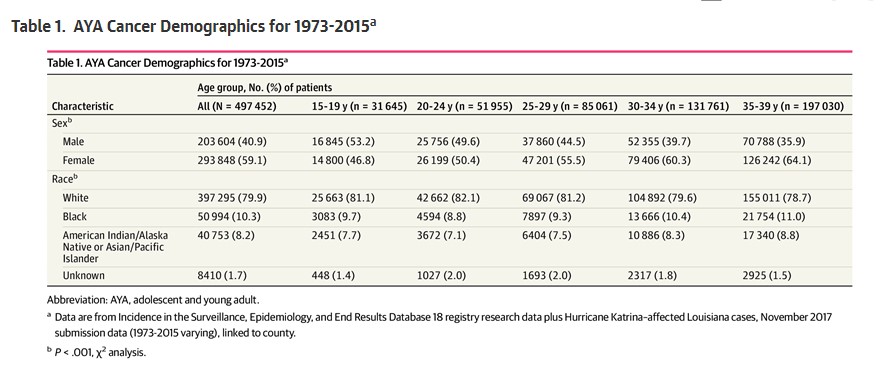
As medical care has improved, doctors are able to screen for cancer earlier than ever, and that is why cancer cases in young adults and adolescents are prevalent enough that they can be considered a distinct population.
Age remains the biggest factor for everything, of course, if you live long enough you are going to get cancer of some kind, it is built into our biology, but the increase in screening and therefore diagnoses means young adults can be considered distinct from pediatric and adult cancers and have their own middle ground for research.
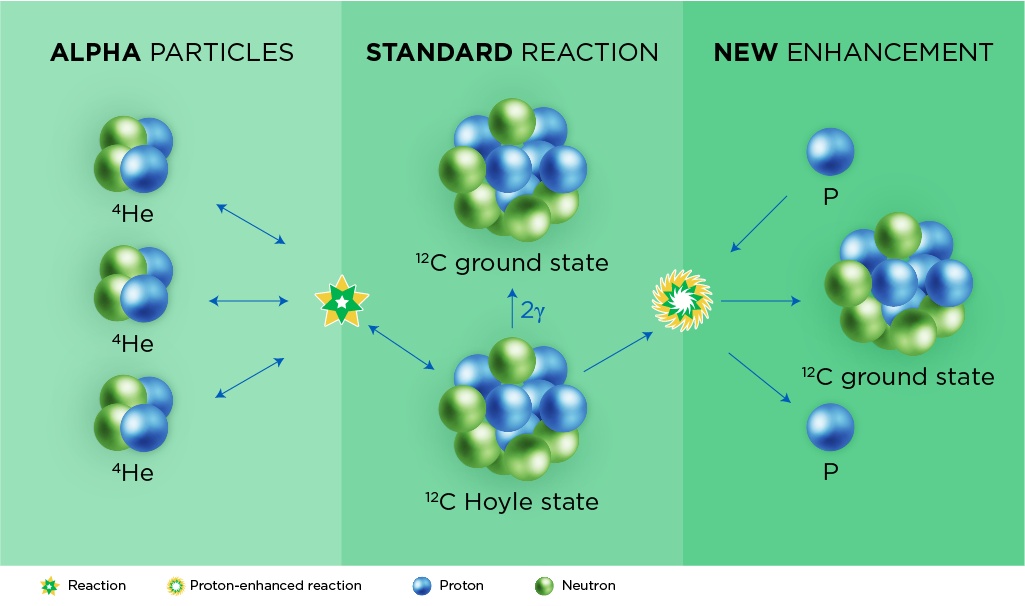
Nearly all of the atoms that make up the our planet and us were forged in stars and the carbon most important to life as we know it was made by the triple-alpha process. The process starts with alpha particles, cores of helium atoms, with each alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons. The triple alpha process is just what it sounds like; three alpha particles are fused inside a star, creating a new particle with six protons and six neutrons - the most common form of carbon in the universe - with a surplus of energy, a Hoyle state. That Hoyle state can split back into three alpha particles or relax to the ground state of stable carbon by releasing gamma rays.
