Phragmites karka Trin. ex Steud. ( Syn P. karka Retz. , P. <?xml:namespace prefix = o ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" />
Scientific Name Entada phaseoloides (Linn.) Merr. syn. E. scandens
Benth. (Ref no.9 page 59 names this as E.pursaetha DC and puts E. scandens Benth.)
Family Fabaceae
Used Part Fruits.
Distribution Area The plant occurs throughout the sub-Himalayan tract,
from Nepal eastwards ascending to 4,000 ft. in Sikkim, in Assam, Bihar and Orissa, and in the monsoon forest of western and eastern ghats; it is abundant in Andaman Islands.
Common Uses . The seeds are considered tonic, emetic, antiperiodic and
anthelmintic. A paste prepared from the seeds is applied locally for inflammatory glandular swellings. The stem is used as emetic. The juice of the wood and bark is used as an external application for ulcers.
Scientific Name Vanda tessellata (Roxb.) Hook ex Don (=V.roxburghii R.BR.)
Family Orchidaceaae
Used Part Root.
Distribution Area An epiphytic orchid, 30-60 cm. high, found from Uttar Pradesh to West Bengal, extending southwards to Kerala.
.
Common Uses . The root is a bitter heating alexiteric, antipyretic, useful in dyspepsia, bronchitis in lammations, rheumatic pains, diseases of the abdomen, hiccough, tremors. In Yunani system root is used as tonic to the liver and brain ; good for bronchitis, piles, lumbago toothache, boils of the scalp; lessens inflammation; heals fractures. The root is said to be fragrant, bitter and useful in rheumatism and allied disorder, in which it is prescribed in a variety of forms.
When some one iterrupted me and told me that he has seen Jatropha growing on bare rocks I could not deny this fact but when people say its a plant for wasteland and Government of over 30 countries go after its mass plantation I feel scared as a botanist. The simple reason is that althogh this plant has the ability to grow in adverse climate that does not mean it will produce fruits also. Our experience of 25 years of work on Jatropha has proved that although it can grow below 300 mm rainfall also but it will need at least 400 to 600 mm of rainfall for bearing fruits.
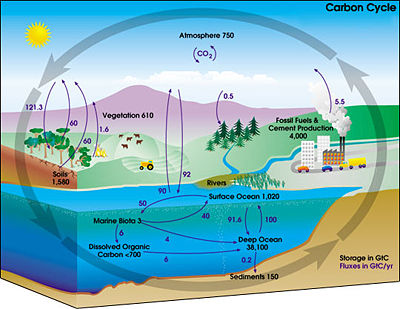
Carbon Sequestration
The Virginia Center for Coal and Energy Research is using the LI-8100 to monitor soil CO2 flux near the injection well.
Southeast Regional Carbon Sequestration Partnership’s Central Appalachian Coal Seam Project Coal Bed Methane Injection well.With the increased concern of global greenhouse gas emissions, scientists are researching ways to limit the amount of CO2 entering the atmosphere in an effort to mitigate the atmospheric CO2 concentration increase. Currently there is a global push to limit CO2 emissions through Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies. These large projects require strategic planning and public acceptance for them to be successful.
 Feeling no pain: plants were first to let it happen
Feeling no pain: plants were first to let it happen Sitopaladi churna is an ayurvedic medicine for cough and cold
Sitopaladi churna is an ayurvedic medicine for cough and cold  Ethnobotany and Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi)
Ethnobotany and Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi)  Gene, gene expression, gene silencing and RNAi
Gene, gene expression, gene silencing and RNAi