Scientists have studied gamma oscillations, high-frequency brain waves, for over 50 years in the belief that they are crucial to understanding consciousness, attention, learning and memory. Now researchers have found a way to induce these waves by shining laser light directly onto the brains of mice.
The work takes advantage of a newly developed technology known as optogenetics, which combines genetic engineering with light to manipulate the activity of individual nerve cells. The research helps explain how the brain produces gamma waves and provides new evidence of the role they play in regulating brain functions — insights that could someday lead to new treatments for a range of brain-related disorders.
Two California children who had not had contact with pigs recently recovered from infections with "unique" swine flu/swine influenza viruses, raising concern about possible human-to-human transmission and putting health authorities on alert, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported.
The two cases were in a 10-year-old boy in San Diego County and a 9-year-old girl in neighboring Imperial County, but they are apparently unrelated, the CDC said in an Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) Dispatch report April 21st.
A piece of chalk in a laboratory at the University of Stavanger in Norway may be the key to unlocking a great mystery.
If the mystery is solved, it will generate billions in additional income. Okay, it will be billions of dollars for the oil industry and Arabs aren't exactly doing great things with their money now but uncovering the mechanisms behind 'water weakening' could provide crucial knowledge for oil companies to be able to predict reservoirs’ behavior.
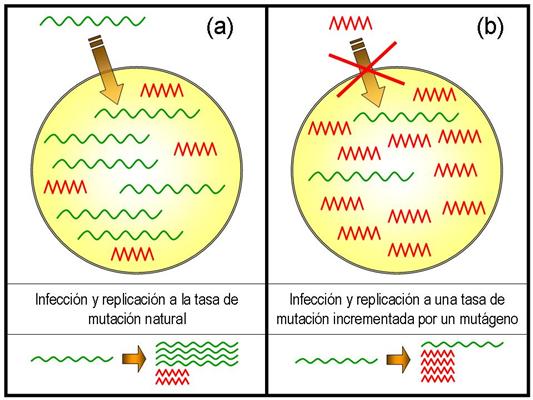
Two researchers from the Spanish Centre of Astrobiology (INTA-CSIC) have developed a mathematical model which demonstrates that a mild increase in the mutation rate of some viruses can reduce their infectivity, driving them to extinction. The study, published recently in Europhysics Letters, could have clinical uses in the medium term.
"The model we present shows how simple evolutionary mechanisms can cause the extinction of populations of fast mutating pathogens, such as certain viruses", co-author of the study and Centre of Astrobiology researcher Susanna C. Manrubia explained to Servicio de Información y Noticias Científicas (SINC).
A study led by researchers from the Madrid Carlos III Institute of Health associates the increase of cholera cases in Zambia with climate factors. They say their results confirm that the increase in environmental temperature six weeks before the rain season increases the number of people affected by this sickness by 4.9%.
DNA sequencing is the next frontier in biological research.As new sequencing technology becomes more efficient and affordable, it is increasingly available to small laboratories. Thus, sequencing data is being generated at a faster rate than ever before.
However, the computing capacity needed to analyze such vast amounts of data still has some catching up to do. Large networks of interconnected computers, called computer clusters, are required to analyze these data. Expensive to establish and maintain, these computer clusters are generally available only to labs that can afford them.
 Opioid Addicts Are Less Likely To Use Legal Opioids At The End Of Their Lives
Opioid Addicts Are Less Likely To Use Legal Opioids At The End Of Their Lives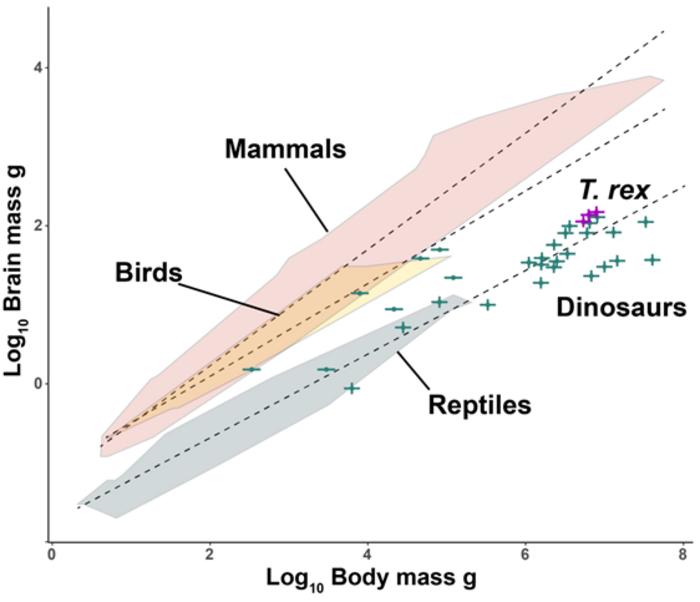 More Like Lizards: Claim That T. Rex Was As Smart As Monkeys Refuted
More Like Lizards: Claim That T. Rex Was As Smart As Monkeys Refuted Study: Caloric Restriction In Humans And Aging
Study: Caloric Restriction In Humans And Aging Science Podcast Or Perish?
Science Podcast Or Perish?