Abrus precatorius Linn.
Vernacular Names :- Assam : Latuwani ; Bengal : Chunhati ; Bombay : Ghungchi ; English : Indian liquorice ; Gujrat : Chanoti ; Hindi : Chirmiti, Rati ; Punjab : Labri Ratak ; Sanskrit : chataki ; Tamil : Adisamiyai ; Telgu : Raktika.
Family :- Papilionaceae.
Distribution :- It is found in Ceylon, Pakistan, throughout the tropical regions and it is found throughout India.
Butea monosperma Roxb. ex Willd.
Vernacular Names :- Assam : Polah ; Bengal : Kinka ; Bihar : Paras ; Bombay : Khakara ; Central provinces : Pharas ; English : Flame of the forest, Bastard teak ; Gujrat : Pallaso ; Hindi : Palas, Dhak , Tesu ; Punjab: Pahal ; Sanskrit : Raktak pushpaka ; Tamil : Palasu ; Telgu : Kimsukamu.
Family :- Papilionaceae.
Distribution :- It is found in Ceylon and throughout India.
The term pharmacognosy derived from Greek, pharmakon, a drug, and gignosco, to acquire knowledge of. Pharmacogonasy is mainly concerned with naturally occurring substances having a medicinal action. It also includes the study of other material used in pharmacy such as flavouring and suspending agents, disintegrants, filtering and support media and so on. It is closely related to both botany and plant chemistry.
3. Acacia catechu Willd. ‘Katha , khadira , khair’ (Catechu tree) :- Kols tribe of Uttar Pradesh use its leaves for blood dysentery (Chakravarthy et al., 1983). The extract of leaves is taken with milk (Maheshwari and Singh, 1987). Seeds exhibit antiviral, antiimflammatory, hepatoprotective and spasmolytic activity (Nirmal et al., 1985). The wood is very hard, durable, takes a fine polish, and is resistant to ants. It is used for house posts, boat buildings, cart construction, wells, agricultural implements, tool handles, rice pestles, oil and sugarcane mills etc. Goldsmiths prize the wood as fire wood. The tree is an important source of vitamin P, cutch, katha and kheersal (Dastur, 1964).
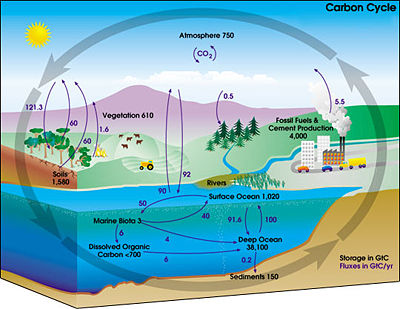
Biomass refers to all the matter that can be obtained from photosynthesis. Most vegetable species use solar energy to create sugars from carbon dioxide and water. They store this energy in the form of glucose or starch molecules, oleaginous, cellulose, and lignocellulose .Biomass appears to be an attractive feedstock for three main reasons. First, it is a renewable resource that could be sustain ably developed in the future. Second, it appears to have formidably positive environmental properties, notably the recycling of carbon in the biological processes, resulting in no net releases of carbon dioxide and a very low sulphur content. Third, it appears to have significant economic potential provided that fossil fuel prices increase, quite substantially, in the future.
 Feeling no pain: plants were first to let it happen
Feeling no pain: plants were first to let it happen Sitopaladi churna is an ayurvedic medicine for cough and cold
Sitopaladi churna is an ayurvedic medicine for cough and cold  Ethnobotany and Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi)
Ethnobotany and Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi)  Gene, gene expression, gene silencing and RNAi
Gene, gene expression, gene silencing and RNAi