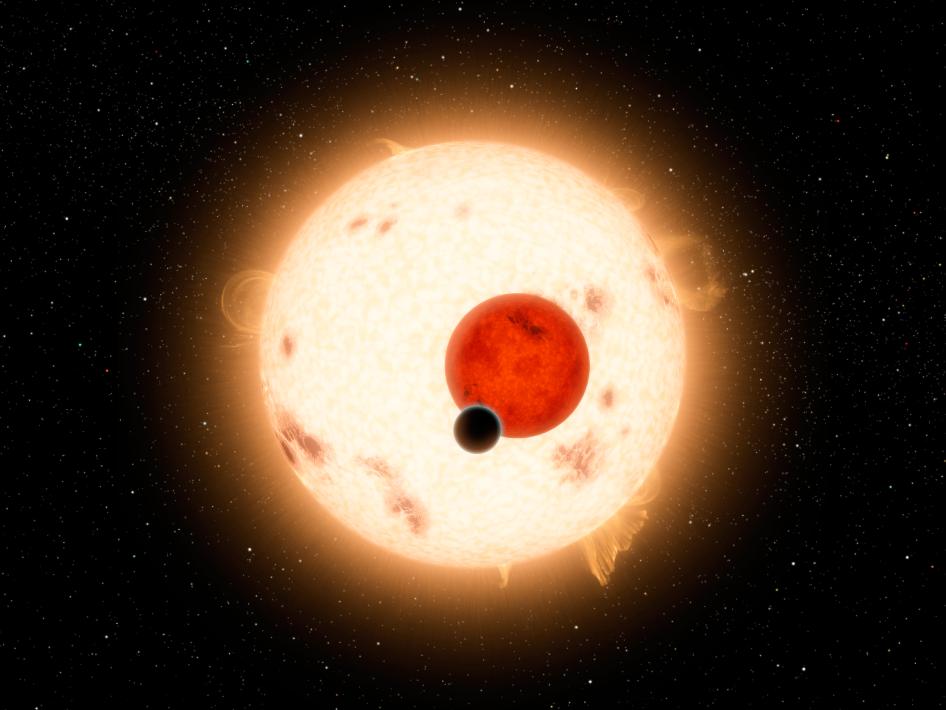
Kepler-16 orbits a slowly rotating K-dwarf that is, nevertheless, very active with numerous star spots. Its other parent star is a small red dwarf. The planetary orbital plane is aligned within half a degree of the stellar binary orbital plane. All these features combine to make Kepler-16 of major interest to studies of planet formation as well as astrophysics. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt
Astronomers further observed that the brightness of the system dipped even when the stars were not eclipsing one another, hinting at a third body. The additional dimming events reappeared at irregular intervals of time, indicating that the stars were in different positions in their orbit each time the third body passed.
UC Santa Cruz astronomer Daniel Fabrycky , a Hubble postdoctoral fellow at UC Santa Cruz, performed the initial interpretation of the precise timings of the planetary transits and the eclipses of the stars, showing that only a planet in a wide orbit around both stars was consistent with the data. The gravitational tug on the stars, measured by changes in their eclipse times, was a good indicator of the mass of the third body. Only a very small gravitational pull was detected, one that could only be caused by a mass as small as a planet.
"This discovery provides confirmation of a new class of planetary systems that could harbor life. Given that most stars in our galaxy are part of a binary system, this means that the opportunities for life are much broader than if planets form only around single stars," said Kepler principal investigator William Borucki. "This milestone discovery confirms a theory that scientists have had for decades but could not definitively prove until now."
The discovery in Science confirms the newest member of the Kepler planet family, Kepler-16b, which is an inhospitable, cold world about the size of Saturn, and thought to be made up of about half rock and half gas. "The planet seems to be a denser version of Saturn," said Fortney, who used the mass and radius of the planet to calculate models of its interior structure.
The parent stars are both smaller than our sun--one is 69 percent and the other only 20 percent the mass of the sun. Kepler-16b orbits around both stars every 229 days, but lies outside the system's habitable zone, the region where liquid water could exist on the surface, because the stars are cooler than our sun. The smaller star of the Kepler-16 system is a type of star called a red dwarf. The Kepler team was able to directly measure its size because it eclipses its companion star every 41 days, causing the starlight to dim and brighten regularly every time the pair orbit around each other.
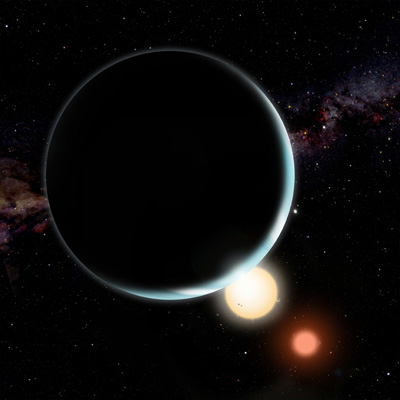

Kepler-16b, shown in this artist's conception, enjoys double sunsets as it circles a pair of stars. The orange and red stars orbit each other every 41 days, while Kepler-16b orbits them both every 229 days at a distance of 65 million miles. Credit: David A. Aguilar (CfA)
"Most of what we know about the sizes of stars comes from such eclipsing binary systems, and most of what we know about the size of planets comes from transits," said lead author and Kepler participating scientist Laurance Doyle of the SETI Institute in Mountain View. "Kepler-16 combines the best of both worlds, with stellar eclipses and planetary transits in one system."
Kepler-16b may not have a habitable surface, but there are hints that rocky planets with double sunsets might be common in our galaxy. In 2007, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope found planetary disks of debris around twin stars, indicating rocky planets may have formed in those systems.
NOTES:
(1) Actually, the "Clone Wars" interstitials/commercials (simple cartoon graphics) long after the newer movies faded from memory were quite good, likely because George Lucas had nothing to do with them. The follow-on series (better graphics, an annoying sidekick that will annoy adults) is decent as well.
(2) “You've never heard of the Millennium Falcon? It's the ship that made the Kessel run in less than 12 parsecs” issued forth by Han Solo was a giant face palm moment even for 12-year-olds who knew a modicum of science in 1977.





Comments