Telomerase is an enzyme that is the hallmark of both aging and the uncontrolled cell division associated with cancer and in an effort to understand and control telomerase activity, researchers at The Wistar Institute have discovered a protein "motif," named TFLY, which is crucial to the function of telomerase.
Altering this motif disrupts telomerase function, they found, a fact that they believe will help them in their efforts to identify inhibitors of telomerase with potential cancer therapeutic properties.
Telomerase is an enzyme that replicates the ends of chromosomes (sections of DNA called telomeres), replacing the DNA lost when chromosomes are copied before cell division and, therefore, maintaining the stability of the genome. It performs this critical service in embryonic development, growing organisms and in a few specialized adult cell lines, including stem cells.
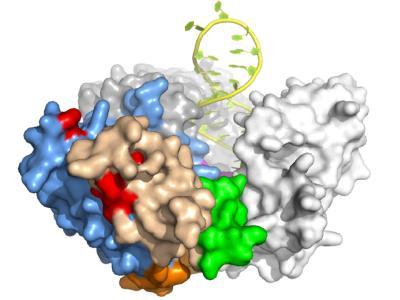
Model structure of the catalytic portion of telomerase shows how the TFLY motif (green) is positioned at the entry of the pocket that guides the RNA template in the interior cavity of the telomerase ring and were the active site of the enzyme if located for catalysis. Credit: Emmanuel Skordalakes/The Wistar Institute
In most normal adult cells, however, telomerase is switched off almost entirely to prevent the dangers of runaway cell proliferation. Without telomerase, adult cells senesce (grow old) after about 50-55 rounds of cell division because the telomeres get too short to provide the buffer required to protect the ends of chromosomes and stabilize the cell's genetic code.
It is now established that nearly 90 percent of cancers develop a way of reactivating telomerase as a means of survival. Inhibiting telomerase function has been viewed as an ideal way to put the brakes on a wide range of cancers. One way to do so would be to disrupt the protein RNA complex that comprises the core of the telomerase enzyme. The RNA binding domain (TRBD) of telomerase is a crucial component to this process and, therefore, the enzyme's ability to work.
"Telomerase is a unique protein-RNA complex where the protein subunit uses its RNA component as a template to add identical fragments of DNA to the end of chromosomes," said senior author Emmanuel Skordalakes, Ph.D., associate professor in the Gene Expression and Regulation program of Wistar's NCI-designated Cancer Center. "We identified a motif in the protein component of telomerase that controls how the enzyme carries out its activity in vertebrates such as ourselves. If you disrupt this segment of the protein, by altering its amino acid sequence, you disrupt the ability of telomerase to function," Skordalakes explained. "Obviously, this information can be used in our efforts to identify drug therapies that kill cancer cells by targeting telomerase activity."
In 2007, the Skordalakes laboratory obtained the three-dimensional structure of TRBD. Since then, his team has been creating molecular inhibitors to target the TRBD RNA-binding pockets as means to inhibit telomerase enzymatic activity.
The present study arose as they sought to better understand the role of TRBD in telomerase function. They engineered a truncated version of the protein subunit of a vertebrate telomerase, consisting of TRBD and a conserved portion of the N-terminal region of the protein. Within this portion they identified the TFLY, a conserved element that they showed is involved in binding the RNA component of telomerase and this interaction is important for telomerase protein-RNA assembly and activity.
"This TFLY motif comprises a significant part of the binding pocket that enables the enzyme to grapple the RNA template and guide it to the active site of the enzyme for catalysis," Skordalakes said, "but it also facilitates the stable association of the protein with its RNA component thus forming a fully functional telomerase enzyme."
Citation: Michael Harkisheimer, Mark Mason, Elena Shuvaeva, Emmanuel Skordalakes, 'A Motif in the Vertebrate Telomerase N-Terminal Linker of TERT Contributes to RNA Binding and Telomerase Activity and Processivity', Structure September 19 2013 DOI:10.1016/j.str.2013.08.013






Comments