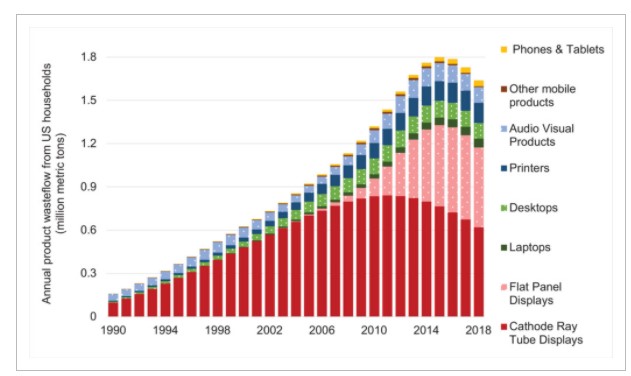
When your Xbox is a gaming console and a 4K Blu-Ray player, you don't need two devices, and when your phone is a camera and a video recorder, there are two fewer things to buy - and eventually throw away.
As smart devices have become more integrated, and more commodities like a dishwasher than technology events, people own fewer things and keep them longer. That means less electronic waste. Yet the story we get from environmental groups is that e-waste is the fastest growing material pollution and only donations to lawyer-run groups can stop it.
In the not so distant future, checkbooks will take their
rightful place in museums alongside answering machines, VCRs and folding paper maps.
Online bill-paying and Apple/Google Pay have narrowed the times when it’s
necessary to resort to the clunky paper-and-pen based payment method, and many
growing up today have never touched one at all. It’s clear the way we handle
our finances is changing. So why not bring the concept of money itself into the
21st century?
In the United States, meat substitutes like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods are now fixtures in culture. Vegetarians who miss meat want to eat them because they use plants while environmental activists don't want to eat them because they use science. That keeps them in the public eye.
Dolutegravir, the HIV wonder drug and current first-line treatment, is less effective in sub-Saharan Africa, and the reason is as old as evolution itself - mutation.
As HIV copies itself and replicates, its genetic code (RNA) can change. While a drug may initially be able to suppress or even kill a virus, certain mutations can allow the virus to develop resistance to its effects. If a mutated strain begins to spread within a population, it can mean once-effective drugs are no longer able to treat people.
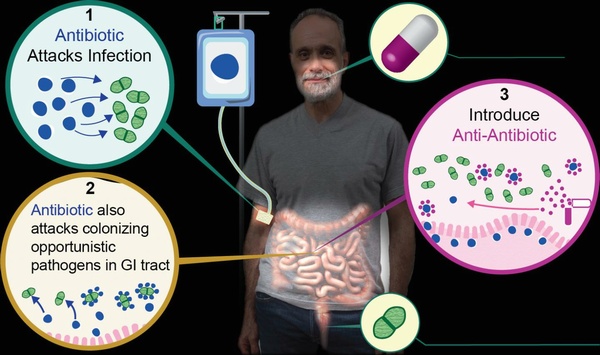
Antibiotic resistance is a serious problem. Nature constantly evolves new ways to kill, which means pathogens will develop new methods of resistance to current treatments, but pharmaceutical companies also have little incentive to develop new antibiotics. Instead, they have obstructions when the U.S. Food and Drug Administration will require a billion dollars in expenses, 10 years of regulatory approval, and then grandstanding politicians will demand it immediately be generic and cost a dollar.
A new paper finds that widely available retinal imaging techniques may help reveal more about brain disease and monitor treatment efficacy, including a currently untreatable form of childhood-onset dementia, Sanfilippo syndrome.
Sanfilippo syndrome is one of a group of about 70 inherited conditions which collectively affect 1 in 2800 children in Australia, and is more common than cystic fibrosis and better known diseases. Around the world 700,000 children and young people are living with childhood dementia. The researchers studied Sanfilippo syndrome in mouse models, discovering for the first time that advancement of retinal disease parallels that occurring in the brain.
Early in the pandemic, many researchers feared people who contracted COVID could be reinfected very quickly. This was because several early studies showed antibodies seemed to wane after the first few months post-infection.
It was also partly because normal human coronaviruses, which are one cause of common colds and are cousins of SARS-CoV-2, do not generate long-lasting immunity, so we can get reinfected with them after 12 months.
Over recent weeks and months, we’ve heard of several COVID cases in which people have tested positive after previously clearing the virus.
Scientists are hopeful being infected with COVID-19 confers immunity for a length of time. But some of these instances have raised concerns about reinfection. Although rare, it seems to be possible.
The other thing which could be at play in many of these cases is “prolonged viral shedding”.