The Galapagos giant tortoise, the largest living species of tortoise (and in the top 10 reptiles), likes to move around.
We know this because scientists with the Max Planck Institute for Ornithology and the Charles Darwin Foundation have used GPS technology and 3-D acceleration measurements to find out that the dominant male tortoise will wander up to 10 kilometers into the highlands of the island - but only the fully grown animals migrate, the young tortoises stay in the lowlands.
Why? And why don't they rest during the dry season? It's a Chelonoidis nigra mystery of science.
Charles Darwin anticipated that the giant tortoises wandered large distances. In the cool dry season, the highlands of Santa Cruz are engulfed in fog which allows the vegetation to grow despite the lack of rain. In the lowlands, however, there is no thick layer of clouds and the tortoises' vegetation is not available year round. Adults, which can weigh up to 250 kilograms, spend the dry season in the higher regions at an elevation of 400 meters above sea level. However, since the food is not as nutritious there, they trek back to the lower zones where there is succulent vegetation, as soon as the rainy season begins.
In order to study the migratory pattern more closely, Stephen Blake from the Max Planck Institute for Ornithology and his colleague Washington Tapia from the Galapagos National Park secured GPS loggers with 3D acceleration monitors onto 17 adult tortoises. This allowed the scientists to determine the animals' exact position and behaviour over a period of two years. In order to gather information on the entire population, the researchers noted the size, sex and location of each tortoise they met on their monthly hikes along the volcanic hillsides. They combined the GPS data with the temperature data and information about availability of vegetation.

Slow and steady. Galapagos giant tortoises move at their own leisurely pace, but they get there. Credit: MPI for Ornithology
The results show that the tortoises have a partial migration system, where not every individual migrates. Only the adult animals wander and only the larger specimens are more likely to move. In June they start their slow, tedious march which can be up to ten kilometers long into the highlands. Adult females remain in the lowlands until they lay their eggs and then they also make their way to the highlands. In contrast, the smaller tortoises stay in the lower elevated areas all year round.
Although giant tortoises are able to survive for up to one year without nourishment, which made them a popular staple for seamen, they nevertheless wander for large distances searching for food as this study shows for the first time. Why don't they just look for a shelter? The question of why the younger animals don't migrate hasn't been answered by the scientists yet. "Either the energy expenditure of this strenuous hike is too high, or there is still enough food available for the smaller animals." Stephen Blake suspects, "perhaps the younger animals can't tolerate the wet cold climate of the higher regions."
In other species, the largest and the most dominant individual does not migrate because it can best defend itself against its competitors. It doesn't have to leave to survive. However, among the Galapagos tortoises, it's usually the largest and most dominant individual which takes on this arduous journey.
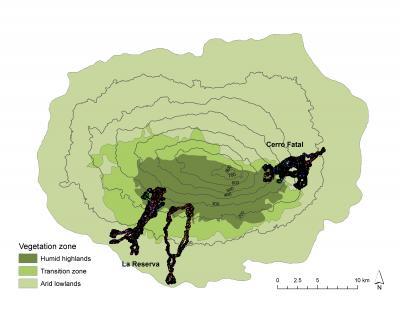
Galapagos tortoises on Santa Cruz migrate along usually linear paths up and down the slopes of the island. Migration routes were up to ten kilometers long, and sometimes took the tortoises to sea level. Credit: Stephen Blake/MPI for Ornithology
Future studies on giant tortoise species of the other Galapagos Islands with varying ecological conditions will show how environment influences the migration scheme of these closely related reptiles. The scientists also want to include factors such as age, size, sex and morphology in their studies to see why the behaviour changes in different lifetime stages and what the trigger of migration is.
Despite the threat of hunting, invasive species such as goats and rats, and the loss of habitat due to man, the Galapagos Tortoise still shows its original migrating behavior. This and future studies will help to maintain this behavior with the help of effective measures such as establishing corridors, preserving key habitats, keeping tortoise-friendly roads and maintaining less urban development.






Comments