Women should go for the broccoli when the relish tray comes around during holiday celebrations this season.
While it has been known for some time that eating cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage, can help prevent breast cancer, the mechanism by which the active substances in these vegetables inhibit cell proliferation was unknown — until now.
Scientists in the UC Santa Barbara laboratories of Leslie Wilson, professor of biochemistry and pharmacology, and Mary Ann Jordan, adjunct professor in the Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, have shown how the healing power of these vegetables works at the cellular level. Their research is published in this month's journal Carcinogenesis.
A South Dakota State University study showed that women who began menstruating at an earlier age had a higher percentage of body fat as adults than women who began menstruating later.
But women who began menstruating earlier also had higher bone mineral density in the hip as adult women. They also had greater bone mass and bone density in the femoral neck region of the hip, a common site for hip fracture.
These are among the findings in a study by assistant professor Teresa Binkley at SDSU’s Ethel Austin Martin Program in Human Nutrition. Binkley worked on the project with Courtney Grimsrud, an undergraduate research assistant at the time, and professor Bonny Specker, director of the Ethel Austin Martin Program.
Since its discovery in the 18th century, cocaine has been a scourge of western society. Strongly stimulating human reward centers in low doses, cocaine is extremely addictive and can be fatal in high doses.
But this potent compound did not evolve to ensnare humans in addiction, it is a powerful insect neurotoxin, protecting coca bushes from munching insects - without rewarding them.
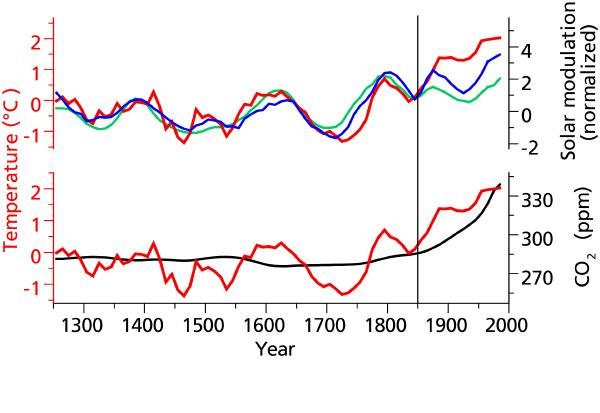
An ice core drilled at the Belukha glacier in the Siberian Altai by a Swiss-Russian research team under the leadership of the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) in 2001 has now provided new findings in climate research. Oxygen isotopes in the ice were used to reconstruct the temperatures in the Altai over the past 750 years. The scientists discovered a strong link between regional temperatures and the solar activity in the period 1250-1850, concluding that the sun was an important driver of preindustrial temperature changes in the Altai.
A study headed by researchers from the University of Barcelona (UB) shows that caffeine has a greater effect on men than women, and that these effects start just 10 minutes after it is drunk. In addition, contrary to what was previously thought, it has also been shown that decaffeinated coffee also produces an increased state of alertness.
“Numerous studies have demonstrated the stimulant effects of caffeine, but none of these have looked at their effects in terms of the consumer’s gender,” Ana Adan, lead author of the study and a researcher in the Psychiatry and Clinical Psychobiology Department of the UB, tells SINC.
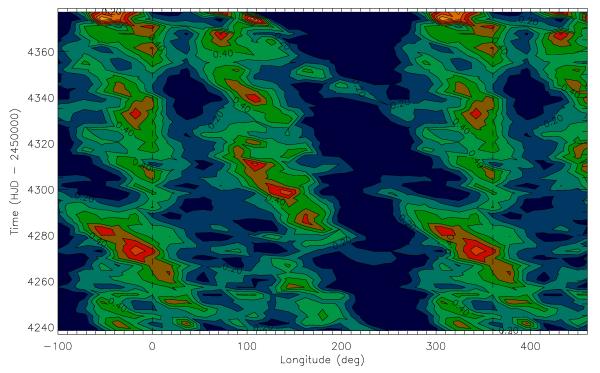
The CoRoT satellite, a space mission led by the French Space Agency CNES with the participation of Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Germany, Spain and the European Space Agency, ESA (RSSD and Science programme, that includes an Italian contribution), has recently observed a star analogous to the young Sun at an age of approximately 500 million years, named CoRoTExo-2a.
 Opioid Addicts Are Less Likely To Use Legal Opioids At The End Of Their Lives
Opioid Addicts Are Less Likely To Use Legal Opioids At The End Of Their Lives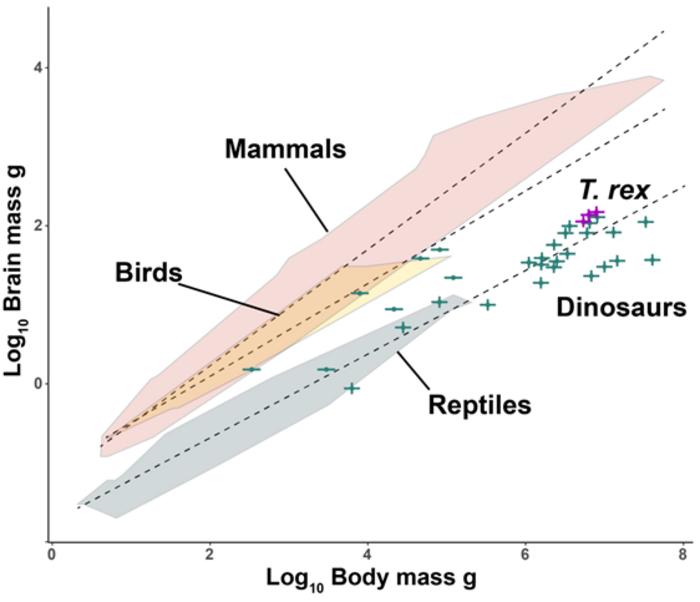 More Like Lizards: Claim That T. Rex Was As Smart As Monkeys Refuted
More Like Lizards: Claim That T. Rex Was As Smart As Monkeys Refuted Study: Caloric Restriction In Humans And Aging
Study: Caloric Restriction In Humans And Aging Science Podcast Or Perish?
Science Podcast Or Perish?